Abstract
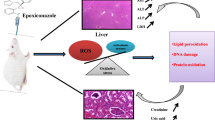
Organophosphate insecticides are increasingly used as substitutes for organochlorine and carbamate insecticides because of their high efficacity and lower persistence in the environment. Chlorpyrifos (CPF) (O,O-diethyl O-3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl phosphorothioate), an organophosphate considered as one of the most widely used insecticides in agriculture worldwide. The aim of this work is to analyze oxidative stress after a chronic exposure per Os to two doses of CPF (375 ppm,750 ppm) and the effect on mitochondrial swelling and respiration and cytoplasmic Cyt c amount. Our results showed a little increase in the activity of mitochondrial GST, level of MDA and a decrease in GPx and CAT activity confirmed by the lack of O2 (respiration inhibition), GSH level in mitochondria. we found an increase in mitochondrial swelling with a significant decrease in respiratory level. The amount of escaped Cytochrome c from mitochondria was significantly increased in treated groups according to the control in doses-dependent manner. Finally, our study showed that Chlorpyrifos caused general mitochondrial dysfunction accompanied with elevated oxidative stress amount in rabbit’s liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Parakasam, A., Sethupathy, S. & Latitha, S. Plasma and RBCs antioxidant status in occupational mal pesticide sprayers. Clin. Chim. Acta. 310, 107–112 (2001).
Geological, U. S. The quality of our nation’s waters -nutrients and pesticides, https://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/ 1999/1225/report.pdf (1999).
US EPA. Reregistration eligibility science chapter for chlorpyrifos. Fate and environmental risk assessment chapter (Revised June), http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/ op/chlorpyrifos/efedrra1.pdf (2000).
Minton, N. A. & Murray, V. S. G. A. Review of Organophosphate Poisoning. Med. Toxicol. Adverse Drug. Exp. 03, 350–375 (1988).
Casida, J. E. & Quistad, G. B. Organophosphate toxicity: Safety aspects of non-acetylcholinesterase secondary targets. Chem. Res. Tox. 17, 983–998 (2004).
Muñoz-Quezada, M. T. et al. Chronic exposure to organophosphate (OP) pesticides and neuropsychological functioning in farm workers: a review. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health. Apr. 29, 1–12 (2016).
Mackay, D. & Shiu, W.-Y. in Physical-chemical Properties and Environmental Fate Handbook (CRC Press LLC., U.S.A., 1999).
Khan, S. M. & Kour, G. Subacute oral toxicity of chlorpyrifos and the protective effect of green tea extract. Pest. Biochem. Phys. 89, 118–123 (2007).
Rigterink, R. H. & Kenaga, E. E. Synthesis and Insecticidal Activity of Some O,O-Dialkyl 0-3,5,6-Trihalo-2-pyridyl Phosphates and Phosphorothioates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 14, 304–306 (1966).
Sittig, M. in Handbook of Toxic and Hazardous Chemicals and Carcinogens 2nd Edn (eds Park Ridge N. J.) 581-582 (Noyes Publications, England and Wales, 1966).
Cremlyn, R. J., Dewhurst, B. B., Wakeford, D. H. & Raja, R. A. Studies of organophosphorochloridates. VI. Reactions of steroid phosphorochloridates with amines and some alcohols. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin. 19, 1171–1179 (1972).
Slotkin, T. A., MacKillop, E. A., Ryde, I. T. & Seidler, F. J. Ameliorating the developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos: a mechanisms-based approach in PC12 cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 115, 1306–1313 (2007).
Slotkin, T. A. Cholinergic systems in brain development and disruption by neurotoxicants: nicotine, environmental tobacco smoke, organophosphates. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 198, 132–151 (2004).
Slotkin, T. A., Levin, E. D. & Seidler, F. J. Compara tive developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate insecticides: Effects on brain development are separable from systemic toxicity. Environ. Health. Perspect. 114, 746–751 (2006).
Yoshikawa, T. & Naito, Y. What is oxidative stress? J. Japan Med. Assoc. 45, 271–276 (2002)
Yoshikawa, T. in Science of Free Radicals (Koudan Sha Saientifikku, Japan, 1997).
Cox, C. Chlorpyrifos, Part 2: human exposure. J. Pest. Ref. 15, 14–20 (1995).
Mitra, N. K., Siong, H. H. & Nadarajah, V. D. Evaluation of neurotoxicity of repeated dermal application of chlorpyrifos on hippocampus of adult mice. Ann. Agric. Env. Med. 15, 211–216 (2008).
Mehta, A., Verma, R. S. & Srivastava, N. Chlorpyrifosinduced alterations in the levels of hydrogen peroxide nitrate and nitrite in rat brain and liver. Pest. Biochem. Phys. 94, 55–59 (2009).
Gultekin, F., Patat, S., Akca, M. & Akdogan, M. Melatonin can suppress the cytotoxic effect of chlorpyrifos on human Hep G2 cell lines. Hum. Exp. Tox. 35, 47–55 (2006).
El-Shenawy, N. S. Effect of insecticides fenitrothion, endosulfan and abamectin on antioxidant parameters of isolated rat hepatocytes. In vitro Toxicol. 24, 1148–1157 (2010).
Levine, R. L., Williams, J. A., Stadtman, E. R. & Shacter, E. Carbonyl assays for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol. 233, 346–357 (1994).
Stadtman, E. R. Oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins by radiolysis and by metal-catalyzed reactions. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 62, 797–821 (1993).
Bebe, F. N. & Panemanogalore, M. Exposure of low doses of endosulfan and chlorpyrifos modifies endogenous antioxidants in tissues of rats. J. Env. Sci. Health. 38, 349–363 (2003).
Verma, R. S., Mehta, A. & Srivastava, N. In vivo chlorpyrifos induced oxidative stress: attenuated by antioxidant vitamins. Pest. Biochem. Phys. 88, 191–196 (2007).
Mansour, S. A. & Mossa, A. H. Oxidative damage, biochemical and histological alterations in rats exposed to chlorpyrifos and the antioxidant role of zinc. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 96, 14–23 (2010).
Peccini, E., Staudenmann, W., Albergoni, V., Gabriel, R. D. & James, P. Purification and primary structure of metallothioneins induced by Cadmium in the protests Tetrahymena pigmentosa and Tetrahymena pyriformis. European J. Biochem. 226, 853–859 (1994).
Masaya, M., Yoshinobu, H., Ai, Y., Maki, K. & Yasuo, O. Determination of cellular levels of nonprotein thiols in phytoplankton and their correlation with susceptibility to mercury. J. Phycol. 38, 983 (2002).
Hopkin, S. P. in Handbook of ecotoxicology (eds Calow P) 397-427 (Blackwell, U.K., 1993).
Franco, J. L. et al. Methylmercury neurotoxicity is associated with inhibition of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 47, 449–457 (2009).
Rouabhi, R., Gasmi, S., Boussekine, S. & Kebieche, M. Hepatic Oxidative Stress Induced by Zinc and Opposite Effect of Selenium in Oryctolagus cuniculus. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 05, 289 (2015).
Carlson, K. & Ehrich, M. Organophophorus compoundinduced modification of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 160, 33–42 (1999).
Tos-Luty, S. et al. Dermal and oral toxicity of Malathion in rats. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 10, 101–106 (2003).
Boulassel, A. Evaluation of the toxicity of two drugs: Paracetamol and Ibuprofen, on a cellular model: Paramecium tetraurelia. Test on the subcellular scale. Doctorate thesis. Universite Badji Mokhtar de Annaba (2014).
Gasmi, S., Rouabhi, R. & Kebieche, M. Deltamethrine induced neurodegeneration and behavioral effect by dysfunction cytosolic antioxidant system in rats’ brain. Algerian J. Nat. Sci. 1, 14–22 (2016).
Taib, C. et al. Toxicity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on oxidative stress status stromal enzymes and mitochondrial respiration and swelling of Oryctolagus cuniculus brain cortex. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Sci. 8, 349–355 (2016).
Bebianno, M. J., Company, R., Serafim, A., Cosson, R. P. & Fiala-Medoni, A. Antioxidant systems and lipid peroxidation in Bathy-modiolusazoricus from Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal vent fields. Aquat. Toxicol. 75, 354–373 (2005).
Lopez, J. et al. Oxidative stress markers in surgically treated patients with refractory epilepsy. Clin. Biochem. 40, 292–298 (2007).
Halliwell, B., Gutteridge, J. M. Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage, and antioxidant therapy. Lancet. 8391, 1396–1397 (1984).
Beal, M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1366, 211–223 (1998).
Turner, K. J. et al. Altered gene expression during rat Wolffian duct development in response to in utero exposure to the antiandrogen linuron. Toxicol. Sci. 74, 114–128 (2003).
Rouabhi, R., Djebar-Berrebbah, H. & Djebar, M. R. Impact of Flufenoxuron, an IGR pesticide on Gallus domesticus embryonic development in ovo. J. Cell Anim. Biol. 2, 087–091 (2008).
Gu, Z. T. et al. Heat stress induced apoptosis is triggered by transcription-independent p53, Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and the subsequent Bax mitochondrial translocation. Sci. Rep. 5, doi:10.1038/srep11497 (2015).
Zou, H., Li, Y., Liu, X. & Wang, X. An APAF-1 cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 11549–11556 (1999).
Jevtic, G. et al. Mitochondrial impairment, apoptosis and autophagy in a rat brain as immediate and longterm effects of perinatal phencyclidine treatment in fluence of restraint stress. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 66, 87–96 (2016).
Fromenty, B. Toxicité mitochondriale et métabolique des médicaments. Réanimation 19, 552–567 (2010).
Rachid, R., Houria, D. B. & Mohammed R. D. Impact of Flufenoxuron, an IGR pesticide on Gallus domesticus embryonic development in ovo. J. Cell Animal Biol. 2, 087–091 (2008).
Ming-Yuan, X. et al. Redox status in liver of rats following subchronic exposure to the combination of low dose dichlorvos and Deltamethrin. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 124, 60–65 (2015).
Ravagnan, L., Roumier, T. & Kroemer, G. Mitochondria the killer organelles and their weapons. J. Cell. Physiol. 192, 131–137 (2002).
Dayal, M. et al. Induction of Rat Brain Cytochrome P450s by Deltamethrin: Regional Specificity and Correlation with Neurobehavioral Toxicity. Neurotox. Res. 3, 351–357 (2001).
Yousef, M., Awad, T. & Mohamed, E. Deltamethrininduced oxidative damage and biochemical alterations in rat and its attenuation by Vitamin E. Toxicol. 227, 240–247 (2001).
DiMauro, S. & Schon, E. A. Mitochondrial disorders in the nervous system. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 31, 91–123 (2008).
Heiskanen, K. et al. Mitochondrial depolarization accompanies cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Biol. Chem. 274, 5654–5658 (1999).
Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantities of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
Kristal, B. S., Park, B. K. & Yu, B. P. 4-hydroxynonénal est un puissant inducteur de la transition de perméabilité mitochondriale. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6033–6038 (1996).
Rouabhi, R., Djebar-Berrebbah, H. & Djebar, M. R. Toxic Effect of a Pesticide, Diflubenzuron on Freshwater Microinvertebrate (Tetrahymena pyriformis). Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 12, 514–517 (2006).
Rouabhi, R., Djebar, H. & Djebar, M. R. Toxic Effects of Combined Molecule from Novaluron and Diflubenzuron on Paramecium caudatum. Am-Euras. J. Toxicol. 1, 74–80 (2009).
Weckbker, G. & Cory, J. G. Ribonucleotide reductase activity and growth of Glutathoine depleted mouse leukemia L1210 cells in vitro. Cancer Lett. 40, 257–264 (1988).
Flohe, L. & Gunzler, W. A. Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 105, 114–121 (1984).
Habig, H., Pabst, M. J. & Jokoby, W. B. Glutathione-S-transferase: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 7130–7139 (1974).
Cakmak, I. & Horst, W. J. Effect of aluminum on lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max). Physiol. Plantarum. 83, 463–468 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toualbia, N., Rouabhi, R. & Salmi, A. Evaluation of cytochrome c level and mitochondrial dysfunction biomarkers of Oryctolagus cuniculus liver exposed to Chlorpyrifos. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 9, 325–331 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-017-0338-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-017-0338-9