Abstract
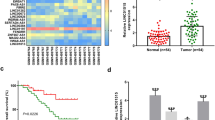
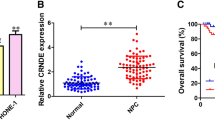
Accumulating studies have shown that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in cancer occurrence and development. Recently a new lncRNA LINC00460 has been reported to be upregulated in several types of cancers. In this study, we investigated the role of LINC00460 in invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). In NPC cell lines named C666-1 and 5-8F, LINC00460 overexpression promoted cancer cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), while depletion of LINC00460 exhibited opposite effects. We further demonstrated that LINC00460 regulated Rap1A expression through competitively binding to miR-30a-3p. LINC00460 knockdown suppressed NPC metastasis in a xenograft mouse model. Taken together, our findings suggested LINC00460 functioned as an oncogene in NPC which promoted invasion and metastasis, shedding lights on LINC00460 as a potential therapeutic target for NPC therapeutics from bench to clinic.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, Chan ATC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2016;387(10022):1012–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00055-0.
Colaco RJ, Betts G, Donne A, Swindell R, Yap BK, Sykes AJ, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective review of demographics, treatment and patient outcome in a single centre. Clin Oncol. 2013;25(3):171–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2012.10.006.
Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan YH, Sze H, Chan C, Lam TH. The battle against nasopharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2012;104(3):272–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.001.
Hattori M, Minato N. Rap1 GTPase: functions, regulation, and malignancy. J Biochem. 2003;134(4):479–84.
Pizon V, Baldacci G. Rap1A protein interferes with various MAP kinase activating pathways in skeletal myogenic cells. Oncogene. 2000;19(52):6074–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203984.
Bos JL. Linking Rap to cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17(2):123–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.009.
Bailey CL, Kelly P, Casey PJ. Activation of Rap1 promotes prostate cancer metastasis. Can Res. 2009;69(12):4962–8. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4269.
Xiang J, Bian C, Wang H, Huang S, Wu D. MiR-203 down-regulates Rap1A and suppresses cell proliferation, adhesion and invasion in prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2015;34:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0125-x.
Wang K, Li J, Guo H, Xu X, Xiong G, Guan X, et al. MiR-196a binding-site SNP regulates RAP1A expression contributing to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk and metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(11):2147–54. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs259.
Huang M, Anand S, Murphy EA, Desgrosellier JS, Stupack DG, Shattil SJ, et al. EGFR-dependent pancreatic carcinoma cell metastasis through Rap1 activation. Oncogene. 2012;31(22):2783–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.450.
Lu L, Wang J, Wu Y, Wan P, Yang G. Rap1A promotes ovarian cancer metastasis via activation of ERK/p38 and notch signaling. Cancer Med. 2016;5(12):3544–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.946.
Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43(6):904–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018.
Hauptman N, Glavac D. Long non-coding RNA in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(3):4655–69. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14034655.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Can Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634.
He R, Hu Z, Wang Q, Luo W, Li J, Duan L, et al. The role of long non-coding RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: as systemic review. Oncotarget. 2017;8(9):16075–83. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14211.
Lian Y, Yan C, Xu H, Yang J, Yu Y, Zhou J, et al. A novel lncRNA, LINC00460, affects cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating KLF2 and CUL4A expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:684–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.06.012.
Wang X, Mo FM, Bo H, Xiao L, Chen GY, Zeng PW, et al. Upregulated expression of long non-coding RNA, LINC00460, suppresses proliferation of colorectal cancer. J Cancer. 2018;9(16):2834–43. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.26046.
Wang F, Liang S, Liu X, Han L, Wang J, Du Q. LINC00460 modulates KDM2A to promote cell proliferation and migration by targeting miR-342-3p in gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018;11:6383–94. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S169307.
Li K, Sun D, Gou Q, Ke X, Gong Y, Zuo Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA linc00460 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018;420:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.060.
Kong YG, Cui M, Chen SM, Xu Y, Xu Y, Tao ZZ. LncRNA-LINC00460 facilitates nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis through sponging miR-149-5p to up-regulate IL6. Gene. 2018;639:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.006.
Liz J, Esteller M. lncRNAs and microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2016;1859(1):169–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.06.015.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
Liu Z, Luo W, Zhou Y, Zhen Y, Yang H, Yu X, et al. Potential tumor suppressor NESG1 as an unfavorable prognosis factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(11):e27887. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027887.
Hu C, Wei W, Chen X, Woodman CB, Yao Y, Nicholls JM, et al. A global view of the oncogenic landscape in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an integrated analysis at the genetic and expression levels. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(7):e41055. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041055.
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S, Hu GF. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in metastasis. Can Res. 2009;69(18):7135–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1618.
Martin MD, Matrisian LM. The other side of MMPs: protective roles in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(3–4):717–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9089-4.
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J, et al. MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(9):2044–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.26218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XDH and WWL conceived and designed the experiments, XL and BW analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, LPL, JW and JHM performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from a legally authorized representative(s) for anonymized patient information to be published in this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors declared that there were no conflicts of interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Ethical approval regarding animal study was granted from the Animal Ethics Committee of Cangzhou Central Hospital. Ethical consent was granted from the Medical Ethics Committee of Cangzhou Central Hospital for study involving patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Liu, W., Jiang, X. et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00460 aggravates invasion and metastasis by targeting miR-30a-3p/Rap1A in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Human Cell 32, 465–476 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00262-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00262-4