Abstract
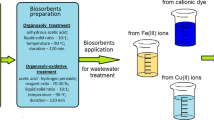
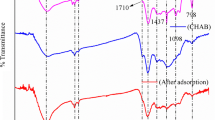
To meet sustainable development criteria, this paper deals with the possible utilization of solid waste materials generated from single and multiple successive processing of sugar beet (i.e., from the production of sugar, bioethanol and pectin) in wastewater treatment. Waste lignocellulose materials after extraction of sucrose, successive extractions of sucrose and pectin, as well as successive extractions of sucrose and pectin followed by enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose were investigated as biosorbents for heavy metal removal. Surface characterization was performed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and Boehm’s titration which showed heterogeneity regarding functional groups and the acidic surface of adsorbents. Also, a possible involvement of certain functional groups (hydroxyl, phenolic, carbonyl, amino) in the adsorption process was discussed. Equilibrium studies showed that these materials had greater adsorption capacity for Cu2+ compared to capacity for Cr6+ ions and that the adsorption process by various adsorbents could not be described by the same isotherm model. Adsorption mechanism study implied that ion exchange was not the only mechanism of Cu2+ binding onto investigated biosorbents. Also, the Cu2+ removal performance of waste materials was successfully predicted by applying a three-layer neural network with 6 neurons in the hidden layer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolali A, Guo WS, Ngo HH et al (2014) Typical lignocellulosic wastes and by-products for biosorption process in water and wastewater treatment: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 160:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.biortech.2013.12.037
Akar ST, Yilmazer D, Celik S et al (2013) On the utilization of a lignocellulosic waste as an excellent dye remover: Modification, characterization and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J 229:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.009
Aleeva SV, Chistyakova GV, Lepilova OV, Koksharov SA (2018) Effect of the state of carboxyl groups of pectin on the sorption binding of copper ions. Russ J Phys Chem A 92:1583–1589. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024418080022
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JRRAS.2014.02.003
Avery SV, Tobin JM (1993) Mechanism of adsorption of hard and soft metal ions to Saccharomyces cerevisiae and influence of hard and soft anions. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2851–2856
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817 (Article ID3039817)
Basha S, Murthy ZVP, Jha B (2008) Sorption of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions onto carica papaya: application of isotherms. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:980–986. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie071210o
Blázquez G, Hernáinz F, Calero M et al (2009) The effect of pH on the biosorption of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) with olive stone. Chem Eng J 148:473–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.09.026
Brdar M, Sciban M, Kukic D, Dosenovic T (2014) Kinetic model for the sorption of copper ions onto sugar beet shreds. Hem Ind Ind 68:793–799. https://doi.org/10.2298/hemind130830005b
Calero M, Pérez A, Blázquez G et al (2013) Characterization of chemically modified biosorbents from olive tree pruning for the biosorption of lead. Ecol Eng 58:344–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.012
Crist RH, Martin JR, Guptill PW et al (1990) Interaction of metals and protons with algae. 2. Ion exchange in adsorption and metal displacement by protons. Environ Sci Technol 24:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00073a008
Elhafez SEA, Hamad HA, Zaatout AA, Malash GF (2017) Management of agricultural waste for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution: adsorption behaviors, adsorption mechanisms, environmental protection, and techno-economic analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1397–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7891-7
Fiol N, Villaescusa I, Martínez M et al (2006) Sorption of Pb(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by olive stone waste. Sep Purif Technol 50:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2005.11.016
Freundlich HMF (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Gautam RK, Mudhoo A, Lofrano G, Chattopadhyaya MC (2014) Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J Environ Chem Eng 2:239–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.12.019
Ghaedi AM, Vafaei A (2017) Applications of artificial neural networks for adsorption removal of dyes from aqueous solution: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 245:20–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.04.015
Goertzen SL, Thériault KD, Oickle AM et al (2010) Standardization of the Boehm titration. Part I. CO2 expulsion and endpoint determination. Carbon NY 48:1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.11.050
Halysh V, Sevastyanova O, Pikus S et al (2020) Sugarcane bagasse and straw as low-cost lignocellulosic sorbents for the removal of dyes and metal ions from water. Cellulose 27:8181–8197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03339-8
Hassan ML, Kassem NF, Abd El-Kader AH (2010) Novel Zr(IV)/sugar beet pulp composite for removal of sulfate and nitrate anions. J Appl Polym Sci 117:2205–2212. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32063
Iqbal M, Saeed A, Zafar SI (2009) FTIR spectrophotometry, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling, ion exchange, and EDX analysis for understanding the mechanism of Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal by mango peel waste. J Hazard Mater 164:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.141
Ivanovska A, Asanovic K, Jankoska M et al (2020) Multifunctional jute fabrics obtained by different chemical modifications. Cellulose 27:8485–8502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03360-x
Ivetić DŽ, Šćiban MB, Antov MG (2012) Enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated sugar beet shreds: Statistical modeling of the experimental results. Biomass Bioenerg 47:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOMBIOE.2012.09.020
Karri RR, Sahu JN, Jayakumar NS (2017) Optimal isotherm parameters for phenol adsorption from aqueous solutions onto coconut shell based activated carbon: error analysis of linear and non-linear methods. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:472–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.08.004
Keren Y, Borisover M, Bukhanovsky N (2015) Sorption interactions of organic compounds with soils affected by agricultural olive mill wastewater. Chemosphere 138:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.085
Khajeh M, Sarafraz-Yazdi A, Natavan ZB (2013) Combination of artificial neural network and genetic algorithm method for modeling of methylene blue adsorption onto wood sawdust from water samples. Toxicol Ind Health 32:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713502842
Kumar KV, Porkodi K (2006) Relation between some two- and three-parameter isotherm models for the sorption of methylene blue onto lemon peel. J Hazard Mater 138:633–635
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li M, Wang LJ, Li D et al (2014) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from de-pectinated sugar beet pulp. Carbohydr Polym 102:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.11.021
Lide DR (ed) (2006) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton
Maghsoudi M, Ghaedi M, Zinali A et al (2015) Artificial neural network (ANN) method for modeling of sunset yellow dye adsorption using zinc oxide nanorods loaded on activated carbon: kinetic and isotherm study. Spectrochim Acta 134:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.106
Mata YN, Blázquez ML, Ballester A et al (2009) Sugar-beet pulp pectin gels as biosorbent for heavy metals: preparation and determination of biosorption and desorption characteristics. Chem Eng J 150:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.001
Mathioudakis V, Gerbens-Leenes PW, Van der Meer TH, Hoekstra AY (2017) The water footprint of second-generation bioenergy: a comparison of biomass feedstocks and conversion techniques. J Clean Prod 148:571–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2017.02.032
Nasr M, Mahmoud AED, Fawzy M, Radwan A (2017) Artificial intelligence modeling of cadmium(II) biosorption using rice straw. Appl Water Sci 7:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0295-x
Nethaji S, Sivasamy A, Mandal AB (2013) Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and mechanism for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes onto carbonaceous particles prepared from Juglans regia shell biomass. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0112-0
Pakade VE, Ntuli TD, Ofomaja AE (2017) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by Macadamia nutshell powder. Appl Water Sci 7:3015–3030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0412-5
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2009) Adsorption of copper (II), chromium (III), nickel (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions by meranti sawdust. J Hazard Mater 170:969–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.066
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611
Sajó I (1973) Komplexometria, 3rd edn. Müszaki Könyvkiadó, Budapest
Salazar-Rabago JJ, Leyva-Ramos R (2016) Novel biosorbent with high adsorption capacity prepared by chemical modification of white pine (Pinus durangensis) sawdust. Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. J Environ Manage 169:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.12.040
Schwanninger M, Rodrigues JC, Pereira H, Hinterstoisser B (2004) Effects of short-time vibratory ball milling on the shape of FT-IR spectra of wood and cellulose. Vib Spectrosc 36:23–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2004.02.003
Šćiban M, Kukić D, Ivetić D et al (2013) Possibility of using of treated beet shreds from process of bioethanol production for animal feed. J Process Energy Agric 17:124–126
Sciban M, Vulic T, Kukic D et al (2016) Characterization of raw and treated sugar beet shreds for copper ions adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 57(31):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1067167
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922
Toth J (1971) State equation of the solid–gas interface layers. Acta Chim Acad Sci Hung 69:311–328
Tran HN, Nguyen HC, Woo SH et al (2019) Removal of various contaminants from water by renewable lignocellulose-derived biosorbents: a comprehensive and critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:2155–2219. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1607442
Vučurović VM, Razmovski RN (2012) Sugar beet pulp as support for Saccharomyces cerivisiae immobilization in bioethanol production. Ind Crops Prod 39:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INDCROP.2012.02.002
Xu AR, Chen L, Guo X et al (2018) Biodegradable lignocellulosic porous materials: fabrication, characterization and its application in water processing. Int J Biol Macromol 115:846–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.133
Yildiz S (2017) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn(II) adsorption in batch process. Korean J Chem Eng 34:2423–2434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0157-3
Funding
The financial support from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (No. 451-03-9/2021-14/200134) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit and that they obtained consent from the responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out before the work was submitted.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukić, D., Šćiban, M., Brdar, M. et al. Sugar beet lignocellulose waste as biosorbents: surface functionality, equilibrium studies and artificial neural network modeling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 2503–2516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04140-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04140-9