Abstract
Background
Angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) is a secreted protein which predominantly expressed in the liver, and involves in upregulation of lipid metabolism. Mutation in ANGPTL3 leads to decrease in the concentration of triglycerides (TGs), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), which makes it a promising candidate for hyperlipidemia.
Objectives
The present study aims to identify the effect of alcohol and high-fat diet, on the ANGPTL3 locus, in the development of hyperlipidemia.
Methods
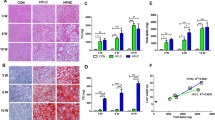
24 male Wister rats divided into four groups viz. control group (regular diet), HFD group (high-fat diet), ALC group (alcohol consuming), and HFD + ALC group (high-fat diet + alcohol consuming). All the groups were followed up for 12 weeks. Malondialdehyde (MDA), total body weight, TG, LDL, and HDL level were measured at the endpoint of study, and gene mutation analysis was also done for ANGPTL3.
Results
MDA level found to be significantly increases in HFD + ALC group, HFD group, and ALC group compared to the control group. RFLP analysis revealed a mutation in the ANGPTL3 gene which occurred only in HFD + ALC group. Moreover, body weight, TG, LDL, and HDL found to increase significantly in HFD + ALC, HFD, and ALC group as compared to the control group.
Conclusions
The present finding indicates is that high-fat diet with alcohol increases the oxidative stress in the liver, which causes a gain of function mutation in ANGPTL3 gene, resulting in hyperlipidemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auberval N, Dal S, Bietiger W, Pinget M, Jeandidier N, Maillard-Pedracini E, et al. Metabolic and oxidative stress markers in Wistar rats after 2 months on a high-fat diet. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014;6(1):130.
Thakur KK, Saini J, Mahajan K, Singh D, Jayswal DP, Mishra S, et al. Therapeutic implications of toll-like receptors in peripheral neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Res. 2017;115:224–32.
Kaur R, Goyal AK, Kaushik D, Sharma RK. In vitro studies on antibiotic activity of Ficus religiosa fruits extract against human pathogenic bacteria. J Chem Pharm Res. 2014;6(11):80–4.
Goyal A. Phytochemistry and in vitro studies on anti-fertility effect of Ficus religiosa fruits extract on uterine morphology of goat (Capra hircus). Int J Drug Dev Res. 2014;6(2):141–58.
Sharma RK, Goyal AK, Yadav SK, Bhat RA. Anti-fertility activity of Ficus religiosa fruits extract on goat uterus in vitro. Int J Drug Dev Res. 2013;5(4):330–5.
Sharma R, Goyal A, Yadav S, Bhat R. Pharmacognostical and phytochemical studies of the fruits of Ficus religiosa. Int J Drug Dev Res. 2013;5(4):211–3.
Sharma R, Goyal A, Bhat R. Antifertility activity of plants extracts on female reproduction: a review. Int J Pharm Biol Sci. 2013;3(3):493–514.
Tikka A, Jauhiainen M. The role of ANGPTL3 in controlling lipoprotein metabolism. Endocrine. 2016;52(2):187–93.
Dijk W, Kersten S. Regulation of lipid metabolism by angiopoietin-like proteins. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2016;27(3):249–56.
Cao JJ, Gregoire BR. A high-fat diet increases body weight and circulating estradiol concentrations but does not improve bone structural properties in ovariectomized mice. Nutr Res. 2016;36(4):320–7.
Samaha FF. Effect of very high-fat diets on body weight, lipoproteins, and glycemic status in the obese. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2005;7(6):412–20.
French MT, Norton EC, Fang H, Maclean JC. Alcohol consumption and body weight. Health Econ. 2010;19(7):814–32.
Li S, Tan H-Y, Wang N, Zhang Z-J, Lao L, Wong C-W, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26087–124.
Valente M, Carvalho F, Bastos M, De Pinho P, Carvalho M. Contribution of oxidative metabolism to cocaine-induced liver and kidney damage. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(33):5601–6.
Bankoglu EE, Tschopp O, Schmitt J, Burkard P, Jahn D, Geier A, et al. Role of PTEN in oxidative stress and DNA damage in the liver of whole-body Pten haplodeficient mice. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166956.
Santulli G. Angiopoietin-like proteins: a comprehensive look. Front Endocrinol. 2014;5.
Musunuru K, Pirruccello JP, Do R, Peloso GM, Guiducci C, Sougnez C, et al. Exome sequencing, ANGPTL3 mutations, and familial combined hypolipidemia. 2010;363(23):2220–2227.
Goyal AK, Bakshi J, Rani S, Anita BK, Anand A: Is rajyoga helpful in maintaining patient’s biochemical and hematological profile during breast cancer treatment? J Complement Integr Med. 2019; 16(3): 1-7
Akshay Anand, AtulKumar Goyal, Jaimanti Bakshi, Kaushal Sharma, Dharam Vir, Anita Didi, (2018) Yoga as an integrative approach for prevention and treatment of oral cancer. International Journal of Yoga 11 (3):177
Deepak Kumar Pal, Ashish Bhalla, Sridhar Bammidi, Shirley Telles, Adarsh Kohli, Saurabh Kumar, Pooja Devi, Navneet Kaur, Kiran Sharma, Raman Kumar, Neeru Malik, Vishakha Thakur, Garima Goswami Bhargava, Atul Kumar Goyal, Geeta Devi, Shalini Chauhan, Gurpreet Singh, Subzar Ahmad, Mamta Joshi, Sharmila Narwal, Kaushal Sharma, Rahul Tyagi, Shweta Modgil, Parul Bali, Vinod Bhatt, Jagdeep Sharma, Amit Singh, Jyoti Negi, Sasidharan K. Rajesh, Guruprasad Sharma, Purnandu Sharma, Ramphal Vats, R. Nagarathna, Ananda Balayogi Bhavanani, Krishna Manasa Burugupalli, Rathinavelu Vetrivendan, H.R. Nagendra, Akshay Anand, (2019) Can Yoga-Based Diabetes Management Studies Facilitate Integrative Medicine in India Current Status and Future Directions. Integrative Medicine International 4 (3-4):125-141
Goyal AK, Bansal A, Saini J: Nature walk decrease the depression by instigating positive mood. Social Health and Behavior. 2018; 1(2): 62-68
Goyal AK, Bhadada S, Anand A et al: Guinness world record attempt as a method to pivot the role of Yoga in Diabetes management. Annals of Neurosciences. 2019; 26 (1): 324:327
Acknowledgements
The present work was conducted at the Department of Biotechnology and Guwahati Medical College & Hospital, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), Guwahati, Assam (26.1599° N, 91.7679° E). The authors highly acknowledge all the colleagues who reviewed the present work.
Funding
The present work is funded by the department’s internal funds provided by NIPER to Jyoti Saini and Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) provided by ICMR, New Delhi, wide file no. 3/13/JRF-2015/HRD to Atul K Goyal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jyoti Saini and Ashok K Jangra designed the concept, conducted the study, and generated the raw data. Atul K Goyal compiled the raw data, did statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC), Guwahati Medical College & Hospital (CPSCEA Registration No. 351;3/1/2001) under Approval No. MC/32/2013/36.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, J., Goyal, A.K. & Jangra, A. High-fat diet with alcohol elevate oxidative stress which cause hyperlipidemia by inducing mutation in the ANGPTL3 locus. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 40, 269–275 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-019-00773-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-019-00773-8