Abstract
Background
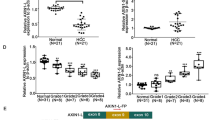
Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) is an oncogene that has been reported to participate in multiple tumorigenic processes. As yet, however, the role of PHPT1 in lung cancer development remains uncharacterized.
Methods
RNA sequencing assay and 18 pairs of tumor and normal tissues from patients were analyzed to reveal the upregulation of PHPT1 in lung cancer, followed by confirming the biological function in vitro and in vivo. Next, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, lung cancer samples, apoptosis assay, mass spectrometry experiments and western blotting were used to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying PHPT1 driven progression in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant lung cancer. Finally, we performed cellular and animal experiments to explore the tumor suppressive function of F-box protein 32 (FBXO32).
Results
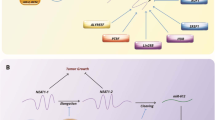
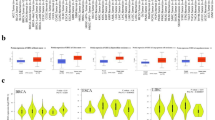
We found that PHPT1 is overexpressed in lung cancer patients and correlates with a poor overall survival. In addition, we found that the expression of PHPT1 is elevated in EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells and primary patient samples. Inhibition of PHPT1 expression in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells significantly decreased their proliferation and clonogenicity, and suppressed their in vitro tumor growth. Mechanistic studies revealed that activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway is driven by PHPT1. PHPT1 is required for maintaining drug resistance to erlotinib in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells. We found that FBXO32 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase for PHPT1, and that knockdown of FBXO32 leads to PHPT1 accumulation, activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway and promotion of the proliferation, clonogenicity and growth of lung cancer cells.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that PHPT1 may serve as a biomarker and therapeutic target for acquired erlotinib resistance in lung cancer patients carrying EGFR mutations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The RNA-sequencing data generated in this research are deposited in Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database. (reviewerlink:https://dataview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/object/PRJNA797898?reviewer=sl2j9hkl157fjs3l0avukv9h8q). Survival data supporting this article are from the Kaplan–Meier plotter website and GEO and TCGA datasets, which have been cited.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PHPT1:
-
Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FBXO32:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- AAb:
-
Autoantibody
- AKT/mTOR pathway:
-
Protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
- ERK/MAPK pathway:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- BMK-1:
-
Big MAP kinase-1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- OD value:
-
Optical density value
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
References
R.A. Smith, K.S. Andrews, D. Brooks, S.A. Fedewa, D. Manassaram-Baptiste, D. Saslow, O.W. Brawley, R.C. Wender, Cancer screening in the United States, 2018: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin 68, 297–316 (2018)
H. Sung, J. Ferlay, R.L. Siegel, M. Laversanne, I. Soerjomataram, A. Jemal, F. Bray, Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71, 209–249 (2021)
M. Duruisseaux, M. Esteller, Lung cancer epigenetics: From knowledge to applications. Semin Cancer Biol 51, 116–128 (2018)
L.M. Seijo, N. Peled, D. Ajona, M. Boeri, J.K. Field, G. Sozzi, R. Pio, J.J. Zulueta, A. Spira, P.P. Massion, P.J. Mazzone, L.M. Montuenga, Biomarkers in Lung Cancer Screening: Achievements. Promises, and Challenges, J Thorac Oncol 14, 343–357 (2019)
P.P. Massion, G.F. Healey, L.J. Peek, L. Fredericks, H.F. Sewell, A. Murray, J.F. Robertson, Autoantibody Signature Enhances the Positive Predictive Power of Computed Tomography and Nodule-Based Risk Models for Detection of Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 12, 578–584 (2017)
V. Doseeva, T. Colpitts, G. Gao, J. Woodcock, V. Knezevic, Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med 13, 55 (2015)
E. Giroux Leprieur, G. Herbretau, C. Dumenil, C. Julie, V. Giraud, S. Labrune, J. Dumoulin, J. Tisserand, J.F. Emile, H. Blons, T. Chinet, Circulating tumor DNA evaluated by Next-Generation Sequencing is predictive of tumor response and prolonged clinical benefit with nivolumab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology 7, e1424675 (2018)
J.D. Merker, G.R. Oxnard, C. Compton, M. Diehn, P. Hurley, A.J. Lazar, N. Lindeman, C.M. Lockwood, A.J. Rai, R.L. Schilsky, A.M. Tsimberidou, P. Vasalos, B.L. Billman, T.K. Oliver, S.S. Bruinooge, D.F. Hayes, N.C. Turner, Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients With Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. J Clin Oncol 36, 1631–1641 (2018)
M. Ehrlich, DNA hypomethylation in cancer cells. Epigenomics 1, 239–259 (2009)
G. Weiss, A. Schlegel, D. Kottwitz, T. Konig, R. Tetzner, Validation of the SHOX2/PTGER4 DNA Methylation Marker Panel for Plasma-Based Discrimination between Patients with Malignant and Nonmalignant Lung Disease. J Thorac Oncol 12, 77–84 (2017)
A.M. Aravanis, M. Lee, R.D. Klausner, Next-Generation Sequencing of Circulating Tumor DNA for Early Cancer Detection. Cell 168, 571–574 (2017)
A.M. Newman, S.V. Bratman, J. To, J.F. Wynne, N.C. Eclov, L.A. Modlin, C.L. Liu, J.W. Neal, H.A. Wakelee, R.E. Merritt, J.B. Shrager, B.W. Loo Jr., A.A. Alizadeh, M. Diehn, An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat Med 20, 548–554 (2014)
D. Consonni, M. Pierobon, M.H. Gail, M. Rubagotti, M. Rotunno, A. Goldstein, L. Goldin, J. Lubin, S. Wacholder, N.E. Caporaso, P.A. Bertazzi, M.A. Tucker, A.C. Pesatori, M.T. Landi, Lung cancer prognosis before and after recurrence in a population-based setting. J Natl Cancer Inst 107, djv059 (2015)
S. Klumpp, J. Hermesmeier, D. Selke, R. Baumeister, R. Kellner, J. Krieglstein, Protein histidine phosphatase: a novel enzyme with potency for neuronal signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22, 1420–1424 (2002)
P. Ek, G. Pettersson, B. Ek, F. Gong, J.P. Li, O. Zetterqvist, Identification and characterization of a mammalian 14-kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase. Eur J Biochem 269, 5016–5023 (2002)
S.X. Han, L.J. Wang, J. Zhao, Y. Zhang, M. Li, X. Zhou, J. Wang, Q. Zhu, 14-kDa Phosphohistidine phosphatase plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncol Lett 4, 658–664 (2012)
S. Srivastava, O. Zhdanova, L. Di, Z. Li, M. Albaqumi, H. Wulff, E.Y. Skolnik, Protein histidine phosphatase 1 negatively regulates CD4 T cells by inhibiting the K+ channel KCa3.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105, 14442–14446 (2008)
A. Xu, J. Hao, Z. Zhang, T. Tian, S. Jiang, J. Hao, C. Liu, L. Huang, X. Xiao, D. He, 14-kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase and its role in human lung cancer cell migration and invasion. Lung Cancer 67, 48–56 (2010)
A. Xu, Y. Li, W. Zhao, F. Hou, X. Li, L. Sun, W. Chen, A. Yang, S. Wu, B. Zhang, J. Yao, H. Wang, J. Huang, PHP14 regulates hepatic stellate cells migration in liver fibrosis via mediating TGF-beta1 signaling to PI3Kgamma/AKT/Rac1 pathway. J Mol Med (Berl) 96, 119–133 (2018)
W. Kolch, Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 827–837 (2005)
J.M. Buonato, M.J. Lazzara, ERK1/2 blockade prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells and promotes their sensitivity to EGFR inhibition. Cancer Res 74, 309–319 (2014)
A. Bahrami, M. Khazaei, M. Hasanzadeh, S. ShahidSales, M. Joudi Mashhad, M. Farazestanian, H.R. Sadeghnia, M. Rezayi, M. Maftouh, S.M. Hassanian, A. Avan, Therapeutic Potential of Targeting PI3K/AKT Pathway in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: Rational and Progress. J Cell Biochem 119, 2460–2469 (2018)
B. Gyorffy, P. Surowiak, J. Budczies, A. Lanczky, Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 8, e82241 (2013)
U. Degirmenci, M. Wang and J. Hu, Targeting Aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling for Cancer Therapy, Cells 9, (2020)
F. Liu, X. Yang, M. Geng, M. Huang, Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 8, 552–562 (2018)
E.K. Kim, E.J. Choi, Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802, 396–405 (2010)
Y.J. Guo, W.W. Pan, S.B. Liu, Z.F. Shen, Y. Xu, L.L. Hu, ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 19, 1997–2007 (2020)
D. Westover, J. Zugazagoitia, B.C. Cho, C.M. Lovly, L. Paz-Ares, Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Oncol 29, i10–i19 (2018)
H. Yasuda, E. Park, C.H. Yun, N.J. Sng, A.R. Lucena-Araujo, W.L. Yeo, M.S. Huberman, D.W. Cohen, S. Nakayama, K. Ishioka, N. Yamaguchi, M. Hanna, G.R. Oxnard, C.S. Lathan, T. Moran, L.V. Sequist, J.E. Chaft, G.J. Riely, M.E. Arcila, R.A. Soo, M. Meyerson, M.J. Eck, S.S. Kobayashi, D.B. Costa, Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 5, 216ra177 (2013)
A.X. Zhu, O. Rosmorduc, T.R. Evans, P.J. Ross, A. Santoro, F.J. Carrilho, J. Bruix, S. Qin, P.J. Thuluvath, J.M. Llovet, M.A. Leberre, M. Jensen, G. Meinhardt, Y.K. Kang, SEARCH: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib plus erlotinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 33, 559–566 (2015)
N. Habel, N. El-Hachem, F. Soysouvanh, H. Hadhiri-Bzioueche, S. Giuliano, S. Nguyen, P. Horak, A.S. Gay, D. Debayle, N. Nottet, G. Beranger, B.B. Paillerets, C. Bertolotto, R. Ballotti, FBXO32 links ubiquitination to epigenetic reprograming of melanoma cells. Cell Death Differ 28, 1837–1848 (2021)
Erratum: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries, CA Cancer J Clin 70, 313 (2020)
Q.Y. Hong, G.M. Wu, G.S. Qian, C.P. Hu, J.Y. Zhou, L.A. Chen, W.M. Li, S.Y. Li, K. Wang, Q. Wang, X.J. Zhang, J. Li, X. Gong, C.X. Bai, S. Lung Cancer Group of Chinese Thoracic and C. Chinese Alliance Against Lung, Prevention and management of lung cancer in China, Cancer 121 Suppl 17, 3080–3088 (2015)
R.S. Herbst, D. Morgensztern, C. Boshoff, The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553, 446–454 (2018)
M. Burotto, V.L. Chiou, J.M. Lee, E.C. Kohn, The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective. Cancer 120, 3446–3456 (2014)
N. Bluthgen, S. Legewie, Systems analysis of MAPK signal transduction. Essays Biochem 45, 95–107 (2008)
H.Y. Yong, M.S. Koh, A. Moon, The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18, 1893–1905 (2009)
T. Ahmed, A. Zulfiqar, S. Arguelles, M. Rasekhian, S.F. Nabavi, A.S. Silva, S.M. Nabavi, Map kinase signaling as therapeutic target for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Res 160, 105090 (2020)
B. Kaminska, A. Gozdz, M. Zawadzka, A. Ellert-Miklaszewska, M. Lipko, MAPK signal transduction underlying brain inflammation and gliosis as therapeutic target. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292, 1902–1913 (2009)
Y.T. Yeung, F. Aziz, A. Guerrero-Castilla, S. Arguelles, Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Therapies. Curr Pharm Des 24, 1449–1484 (2018)
R. Rosell, E. Carcereny, R. Gervais, A. Vergnenegre, B. Massuti, E. Felip, R. Palmero, R. Garcia-Gomez, C. Pallares, J.M. Sanchez, R. Porta, M. Cobo, P. Garrido, F. Longo, T. Moran, A. Insa, F. De Marinis, R. Corre, I. Bover, A. Illiano, E. Dansin, J. de Castro, M. Milella, N. Reguart, G. Altavilla, U. Jimenez, M. Provencio, M.A. Moreno, J. Terrasa, J. Muñoz-Langa, J. Valdivia, D. Isla, M. Domine, O. Molinier, J. Mazieres, N. Baize, R. Garcia-Campelo, G. Robinet, D. Rodriguez-Abreu, G. Lopez-Vivanco, V. Gebbia, L. Ferrera-Delgado, P. Bombaron, R. Bernabe, A. Bearz, A. Artal, E. Cortesi, C. Rolfo, M. Sanchez-Ronco, A. Drozdowskyj, C. Queralt, I. de Aguirre, J.L. Ramirez, J.J. Sanchez, M.A. Molina, M. Taron, L. Paz-Ares, Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13, 239–246 (2012)
J.R. Skaar, J.K. Pagan and M. Pagano, SnapShot: F box proteins I, Cell 137, 1160–1160.e1161 (2009)
E.T. Kipreos and M. Pagano, The F-box protein family, Genome Biol 1, REVIEWS3002 (2000)
M.D. Gomes, S.H. Lecker, R.T. Jagoe, A. Navon, A.L. Goldberg, Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98, 14440–14445 (2001)
S.C. Bodine, E. Latres, S. Baumhueter, V.K. Lai, L. Nunez, B.A. Clarke, W.T. Poueymirou, F.J. Panaro, E. Na, K. Dharmarajan, Z.Q. Pan, D.M. Valenzuela, T.M. DeChiara, T.N. Stitt, G.D. Yancopoulos, D.J. Glass, Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294, 1704–1708 (2001)
J.L. Chou, H.Y. Su, L.Y. Chen, Y.P. Liao, C. Hartman-Frey, Y.H. Lai, H.W. Yang, D.E. Deatherage, C.T. Kuo, Y.W. Huang, P.S. Yan, S.H. Hsiao, C.K. Tai, H.J. Lin, R.V. Davuluri, T.K. Chao, K.P. Nephew, T.H. Huang, H.C. Lai, M.W. Chan, Promoter hypermethylation of FBXO32, a novel TGF-beta/SMAD4 target gene and tumor suppressor, is associated with poor prognosis in human ovarian cancer. Lab Invest 90, 414–425 (2010)
H. Zhou, Y. Liu, R. Zhu, F. Ding, Y. Wan, Y. Li, Z. Liu, FBXO32 suppresses breast cancer tumorigenesis through targeting KLF4 to proteasomal degradation. Oncogene 36, 3312–3321 (2017)
Z. Mei, D. Zhang, B. Hu, J. Wang, X. Shen, W. Xiao, FBXO32 Targets c-Myc for Proteasomal Degradation and Inhibits c-Myc Activity. J Biol Chem 290, 16202–16214 (2015)
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for support.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81972740 to H.Y.Z.) and the Zhuhai Science and Technology Project (20181117E030079 to Y.F.L. and 20171009E030079 to M.X.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.Z., Y.F.L. and W.Z.L. performed the experiments. Y.Q.Q. and N.C. analyzed and interpreted data. S.D.Z. polished the manuscript. M.X. and H.Y.Z. provided ideas and critical comments. M.X. and H.Y.Z. conceived and designed the study and co-wrote the paper with feedback from all authors. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All human specimen and cell studies were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, and informed written consent was obtained from all donors.
Animal experiments
This study is compliant with all relevant ethical regulations regarding animal research. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfare Research Committee of the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and performed in accordance with established ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Supplementary Fig. 1
(PNG 776 KB)

Supplementary Fig. 1
(PNG 1095 KB)

Supplementary Fig. 1
(PNG 499 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Liao, Y., Lv, W. et al. FBXO32 targets PHPT1 for ubiquitination to regulate the growth of EGFR mutant lung cancer. Cell Oncol. 45, 293–307 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00669-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00669-6