Abstract
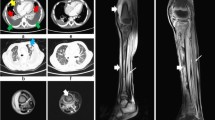
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a rare cause of community acquired soft tissue infection in Europe. We report a case of severe soft tissue infection caused by a MRSA strain originating from a pig bite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsueh PR, Chen WH, Luh KT: Relationships between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections from 1991–2003 at a university hospital in Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2005; 26: 463–472.
Paterson DL: “Collateral damage” from cephalosporin or quinolone antibiotic therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 38: S341–S345.
Albrich WC, Monnet DL, Harbarth S: Antibiotic selection pressure and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Emerg Infect Dis 2004; 10: 514–517.
Goossens H, Ferech M, Vander Stichele R, Elseviers M: Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet 2005; 365: 579–587.
Malhotra-Kumar S, Lammens C, Coenen S, Van Herck K, Goossens H: Effect of azithromycin and clarithromycin therapy on pharyngeal carriage of macrolide-resistant streptococci in healthy volunteers: a randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Lancet 2007; 369: 482–490.
de With K, Bergner J, Buhner R, Dorje F, Gonnermann C, Haber M, Hartmann M, Rothe U, Strehl E, Steib-Bauert M, Kern WV: Antibiotic use in German university hospitals 1998–2000 (Project INTERUNI-II). Int J Antimicrob Agents 2004; 24: 213–218.
Janknegt R, Oude Lashof A, Gould IM, van der Meer JW: Antibiotic use in Dutch hospitals 1991–1996. J Antimicrob Chemother 2000; 45: 251–256.
Lodise TP, McKinnon PS: Clinical and economic impact of methicillin resistance in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2005; 52: 113–122.
Lee NY, Lee HC, Ko NY, Chang CM, Shih HI, Wu CJ, Ko WC: Clinical and economic impact of multidrug resistance in nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2007; 28: 713–719.
WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Guidelines for ATC classification and DDD assignment 2007. Oslo, 2006. Available at: http://www.whocc.no/atcddd Accessed 9 September 2007.
Platt R: Toward better benchmarking. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2005; 26: 433–434.
Westh H: Benchmarking. In: Gould IM, Meer JWM van der (eds): Antibiotic policies. Theory and practice. Kluwer Academic, New York 2005, pp 119–132.
Polk RE, Fox C, Mahoney A, Letcavage J, MacDougall C: Measurement of adult antibacterial drug use in 130 US hospitals: comparison of defined daily dose and days of therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 664–670.
Kern WV, Steib-Bauert M, de With K, Reuter S, Bertz H, Frank U, von Baum H: Fluoroquinolone consumption and resistance in haematology-oncology patients: ecological analysis in two university hospitals 1999–2002. J Antimicrob Chemother 2005; 55: 57–60.
Kern WV, de With K, Steib-Bauert M, Fellhauer M, Plangger A, Probst W: Antibiotic use in non-university regional acute care general hospitals in southwestern Germany, 2001–2002. Infection 2005; 33: 333–339.
de With K, Maier L, Steib-Bauert M, Kern P, Kern WV: Trends in antibiotic use at a university hospital: defined or prescribed daily doses? Patient days or admissions as denominator? Infection 2006; 34: 91–94.
Kritsotakis EI, Gikas A: Surveillance of antibiotic use in hospitals: methods, trends and targets. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006; 12: 701–704.
Keenan SP, Dodek P, Martin C, Priestap F, Norena M, Wong H: Variation in length of intensive care unit stay after cardiac arrest: where you are is as important as who you are. Crit Care Med 2007; 35: 836–841.
DeFrances CJ, Hall MJ: National hospital discharge survey. Adv Data 2005; 2007: 1–19.
Westert GP, Lagoe RJ, Keskimaki I, Leyland A, Murphy M: An international study of hospital readmissions and related utilization in Europe and the USA. Health Policy 2002; 61: 269–278.
Theurl E, Winner H: The impact of hospital financing on the length of stay: evidence from Austria. Health Policy 2007; 82: 375–389.
Esposito S, Noviello S, Leone S, Tice A, Seibold G, Nathwani D, Scaglione F: Outpatient parenteral antibiotic therapy (OPAT) in different countries: a comparison. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2004; 24: 473–478.
Monnet DL: ABC Calc — Antibiotic consumption calculator [Microsoft Excel application]. Version 3.0. Statens Serum Institute, Copenhagen, 2005.
Loeffler JM, Garbino J, Lew D, Harbarth S, Rohner P: Antibiotic consumption, bacterial resistance and their correlation in a Swiss university hospital and its adult intensive care units. Scand J Infect Dis 2003; 35: 843–850.
Ruttimann S, Keck B, Hartmeier C, Maetzel A, Bucher HC: Longterm antibiotic cost savings from a comprehensive intervention program in a medical department of a university-affiliated teaching hospital. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 38: 348–356.
Mach R, Vlcek J, Prusova M, Batka P, Rysavy V, Kubena A: Impact of a multidisciplinary approach on antibiotic consumption, cost and microbial resistance in a Czech hospital. Pharm World Sci 2007; 29: 565–572.
Muller-Pebody B, Muscat M, Pelle B, Klein BM, Brandt CT, Monnet DL: Increase and change in pattern of hospital antimicrobial use, Denmark, 1997–2001. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 54: 1122–1126.
DANMAP: Use of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from food animals, foods and humans in Denmark. 2006. ISSN 1600–2032.
Naaber P, Koljalg S, Maimets M: Antibiotic usage and resistance - trends in Estonian University Hospitals. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2000; 16: 309–315.
Muller A, Monnet DL, Talon D, Henon T, Bertrand X: Discrepancies between prescribed daily doses and WHO defined daily doses of antibacterials at a university hospital. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006; 61: 585–591.
Rogues AM, Placet-Thomazeau B, Parneix P, Vincent I, Ploy MC, Marty N, Merillou B, Labadie JC, Gachie JP: Use of antibiotics in hospitals in south-western France. J Hosp Infect 2004; 58: 187–192.
de With K, Steib-Bauert M, Straach P, Kern WV: Is there significant regional variation in hospital antibiotic consumption in Germany? Infection 2006; 34: 274–277.
de With K, Meyer E, Steib-Bauert M, Schwab F, Daschner FD, Kern WV: Antibiotic use in two cohorts of German intensive care units. J Hosp Infect 2006; 64: 231–237.
Bassetti M, Di Biagio A, Rebesco B, Amalfitano ME, Topal J, Bassetti D: The effect of formulary restriction in the use of antibiotics in an Italian hospital. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 57: 529–534.
Blix HS, Hartug S: Hospital usage of antibacterial agents in relation to size and type of hospital and geographical situation. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2005; 14: 647–649.
Goryachkina K, Babak S, Burbello A, Wettemark B, Bergman U: Quality use of medicines: a new method of combining antibiotic consumption and sensitivity data-application in a Russian hospital. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2008; 17: 636–644.
Hermosilla Najera L, Canut Blasco A, Ulibarrena Sanz M, Abasolo Osinaga E, Abecia Inchaurregui LC: Trends in antimicrobial utilization at a Spanish general hospital during a 5-year period. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2003; 12: 243–247.
Walther SM, Erlandsson M, Burman LG, Cars O, Gill H, Hoffman M, Isaksson B, Kahlmeter G, Lindgren S, Nilsson L, Olsson-Liljequist B, Hanberger H: Antibiotic prescription practices, consumption and bacterial resistance in a cross section of Swedish intensive care units. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2002; 46: 1075–1081.
Bergman U, Risinggard H, Vlahovic-Palcevski V, Ericsson O: Use of antibiotics at hospitals in Stockholm: a benchmarking project using internet. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2004; 13: 465–471.
SWEDRES: A report on Swedish antibiotic utilisation and resistance in human medicine 2006. ISSN 1400–3473.
Liem TB, Filius FM, van der Linden PD, Janknegt R, Natsch S, Vulto AG: Changes in antibiotic use in Dutch hospitals over a six-year period: 1997 to 2002. Neth J Med 2005; 63: 354–360.
Filius PM, Liem TB, van der Linden PD, Janknegt R, Natsch S, Vulto AG, Verbrugh HA: An additional measure for quantifying antibiotic use in hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother 2005; 55: 805–808.
SWAB: NethMap 2007 — consumption of antimicrobial agents and antimicrobial resistance among medically important bacteria in The Netherlands.
Curtis C, Marriott J, Langley C: Development of a prescribing indicator for objective quantification of antibiotic usage in secondary care. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 54: 529–533.
Dancer SJ, Coyne M, Robertson C, Thomson A, Guleri A, Alcock S: Antibiotic use is associated with resistance of environmental organisms in a teaching hospital. J Hosp Infect 2006; 62: 200–206.
Vander Stichele RH, Elseviers MM, Ferech M, Blot S, Goossens H: Hospital consumption of antibiotics in 15 European countries: results of the ESAC retrospective data collection (1997–2002). J Antimicrob Chemother 2006; 58: 159–167.
MacKenzie FM, Monnet DL, Gould IM: Relationship between the number of different antibiotics used and the total use of antibiotics in European hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006; 58: 657–660.
Ansari F: Utilization review of systemic antiinfective agents in a teaching hospital in Tehran, Iran. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 57: 541–546.
Apisarnthanarak A, Danchaivijitr S, Khawcharoenporn T, Limsrivilai J, Warachan B, Bailey TC, Fraser VJ: Effectiveness of education and an antibiotic-control program in a tertiary care hospital in Thailand. Clin Infect Dis 2006; 42: 768–775.
Bantar C, Sartori B, Vesco E, Heft C, Saul M, Salamone F, Oliva ME: A hospitalwide intervention program to optimize the quality of antibiotic use: impact on prescribing practice, antibiotic consumption, cost savings, and bacterial resistance. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 37: 180–186.
Berild D, Ringertz SH, Lelek M, Fosse B: Antibiotic guidelines lead to reductions in the use and cost of antibiotics in a university hospital. Scand J Infect Dis 2001; 33: 63–67.
Kritsotakis EI, Assithianakis P, Kanellos P, Tzagarakis N, Ioannides MC, Gikas A: Surveillance of monthly antimicrobial consumption rates stratified by patient-care area: a tool for triggering and targeting antibiotic policy changes in the hospital. J Chemother 2006; 18: 394–401.
White RL, Friedrich LV, Mihm LB, Bosso JA: Assessment of the relationship between antimicrobial usage and susceptibility: differences between the hospital and specific patient-care areas. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 31: 16–23.
Ronning M, Blix HS, Strom H, Skovlund E, Andersen M, Stichele RV: Problems in collecting comparable national drug use data in Europe: the example of antibacterials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2003; 58: 843–849.
Monnet DL: Measuring antimicrobial use: the way forward. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 671–673.
Dellit TH, Owens RC, McGowan JE Jr, Gerding DN, Weinstein RA, Burke JP, Huskins WC, Paterson DL, Fishman NO, Carpenter CF, Brennan PJ, Billeter M, Hooton TM: Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guidelines for developing an institutional program to enhance antimicrobial stewardship. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 159–177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-9029-9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Declercq, P., Petré, D., Gordts, B. et al. Complicated Community-Acquired Soft Tissue Infection by MRSA from Porcine Origin. Infection 36, 590–592 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-7029-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-7029-4