Abstract
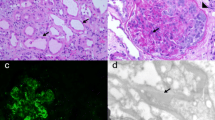
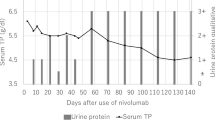
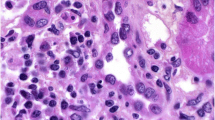
Nivolumab, an anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) antibody, has attracted increasing attention as a new treatment modality for gastric cancer. Herein, a case of acute kidney injury in a 66-year-old man with gastric cancer treated with nivolumab is presented. Kidney biopsy revealed severe acute interstitial nephritis and mild immunoglobulin A nephropathy. The cause of acute kidney injury was considered as acute interstitial nephritis because the main site of the lesion was the tubulointerstitium. Cessation of nivolumab and oral prednisolone administration rapidly improved the patient’s renal function. Nivolumab was then restarted without worsening of renal function. To the best of the authors knowledge, this is the first case in which reintroduction of nivolumab was successfully performed in a patient with gastric cancer. Further, the relevant literature was reviewed on nivolumab-induced acute interstitial nephritis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pardoll DM (2012) The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12:252–264
Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T et al (2017) Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 390:2461–2471
Wang PF, Chen Y, Song SY et al (2017) Immune-related adverse events associated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment for malignancies: a meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol 8:730
Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M et al (2017) Current diagnosis and management of immune related adverse events (irAEs) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Front Pharmacol 8:49
Sury K, Perazella MA, Shirali AC (2018) Cardiorenal complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Nephrol 14:571–588
Manohar S, Kompotiatis P, Thongprayoon C et al (2019) Programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment is associated with acute kidney injury and hypocalcemia: meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:108–117
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R et al (2019) Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 381:1535–1546
Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R et al (2019) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 381:2020–2031
Sharma P, Callahan MK, Bono P et al (2016) Nivolumab monotherapy in recurrent metastatic urothelial carcinoma (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, two-stage, multi-arm, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:1590–1598
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J et al (2016) Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N Engl J Med 375:1856–1867
Kato K, Doki Y, Ura T et al. (2020) Long-term efficacy and predictive correlates of response to nivolumab in Japanese patients with esophageal cancer. Cancer Sci 111(5):1676–1684
Shirali AC, Perazella MA, Gettinger S (2016) Association of acute interstitial nephritis with programmed cell death 1 inhibitor therapy in lung cancer patients. Am J Kidney Dis 68:287–291
Cortazar FB, Marrone KA, Troxell ML et al (2016) Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int 90:638–647
Tanaka A, Ikinaga K, Kiyohara E et al (2017) Critical renal adverse event induced by nivolumab therapy in a stage IV melanoma patient. J Dermatol 44:727–728
Belliere J, Meyer N, Mazieres J et al (2016) Acute interstitial nephritis related to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Br J Cancer 115:1457–1461
Escandon J, Peacock S, Trabolsi A et al (2017) Interstitial nephritis in melanoma patients secondary to PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor. J Immunother Cancer 5:3
Bottlaender L, Breton AL, de Laforcade L et al (2017) Acute interstitial nephritis after sequential ipilumumab—nivolumab therapy of metastatic melanoma. J Immunother Cancer 5:57
Koda R, Watanabe H, Tsuchida M et al (2018) Immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab)-associated kidney injury and the importance of recognizing concomitant medications known to cause acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: a case report. BMC Nephrol 19:48
Nakatani Y, Kawakami H, Ichikawa M et al (2018) Nivolumab-induced acute granulomatous tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with gastric cancer. Invest New Drugs 36:726–731
Tabei A, Watanabe M, Ikeuchi H et al (2018) The analysis of renal infiltrating cells in acute tubulointerstitial nephritis induced by anti-PD-1 antibodies: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med 57:3135–3139
Georgianos PI, Vaios V, Leontaridou E et al (2019) Acute interstitial nephritis in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer under immunotherapy with nivolumab. Case Rep Nephrol 2019:3614980
Ryuzaki M, Tokuyama H, Uchiyama K et al (2019) Acute interstitial nephritis with karyomegalic epithelial cells after nivolumab treatment-two case reports. Clin Med Insights Case Rep 12:1179547619853647
Hattahara K, Yamasaki T, Sawada A et al (2019) A case of late onset nivolumab-induced interstitial nephritis in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Hinyokika Kiyo 65:157–161
Oliveira DS, Mesquita JL, Garcia YDO et al (1992) Interstitial nephritis associated with nivolumab in a patient with hodgkin lymphoma. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2019(65):934–936
Irifuku T, Satoh A, Tani H et al (2020) Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and IgM deposits on glomerular capillary walls after immunotherapy with nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. CEN Case Rep 9:48–54
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the following grant: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Science Research (Grant numbers JP19K16718).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Qingjiang Hu and Hirofumi Hasuda. Kidney biopsy and diagnosis of acute interstitial nephritis were performed by Kenji Ueki and Akihiro Tsuchimoto (nephrologist). The first draft of the manuscript was written by Qingjiang Hu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Eiji Oki received honorarium from Ono Pharma.
Research involving human rights and animal participants
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that this study conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all human participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Hasuda, H., Ueki, K. et al. Reintroduction of nivolumab in a patient with gastric cancer after improvement of nivolumab-induced acute interstitial nephritis: a case report. Int Canc Conf J 9, 127–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13691-020-00418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13691-020-00418-2