Abstract
Objective
Individualized dose prescription for liver stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) requires effective volume calculation and biological modeling to estimate the risk of liver injury. This study determined dose-volumetric (DV) parameters associated with low risk for radiation-induced liver disease (RILD) derived from normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) modeling with three-fraction and five-fraction SBRT for hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) > 5 cm.
Methods
Prescription dose was 24–36 Gy in three fractions and 40–45 Gy in five fractions. Effective volume was determined for 20 liver SBRT plans using the linear-quadratic (LQ) equation. Lyman-Kutcher-Burman NTCP model estimated the risk of liver toxicity. Mean dose to normal liver (MLD) was tabulated from plans associated with < 6 % toxicity prediction. Sensitivity analysis of model parameters and DV relationships to critical volume constraints was performed.
Results
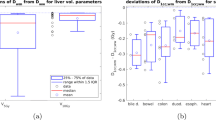
Median normal liver volume was 1144 cm3 (710–2916 cm3) and the median planning target volume (PTV) was 633 cm3 (186–2388 cm3). MLD predicting low hepatic toxicity for three-fraction SBRT plans was 13.8 ± 0.6 Gy, while MLD from five-fraction SBRT plans was 16.1 ± 1.0 Gy. Lower n, α/β, and D 50 parameters and a higher m parameter increased %RILD, and vice versa. An estimated 1200 cm3 of normal liver was needed in 7 of 10 three-fraction plans for very large tumors to functionally preserve 700 cm3and 800 cm3 to ≤ 15 and ≤ 18 Gy, respectively.
Conclusions
MLD values derived for three-fraction and five-fraction SBRT by the NTCP method were consistent with established SBRT liver dose constraints. However, SBRT for large hepatocellular carcinomas may be limited by critical volume dose objectives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J, Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer G (2004) The Barcelona approach: diagnosis, staging, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant Off Publ Am Assoc Stud Liver Dis Int Liver Transpl Soc 10(2 Suppl 1):S115–S120. doi:10.1002/lt.20034
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G, Kim JJ, Cummings B, Knox J, Sherman M, Dawson LA (2008) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(4):657–664. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.3529
Mendez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM, De Pooter JA, Heijmen BJ, Nowak PC, Nuyttens JJ, Brandwijk RP, Verhoef C, Ijzermans JN, Levendag PC (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: A single institution phase i-ii study. Acta Oncol 45(7):831–837. doi:10.1080/02841860600897934
Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M, Kwo P, Tector AJ, Zook J, Johnstone PA, Cardenes HR (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(4):e447–e453. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.011
Shin YJ, Kim MS, Yoo SY, Cho CK, Seo YS, Kang JK, Park SC, Han CJ, Kim SB, Lee BH, Lees DH (2010) Pilot study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma unsuitable for other therapies. Tumori 96(1):65–70
Allen Li X, Alber M, Deasy JO, Jackson A, Ken Jee KW, Marks LB, Martel MK, Mayo C, Moiseenko V, Nahum AE, Niemierko A, Semenenko VA, Yorke ED (2012) The use and QA of biologically related models for treatment planning: short report of the TG-166 of the therapy physics committee of the AAPM. Med Phys 39(3):1386–1409. doi:10.1118/1.3685447
Fuks Z, Kolesnick R (2005) Engaging the vascular component of the tumor response. Cancer Cell 8(2):89–91. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.07.014
Kutcher GJ, Burman C (1989) Calculation of complication probability factors for non-uniform normal tissue irradiation: the effective volume method. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 16(6):1623–1630
Dawson LA, Normolle D, Balter JM, McGinn CJ, Lawrence TS, Ten Haken RK (2002) Analysis of radiation-induced liver disease using the Lyman NTCP model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53(4):810–821
Dawson LA, Eccles C, Craig T (2006) Individualized image guided iso-NTCP based liver cancer SBRT. Acta Oncol 45(7):856–864. doi:10.1080/02841860600936369
Cardenes HR, Price TR, Perkins SM, Maluccio M, Kwo P, Breen TE, Henderson MA, Schefter TE, Tudor K, Deluca J, Johnstone PA (2010) Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol Off Publ Fed Span Oncol Soc Natl Cancer Inst Mex 12(3):218–225. doi:10.1007/s12094-010-0492-x
Son SH, Choi BO, Ryu MR, Kang YN, Jang JS, Bae SH, Yoon SK, Choi IB, Kang KM, Jang HS (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with unresectable primary hepatocellular carcinoma: dose-volumetric parameters predicting the hepatic complication. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(4):1073–1080. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.009
Pan CC, Kavanagh BD, Dawson LA, Li XA, Das SK, Miften M, Ten Haken RK (2010) Radiation-associated liver injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S94–S100. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.092
Murphy JD, Hattangadi-Gluth J, Song WY, Vollans E, Camborde M-L, Kosztyla R, Loewen SK, Crumley C, Moiseenko V (2014) Liver toxicity prediction with stereotactic body radiation therapy: The impact of accounting for fraction size. Pract Radiat Oncol. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2013.12.004
Sheu T, Molkentine J, Transtrum MK, Buchholz TA, Withers HR, Thames HD, Mason KA (2013) Use of the LQ model with large fraction sizes results in underestimation of isoeffect doses. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol 109(1):21–25. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.08.027
Guerrero M, Li XA (2004) Extending the linear-quadratic model for large fraction doses pertinent to stereotactic radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol 49(20):4825–4835
Park C, Papiez L, Zhang S, Story M, Timmerman RD (2008) Universal survival curve and single fraction equivalent dose: useful tools in understanding potency of ablative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(3):847–852. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.10.059
Brenner DJ (2008) The linear-quadratic model is an appropriate methodology for determining isoeffective doses at large doses per fraction. Semin Radiat Oncol 18(4):234–239. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.004
Kirkpatrick JP, Meyer JJ, Marks LB (2008) The linear-quadratic model is inappropriate to model high dose per fraction effects in radiosurgery. Semin Radiat Oncol 18(4):240–243. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.005
Son SH, Jang HS, Lee H, Choi BO, Kang YN, Jang JW, Yoon SK, Kay CS (2013) Determination of the alpha/beta ratio for the normal liver on the basis of radiation-induced hepatic toxicities in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol 8:61. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-8-61
Clavien PA, Oberkofler CE, Raptis DA, Lehmann K, Rickenbacher A, El-Badry AM (2010) What is critical for liver surgery and partial liver transplantation: size or quality? Hepatology 52(2):715–729. doi:10.1002/hep.23713
Clavien PA, Petrowsky H, DeOliveira ML, Graf R (2007) Strategies for safer liver surgery and partial liver transplantation. N Engl J Med 356(15):1545–1559. doi:10.1056/NEJMra065156
Bujold A, Massey CA, Kim JJ, Brierley J, Cho C, Wong RK, Dinniwell RE, Kassam Z, Ringash J, Cummings B, Sykes J, Sherman M, Knox JJ, Dawson LA (2013) Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 31(13):1631–1639. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.44.1659
Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 1112 (2013) Randomized phase III study of sorafenib versus stereotactic body radiation therapy followed by sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. http://www.rtog.org/ClinicalTrials/ProtocolTable/StudyDetails.aspx?study=1112
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research grant from Varian Medical Systems.
Conflict of interest
Shaun K. Loewen, Emily Vollans, Catherine Crumley, Hardeep Sahota, Robert Kosztyla, Mitchell Liu, Devin Schellenberg, Marie-Laure Camborde, Cheryl Duzenli, Vitali Moiseenko, Mohamed Khan, and Roy Ma declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loewen, S.K., Vollans, E., Crumley, C. et al. Liver dosimetric evaluation in biologically based stereotactic body radiotherapy for large inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Radiat Oncol 4, 177–184 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-015-0195-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-015-0195-6