Abstract
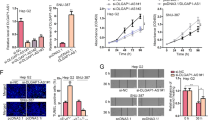
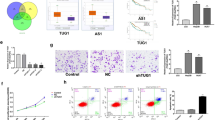
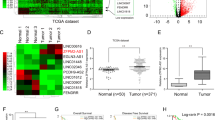
Emerging evidence has uncovered that noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) contribute to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Nevertheless, the functions of the majority of long ncRNAs (lncRNAs) in HCC are unknown. Here, we intend to probe the function of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 in the evolvement of HCC and the related mechanism. Expression levels of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1, miR-186-5p and KLF7 mRNA in HCC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues were monitored. Gain- or loss-of-function assays were utilized to investigate the biological functions of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1, miR-186-5p and KLF7 in HCC cell lines (including HCCLM3 and Huh7). Western blot was implemented for the detection of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins (including E-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail), KLF7, Wnt, β-catenin, and stemness-related proteins (Nanog, OCT4, YKL40, and CD133). Furthermore, the targeted associations between lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1, miR-186-5p, and KLF7 were verified by bioinformatics analysis, dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. As a result, lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 and KLF7 profiles were heightened in the HCC tissues versus adjacent normal tissues, while miR-186-5p had the opposite expression tendency. Up-regulation of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 was related to tumor size, advanced tumor stage, and lymph node metastasis of HCC patients. Functionally, overexpression of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 heightened HCC cells’ growth, invasion, EMT, and stemness and repressed their apoptosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In contrast, up-regulation of miR-186-5p or inhibition of KLF7 had reverse effects. In vivo, lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 overexpression facilitated tumor growth and EMT, accompanied by declined miR-186-5p levels and enhanced KLF7 expression. The mechanistic studies revealed that miR-186-5p served as a common target of lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 and KLF7. As hinted by the rescue experiments, NUTM2A-AS1 partly abated miR-186-5p-mediated anti-tumor effects in HCC cells, whereas KLF7 knockdown reversed the promotive effects of NUTM2A-AS1. LncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 accelerated the evolution of HCC by up-regulating the KLF7/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway through sponging miR-186-5p.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data sets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Grandhi MS, Kim AK, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Kamel IR, Ghasebeh MA, Pawlik TM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: From diagnosis to treatment. Surg Oncol. 2016;25(2):74–85.
Li S, Yang F, Ren X. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Discov Ther. 2015;9(5):363–71.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):1245–55.
Xu JM. Current treatment in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and prospects for immuno-oncology therapy. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017;39(8):561–5.
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet. 2015;47(3):199–208.
Acha-Sagredo A, Uko B, Pantazi P, Bediaga NG, Moschandrea C, Rainbow L, Marcus MW, Davies MPA, Field JK, Liloglou T. Long noncoding RNA dysregulation is a frequent event in non-small cell lung carcinoma pathogenesis. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(7):1050–8.
Wang J, Yu Z, Wang J, Shen Y, Qiu J, Zhuang Z. lncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 positively modulates TET1 and HIF-1A to enhance gastric cancer tumorigenesis and drug resistance by sponging miR-376a. Cancer Med. 2020;9(24):9499–510.
Xu X, Wang Y, Mojumdar K, Zhou Z, Jeong KJ, Mangala LS, et al. A-to-I-edited miRNA-379-5p inhibits cancer cell proliferation through CD97-induced apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5343–56.
Feng H, Zhang Z, Qing X, French SW, Liu D. miR-186-5p promotes cell growth, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting PTEN. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;108:105–13.
Zhang Z, Zhang W, Mao J, Xu Z, Fan M. miR-186-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in human osteosarcoma by targeting FOXK1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(3):553–64.
Islam F, Qiao B, Smith RA, Gopalan V, Lam AK. Cancer stem cell: fundamental experimental pathological concepts and updates. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015;98(2):184–91.
Yu Y, Cai O, Wu P, Tan S. MiR-490-5p inhibits the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ECT2. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(1):967–76.
Gupta R, Malvi P, Parajuli KR, Janostiak R, Bugide S, Cai G, Zhu LJ, Green MR, Wajapeyee N. KLF7 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis by up-regulating ISG expression and maintaining Golgi complex integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(22):12341–51.
Yao J, Zhang H, Liu C, Chen S, Qian R, Zhao K. miR-450b-3p inhibited the proliferation of gastric cancer via regulating KLF7. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:47.
Zhao L, Zhang Y, Liu J, Yin W, Jin D, Wang D, Zhang W. miR-185 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting KLF7. Oncol Res. 2019;27(9):1015–23.
Wang W, Smits R, Hao H, He C. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(7):926.
Huang A, Jin S, Han W, Wang Y, Ma S, Wang Z, Lin K, Zou Q, Zhou J, Li Z, Chen L. Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 contributes to tumor growth and activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in osteosarcoma by targeting the miR-3666/KLF7 axis. Int J Mol Med. 2020;47(1):387–96.
Wallace MC, Preen D, Jeffrey GP, Adams LA. The evolving epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global perspective. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;9(6):765–79.
Lim LJ, Wong SYS, Huang F, Lim S, Chong SS, Ooi LL, Kon OL, Lee CG. Roles and regulation of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019;79(20):5131–9.
Huang X, Gao Y, Qin J, Lu S. lncRNA MIAT promotes proliferation and invasion of HCC cells via sponging miR-214. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018;314(5):G559–65.
Chen J, Huang X, Wang W, Xie H, Li J, Hu Z, Zheng Z, Li H, Teng L. lncRNA CDKN2BAS predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes metastasis via the miR-153-5p/ARHGAP18 signaling axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(11):3371–81.
Zhang J, Lou W. A key mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA competing endogenous RNA triple sub-network linked to diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:340.
Sun J, Lu H, Wang X, Jin H. MicroRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: regulation, function, and clinical implications. Sci World J. 2013;2013: 924206.
Wang Y, Tai Q, Zhang J, Kang J, Gao F, Zhong F, Cai L, Fang F, Gao Y. MiRNA-206 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration but promotes apoptosis by modulating cMET expression. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019;51(3):243–53.
Shi J, Li X, Hu Y, Zhang F, Lv X, Zhang X, Chen Q, Hu S. MiR-1203 is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma metastases and indicates a poor prognosis. Neoplasma. 2020;67(2):267–76.
Wu SM, Ai HW, Zhang DY, Han XQ, Pan Q, Luo FL, Zhang XL. MiR-141 targets ZEB2 to suppress HCC progression. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(10):9993–7.
Song Y, Wang G, Zhuang J, Ni J, Zhang S, Ye Y, Xia W. MicroRNA-584 prohibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting BDNF. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(2):1994–2001.
Guo L, Li B, Miao M, Yang J, Ji J. MicroRNA-663b targets GAB2 to restrict cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):2913–20.
Zhu K, Su Y, Xu B, Wang Z, Sun H, Wang L, Sun C, He X. MicroRNA-186-5p represses neuroblastoma cell growth via down-regulation of Eg5. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(4):2245–56.
Islam F, Gopalan V, Vider J, Wahab R, Ebrahimi F, Lu CT, Kasem K, Lam AKY. MicroRNA-186-5p overexpression modulates colon cancer growth by repressing the expression of the FAM134B tumour inhibitor. Exp Cell Res. 2017;357(2):260–70.
Jones DZ, Schmidt ML, Suman S, Hobbing KR, Barve SS, Gobejishvili L, Brock G, Klinge CM, Rai SN, Park J, Clark GJ, Agarwal R, Kidd LR. Micro-RNA-186-5p inhibition attenuates proliferation, anchorage independent growth and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):421.
Shan Y, Li P. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 665 regulates viability, apoptosis, and autophagy via the MiR-186-5p/MAP4K3 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(9):842–53.
Kaczynski J, Cook T, Urrutia R. Sp1- and Kruppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol. 2003;4(2):206.
Li Y, Tu S, Zeng Y, Zhang C, Deng T, Luo W, Lian L, Chen L, Xiong X, Yan X. KLF2 inhibits TGF-β-mediated cancer cell motility in hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020;52(5):485–94.
Xue M, Zhou C, Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Wang S, Fu Y, Atyah M, Xue X, Zhu L, Dong Q, Jia H, Ren N, Hu R. The association between KLF4 as a tumor suppressor and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(15):15566–80.
Cai M, Shao W, Yu H, Hong Y, Shi L. Paeonol inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:5931–43.
Lyu J, Wang J, Miao Y, Xu T, Zhao W, Bao T, Zhu H. KLF7 is associated with poor prognosis and regulates migration and adhesion in tongue cancer. Oral Dis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.13767.
Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;62:50–60.
Vilchez V, Turcios L, Marti F, Gedaly R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(2):823–32.
He S, Tang S. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110851.
Evans PM, Chen X, Zhang W, Liu C. KLF4 interacts with beta-catenin/TCF4 and blocks p300/CBP recruitment by beta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(2):372–81.
Liang X, Xu W. miR-181a-5p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of glomerular mesangial cells by targeting KLF6. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):1121–8.
Li K, Yuan C. MicroRNA-103 modulates tumor progression by targeting KLF7 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(3):1013–28.
Funding
The study was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2022JJ30545), Key special funds project of Hunan Science and Technology Department (2020SKC2009), The Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission (20201954, A2017012, A2017015) and The Special Funding for the Construction of Innovative Provinces in Hunan (2021SK4031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: LQ. Performed the experiments: JL; FL; YY. Statistical analysis: FL; XZ; XL. Wrote the paper: JL; all the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study has been approved by The Affiliated Nanhua Hospital of University of South China. All animal procedures were performed according to the instructions of the ethics committee of The Affiliated Nanhua Hospital of University of South China.
Consent for publication
All the patients involved agreed to participate in this study and signed informed consent form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Liu, L., Yang, X. et al. LncRNA NUTM2A-AS1 aggravates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the miR-186-5p/KLF7-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Human Cell 36, 312–328 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00802-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00802-5