Abstract
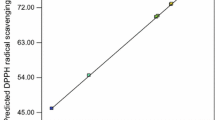
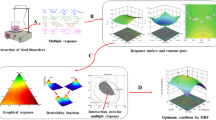
Response surface methodology (RSM) was utilized to optimize extraction conditions for the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor from Rhodiola sachalinensis. Optimized values for AChE inhibition and extraction yield were 19.41 and 13.35%, respectively, and these were in good agreement with the experimental values from validation, suggesting that RSM is a useful tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, and Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76, 965–77.
Chopra K, Misra S, and Kuhad A (2011) Neurobiological aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15, 535–55.
Contestabile A (2011) The history of the cholinergic hypothesis. Behav Brain Res 221, 334–40.
Darbinyan V, Kteyan A, Panossian A, Gabrielian E, Wikman G, and Wagner H (2000) Rhodiola rosea in stress induced fatigue—a double blind cross-over study of a standardized extract SHR-5 with a repeated low-dose regimen on the mental performance of healthy physicians during night duty. Phytomedicine 7, 365–71.
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Jr., and Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7, 88–95.
Gfrerer M and Lankmayr E (2005) Screening, optimization and validation of microwave-assisted extraction for the determination of persistent organochlorine pesticides. Anal Chim Acta 533, 203–11.
Gottwald MD and Rozanski RI (1999) Rivastigmine, a brain-region selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for treating Alzheimer’s disease: review and current status. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 8, 1673–82.
Gron G, Brandenburg I, Wunderlich AP, and Riepe MW (2006) Inhibition of hippocampal function in mild cognitive impairment: targeting the cholinergic hypothesis. Neurobiol Aging 27, 78–87.
Jansson ET (2005) Alzheimer disease is substantially preventable in the United States — review of risk factors, therapy, and the prospects for an expert software system. Med Hypotheses 64, 960–7.
Kelly CA, Harvey RJ, and Cayton H (1997) Drug treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. BMJ 314, 693–4.
Kim JK, Bae H, Kim MJ, Choi SJ, Cho HY, Hwang HJ, Kim YJ, Lim ST, Kim EK, Kim HK, Kim BY, and Shin DH (2009) Inhibitory effect of Poncirus trifoliate on acetylcholinesterase and attenuating activity against trimethyltin-induced learning and memory impairment. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73, 1105–12.
Li XD, Kang ST, Li GY, Li X, and Wang JH (2011) Synthesis of some phenylpropanoid glycosides (PPGs) and their acetylcholinesterase/xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. Molecules 16, 3580–96.
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Shenk JC, Nunomura A, Smith MA, Zhu X, and Perry G (2008) Alzheimer disease and the role of free radicals in the pathogenesis of the disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 7, 3–10.
Mukherjee PK, Kumar V, Mal M, and Houghton PJ (2007) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants. Phytomedicine 14, 289–300.
Ooi DJ, Iqbal S, and Ismail M (2012) Proximate composition, nutritional attributes and mineral composition of Peperomia pellucida L. (Ketumpangan Air) grown in Malaysia. Molecules 17, 11139–45.
Spasov AA, Wikman GK, Mandrikov VB, Mironova IA, and Neumoin VV (2000) A double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of the stimulating and adaptogenic effect of Rhodiola rosea SHR-5 extract on the fatigue of students caused by stress during an examination period with a repeated low-dose regimen. Phytomedicine 7, 85–9.
Stafiej A, Pyrzynska K, Ranz A, and Lankmayr E (2006) Screening and optimization of derivatization in heating block for the determination of aliphatic aldehydes by HPLC. J Biochem Biophys Methods 69, 15–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C.R., Kim, J.K., Shin, EC. et al. Application of response surface methodology to optimize the extraction of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Rhodiola sachalinensis . J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 57, 807–811 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4293-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4293-8