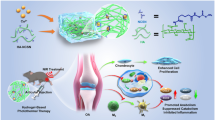
Abstract
Background:
Implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) is a potential alternative for promoting bone defects healing or osseointegration in osteoporosis. However, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulated and excessive inflammation in the osteoporotic microenvironment could weaken the self-replication and multi-directional differentiation of transplanted BMSCs.
Methods:
In this study, to improve the hostile microenvironment in osteoporosis, Poloxamer 407 and hyaluronic acid (HA) was crosslinked to synthetize a thermos-responsive and injectable hydrogel to load MnO2 nanoparticles as a protective carrier (MnO2@Pol/HA hydrogel) for delivering BMSCs.
Results:
The resulting MnO2@Pol/HA hydrogel processed excellent biocompatibility and durable retention time, and can eliminate accumulated ROS effectively, thereby protecting BMSCs from ROS-mediated inhibition of cell viability, including survival, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation. In osteoporotic bone defects, implanting of this BMSCs incorporated MnO2@Pol/HA hydrogel significantly eliminated ROS level in bone marrow and bone tissue, induced macrophages polarization from M1 to M2 phenotype, decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) and osteogenic related factors (e.g., TGF-β and PDGF).
Conclusion:
This hydrogel-based BMSCs protected delivery strategy indicated better bone repair effect than BMSCs delivering or MnO2@Pol/HA hydrogel implantation singly, which providing a potential alternative strategy for enhancing osteoporotic bone defects healing.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are accessible from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Yin Y, Wang Q, Xie C, Chen H, Jin J, Miao D. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal stem cells-based therapy improves Bmi-1-deficient mandible osteoporosis through stimulating osteoblastic bone formation and inhibiting osteoclastic bone resorption. J Tissue Eng and Regen Med. 2022;16:538–49.
Soliman T, Ali Z, Zayed M, Sabry D, AbuBakr N. Assessing the bone-healing potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in jawbone osteoporosis in albino rats. Dent Med Probl. 2022;59:75–83.
Niu Q, He J, Wu M, Liu J, Lu X, Zhang L, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and fibrin glue into extraction socket in maxilla promoted bone regeneration in osteoporosis rat. Life Sci. 2022;290:119480.
Bai H, Zhao Y, Wang C, Wang Z, Wang J, Liu H, et al. Enhanced osseointegration of three-dimensional supramolecular bioactive interface through osteoporotic microenvironment regulation. Theranostics. 2020;10:4779–94.
Zhang M, Gao Y, Li Q, Cao H, Yang J, Cai X, et al. Downregulation of DNA methyltransferase-3a ameliorates the osteogenic differentiation ability of adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:397.
Peng S, Gao Y, Shi S, Zhao D, Cao H, Fu T, et al. LncRNA-AK137033 inhibits the osteogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis by regulating Wnt signaling pathway via DNA methylation. Cell Prolif. 2022;55:e13174.
Hu M, Zhu X, Yuan H, Li H, Liao H, Chen S. The function and mechanism of the miR-210-3p/KRAS axis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell from patients with osteoporosis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(8):699–711.
Li B, He X, Dong Z, Xuan K, Sun W, Gao L, et al. Ionomycin ameliorates hypophosphatasia via rescuing alkaline phosphatase deficiency-mediated L-type Ca2+ channel internalization in mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Res. 2020;8:19.
Wasnik S, Lakhan R, Baylink DJ, Rundle CH, Xu Y, Zhang J, et al. Cyclooxygenase 2 augments osteoblastic but suppresses chondrocytic differentiation of CD90(+) skeletal stem cells in fracture sites. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaaw2108.
McNeill EP, Zeitouni S, Pan S, Haskell A, Cesarek M, Tahan D, et al. Characterization of a pluripotent stem cell-derived matrix with powerful osteoregenerative capabilities. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3025.
Lan Y, Xie H, Jin Q, Zhao X, Shi Y, Zhou Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from neural EGFL-Like 1-modified mesenchymal stem cells improve acellular bone regeneration via the miR-25-5p-SMAD2 signaling axis. Bioact Mater. 2022;17:457–70.
Shu HS, Liu YL, Tang XT, Zhang XS, Zhou B, Zou W, et al. Tracing the skeletal progenitor transition during postnatal bone formation. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:2122–36.
Zhang J, Zhang W, Dai J, Wang X, Shen SG. Overexpression of Dlx2 enhances osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and MC3T3-E1 cells via direct upregulation of Osteocalcin and Alp. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11:12.
Chen M, Sun Y, Hou Y, Luo Z, Li M, Wei Y, et al. Constructions of ROS-responsive titanium-hydroxyapatite implant for mesenchymal stem cell recruitment in peri-implant space and bone formation in osteoporosis microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:56–71.
Hong I-S. Enhancing stem cell-based therapeutic potential by combining various bioengineering technologies. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:901661.
Shafiq M, Ali O, Han S-B, Kim D-H. Mechanobiological strategies to enhance stem cell functionality for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:747398.
Zhao Y, Song S, Wang D, Liu H, Zhang J, Li Z, et al. Nanozyme-reinforced hydrogel as a H2O2-driven oxygenerator for enhancing prosthetic interface osseointegration in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6758.
Li Z, Zhao Y, Huang H, Zhang C, Liu H, Wang Z, et al. A nanozyme-immobilized hydrogel with endogenous ROS-scavenging and oxygen generation abilities for significantly promoting oxidative diabetic wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11:e2201524.
Sui B-D, Hu C-H, Liu A-Q, Zheng C-X, Xuan K, Jin Y. Stem cell-based bone regeneration in diseased microenvironments: challenges and solutions. Biomaterials. 2019;196:18–30.
Chen Q, Li J, Han F, Meng Q, Wang H, Wei Q, et al. A multifunctional composite hydrogel that rescues the ROS microenvironment and guides the immune response for repair of osteoporotic bone defects. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32:2201067.
Zheng L, Zhuang Z, Li Y, Shi T, Fu K, Yan W, et al. Bone targeting antioxidative nano-iron oxide for treating postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bioact Mater. 2021;14:250–61.
Ding W, Zhou Q, Lu Y, Wei Q, Tang H, Zhang D, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel as protective carrier to regulate stem cells activity and promote osteointegration of 3D printed porous titanium prosthesis in osteoporosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1103611.
Shen X, Fang K, Yie KHR, Zhou Z, Shen Y, Wu S, et al. High proportion strontium-doped micro-arc oxidation coatings enhance early osseointegration of titanium in osteoporosis by anti-oxidative stress pathway. Bioact Mater. 2022;10:405–19.
Shao D, Li K, Hu T, Wang S, Xu H, Zhang S, et al. Titania nanotube array supported nanoceria with redox cycling stability ameliorates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis. Chem Eng J. 2021;415:128913.
Huang Y, Du Z, Wei P, Chen F, Guan B, Zhao Z, et al. Biodegradable microspheres made of conductive polyorganophosphazene showing antioxidant capacity for improved bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020;397:125352.
Yang R, Fan Y, Ye R, Tang Y, Cao X, Yin Z, et al. MnO2-based materials for environmental applications. Adv Mater. 2021;33:2004862.
Li L, Xiao B, Mu J, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Cao H, et al. A MnO2 nanoparticle-dotted hydrogel promotes spinal cord repair via regulating reactive oxygen species microenvironment and synergizing with mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Nano. 2019;13:14283–93.
Zhai P, Peng X, Li B, Liu Y, Sun H, Li X. The application of hyaluronic acid in bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:1224–39.
D’Albis G, D’Albis V, Palma M, Plantamura M, Nizar AK. Use of hyaluronic acid for regeneration of maxillofacial bones. Genesis. 2022;60:e23497.
Bo C, Jibing W, Xing J, Xin W, Zhangling F, Yuxin Z, et al. Rapamycin incorporating hydrogel improves the progression of osteoarthritis by inducing synovial macrophages polarization and reducing intra-articular inflammation. Mater Des. 2023;225:111542.
Zhu Y, Ye L, Cai X, Li Z, Fan Y, Yang F. Icariin-loaded hydrogel regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and promotes cartilage repair in osteoarthritis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:755260.
Li Z, Zhao Y, Liu H, Ren M, Wang Z, Wang X, et al. pH-responsive hydrogel loaded with insulin as a bioactive dressing for enhancing diabetic wound healing. Mater Des. 2021;210:110104.
Guo J, Zu L, Han L, Zhe J, YaS HL, et al. Green tea derivative-based hydrogel with ROS-scavenging property for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Mater Design. 2023;225:111452.
Li Z, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Ren M, Wang X, Liu H, et al. Engineering multifunctional hydrogel-integrated 3D printed bioactive prosthetic interfaces for osteoporotic osseointegration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11:e2102535.
Li Z, Bai H, Wang Z, Liu Y, Ren M, Wang X, et al. Ultrasound-mediated rapamycin delivery for promoting osseointegration of 3D printed prosthetic interfaces via autophagy regulation in osteoporosis. Mater Des. 2022;216:110586.
Wang X, Yu Y, Yang C, Shao C, Shi K, Shang L, et al. Microfluidic 3D printing responsive scaffolds with biomimetic enrichment channels for bone regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;31:2105190.
Yang Y, Sun Y, Mao W-W, Zhang H, Ni B, Jiang L. Oxidative stress induces downregulation of TP53INP2 and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs during osteoporosis through the autophagy degradation pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:226–37.
Li Y, He Y, Chen G, Huang Z, Yi C, Zhang X, et al. Selenomethionine protects oxidative-stress-damaged bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via an antioxidant effect and the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2021;408:112864.
Li J, Mooney DJ. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1:16071.
Lee SY, Jeon SI, Sim SB, Byun Y, Ahn C-H. A supramolecular host-guest interaction-mediated injectable hydrogel system with enhanced stability and sustained protein release. Acta Biomater. 2021;131:286–301.
Bernhard S, Tibbitt MW. Supramolecular engineering of hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;171:240–56.
Jung Y-s, Park W, Park H, Lee D-K, Na K. Thermo-sensitive injectable hydrogel based on the physical mixing of hyaluronic acid and Pluronic F-127 for sustained NSAID delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;156:403–8.
Gong T-T, Guo Q, Li X, Zhang T-N, Liu F-H, He X-H, et al. Isothiocyanate Iberin inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in the progression of ovarian cancer by mediating ROS accumulation and GPX1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;142:111533.
GilardiniMontani MS, Santarelli R, Granato M, Gonnella R, Torrisi MR, Faggioni A, et al. EBV reduces autophagy, intracellular ROS and mitochondria to impair monocyte survival and differentiation. Autophagy. 2019;15:652–67.
Yao D, Bailong T, Ruichen M, Xin Z, Peng L, Kaiyong C. Surface modification of titanium implant for repairing/improving microenvironment of bone injury and promoting osseointegration. J Mater Sci & Tech. 2023;143:1–11.
Chen K, Qiu P, Yuan Y, Zheng L, He J, Wang C, et al. Pseurotin a inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomized-induced bone loss by suppressing reactive oxygen species. Theranostics. 2019;9:1634–50.
Zhao S-J, Kong F-Q, Jie J, Li Q, Liu H, Xu A-D, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10:17–35.
Choi S-H, Aid S, Kim H-W, Jackson SH, Bosetti F. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase promotes alternative and anti-inflammatory microglial activation during neuroinflammation. J Neurochem. 2012;120:292–301.
Zeng F, Wu Y, Li X, Ge X, Guo Q, Lou X, et al. Custom-made ceria nanoparticles show a neuroprotective effect by modulating phenotypic polarization of the microglia. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57:5808–12.
Delavary BM, van der Veer WM, van Egmond M, Niessen FB, Beelen RHJ. Macrophages in skin injury and repair. Immunobiology. 2011;216:753–62.
Toita R, Kang J-H, Tsuchiya A. Phosphatidylserine liposome multilayers mediate the M1-to-M2 macrophage polarization to enhance bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:583–96.
Sheng-Ping F, Si-Yu C, Qi-Ming P, Meng Z, Xiang-Chong W, Xue W, et al. Advances in the research of the role of macrophage/microglia polarization-mediated inflammatory response in spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1014013.
Zhao Q, Shi M, Yin C, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Wang J, et al. Dual-wavelength photosensitive nano-in-micro scaffold regulates innate and adaptive immune responses for osteogenesis. Nanomicro Lett. 2020;13:28.
Zhao F, Lei B, Li X, Mo Y, Wang R, Chen D, et al. Promoting in vivo early angiogenesis with sub-micrometer strontium-contained bioactive microspheres through modulating macrophage phenotypes. Biomaterials. 2018;178:36–47.
Shen X, Fang K, Ru Yie KH, Zhou Z, Shen Y, Wu S, et al. High proportion strontium-doped micro-arc oxidation coatings enhance early osseointegration of titanium in osteoporosis by anti-oxidative stress pathway. Bioact Mater. 2021;10:405–19.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Foundation of Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515140046 & 2022A1515140151 & 2022A1515140071) and Huizhou Priority Clinical Speciality Cultivation Project (Orthopedics and Sports Medicine) and Scientific Research Projects of Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine (20221400 & 20222241) and Research and Innovation Fund of Huizhou First Hospital (2022ZD001 & 2022ZD002) and Huizhou Science and Technology Project (2022CZ010146 & 2022CZ010423).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Huizhou First Hospital, Guangdong Medical University (IACUC no. 2021113).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Y., Zhong, H., Huang, S. et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Hydrogel Regulates Stem Cell Behavior and Promotes Bone Healing in Osteoporosis. Tissue Eng Regen Med 20, 981–992 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-023-00561-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-023-00561-w