Abstract
Background
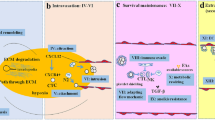
The transition of a primary tumour to metastatic progression is driven by dynamic molecular changes, including genetic and epigenetic alterations. The metastatic cascade involves bidirectional interactions among extracellular and intracellular components leading to disintegration of cellular junctions, cytoskeleton reorganization and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. These events promote metastasis by reprogramming the primary cancer cell’s molecular framework, enabling them to cause local invasion, anchorage-independent survival, cell death and immune resistance, extravasation and colonization of distant organs. Metastasis follows a site-specific pattern that is still poorly understood at the molecular level. Although various drugs have been tested clinically across different metastatic cancer types, it has remained difficult to develop efficacious therapeutics due to complex molecular layers involved in metastasis as well as experimental limitations.
Conclusions
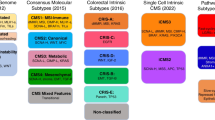
In this review, a systemic evaluation of the molecular mechanisms of metastasis is outlined and the potential molecular components and their status as therapeutic targets and the associated pre-clinical and clinical agents available or under investigations are discussed. Integrative methods like pan-cancer data analysis, which can provide clinical insights into both targets and treatment decisions and help in the identification of crucial components driving metastasis such as mutational profiles, gene signatures, associated pathways, site specificities and disease-gene phenotypes, are discussed. A multi-level data integration of the metastasis signatures across multiple primary and metastatic cancer types may facilitate the development of precision medicine and open up new opportunities for future therapies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Chatterjee, E.J. Rodger, M.R. Eccles, Epigenetic drivers of tumourigenesis and cancer metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 51, 149–159 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.004
D.F. Quail, J.A. Joyce, Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 19, 1423–1437 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3394
D.R. Welch, D.R. Hurst, Defining the hallmarks of metastasis. Cancer Res. 79, 3011–3027 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-19-0458
M. Teeuwssen, R. Fodde, Cell heterogeneity and phenotypic plasticity in metastasis formation: The case of colon cancer. Cancers 11, 1368 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091368
D.A. Lawson, K. Kessenbrock, R.T. Davis, N. Pervolarakis, Z. Werb, Tumour heterogeneity and metastasis at single-cell resolution. Nat. Cell Biol. 20, 1349–1360 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0236-7
L.J. Brylka, T. Schinke, Chemokines in physiological and pathological bone remodeling. Front. Immunol. 10, 2182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02182
A.C. Obenauf, J. Massagué, Surviving at a distance: Organ-specific metastasis. Trends Cancer 1, 76–91 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2015.07.009
R.L. Anderson, T. Balasas, J. Callaghan, R.C. Coombes, J. Evans, J.A. Hall, S. Kinrade, D. Jones, P.S. Jones, R. Jones, J.F. Marshall, M.B. Panico, J.A. Shaw, P.S. Steeg, M. Sullivan, W. Tong, A.D. Westwell, J.W.A. Ritchie, Cancer Research UK and Cancer Therapeutics CRC Australia Metastasis Working Group, A framework for the development of effective anti-metastatic agents. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16, 185–204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-018-0134-8
S. Paget, The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet. 133, 571–573 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)49915-0
A. Gandalovičová, D. Rosel, M. Fernandes, P. Veselý, P. Heneberg, V. Čermák, L. Petruželka, S. Kumar, V. Sanz-Moreno, J. Brábek, Migrastatics-anti-metastatic and anti-invasion drugs: Promises and challenges. Trends Cancer Res. 3, 391–406 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2017.04.008
A.W. Lambert, D.R. Pattabiraman, R.A. Weinberg, Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell 168, 670–691 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.037
S. Valastyan, R.A. Weinberg, Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 147, 275–292 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
I. Rodriguez-Hernandez, G. Cantelli, F. Bruce, V. Sanz-Moreno, Rho, ROCK and actomyosin contractility in metastasis as drug targets. F1000Res. 5, 783 (2016). https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7909.1
T. Alkasalias, A. Alexeyenko, K. Hennig, F. Danielsson, R.J. Lebbink, M. Fielden, S.P. Turunen, K. Lehti, V. Kashuba, H.S. Madapura, B. Bozoky, E. Lundberg, M. Balland, H. Guvén, G. Klein, A.K.B. Gad, T. Pavlova, RhoA knockout fibroblasts lose tumor-inhibitory capacity in vitro and promote tumor growth in vivo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, E1413–E1421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1621161114
M. Morgan-Fisher, U.M. Wewer, A. Yoneda, Regulation of ROCK activity in cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 61, 185–198 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155412470834
D.-F. Meng, P. Xie, L.-X. Peng, R. Sun, D.-H. Luo, Q.-Y. Chen, X. Lv, L. Wang, M.-Y. Chen, H.-Q. Mai, L. Guo, X. Guo, L.-S. Zheng, L. Cao, J.-P. Yang, M.-Y. Wang, Y. Mei, Y.-Y. Qiang, Z.-M. Zhang, J.-P. Yun, B.-J. Huang, C.-N. Qian, Erratum to: CDC42-interacting protein 4 promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by mediating invadopodia formation and activating EGFR signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 36, 33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0503-7
S. Jansen, R. Gosens, T. Wieland, M. Schmidt, Paving the Rho in cancer metastasis: Rho GTPases and beyond. Pharmacol. Ther. 183, 1–21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.09.002
C.X. Sun, M.A.O. Magalhães, M. Glogauer, Rac1 and Rac2 differentially regulate actin free barbed end formation downstream of the fMLP receptor. J. Cell Biol. 179, 239–245 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200705122
M. Schaks, H. Döring, F. Kage, A. Steffen, T. Klünemann, W. Blankenfeldt, T. Stradal, K. Rottner, RhoG and Cdc42 can contribute to Rac-dependent lamellipodia formation through WAVE regulatory complex-binding. Small GTPases 2, 122–132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2019.1657755
B. Frugtniet, W.G. Jiang, T.A. Martin, Role of the WASP and WAVE family proteins in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer 7, 99–109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2147/BCTT.S59006
K. Kazazian, C. Go, H. Wu, O. Brashavitskaya, R. Xu, J.W. Dennis, A.-C. Gingras, C.J. Swallow, Plk4 promotes cancer invasion and metastasis through Arp2/3 complex regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Res. 77, 434–447 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2060
G. Mouneimne, V. DesMarais, M. Sidani, E. Scemes, W. Wang, X. Song, R. Eddy, J. Condeelis, Spatial and temporal control of cofilin activity is required for directional sensing during chemotaxis. Curr. Biol. 16, 2193–2205 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.016
C.M. Fife, J.A. McCarroll, M. Kavallaris, Movers and shakers: cell cytoskeleton in cancer metastasis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 171, 5507–5523 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12704
F. Gertler, J. Condeelis, Metastasis: tumor cells becoming MENAcing. Trends Cell Biol. 21, 81–90 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2010.10.001
P. Pandey, S. Rachagani, S. Das, P. Seshacharyulu, Y. Sheinin, N. Naslavsky, Z. Pan, B.L. Smith, H.L. Peters, P. Radhakrishnan, N.R. McKenna, S.S.P. Giridharan, D. Haridas, S. Kaur, M.A. Hollingsworth, R.G. MacDonald, J.L. Meza, S. Caplan, S.K. Batra, J.C. Solheim, Amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2) affects the actin cytoskeleton and increases pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget 6, 2064–2075 (2015). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2990
N.A. Afratis, D. Nikitovic, H.A.B. Multhaupt, A.D. Theocharis, J.R. Couchman, N.K. Karamanos, Syndecans – key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J. 284, 27–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13940
S. Gopal, H.A.B. Multhaupt, R. Pocock, J.R. Couchman, Cell-extracellular matrix and cell-cell adhesion are linked by syndecan-4. Matrix Biol. 60–61, 57–69 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2016.10.006
Y.-L. Tai, L.-C. Chen, T.-L. Shen, Emerging roles of focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 690690 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/690690
R. Peláez, A. Pariente, Á Pérez-Sala, I.M. Larrayoz, Integrins: Moonlighting proteins in invadosome formation. Cancers 11, 615 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050615
A.M. López-Colomé, I. Lee-Rivera, R. Benavides-Hidalgo, E. López, Paxillin: a crossroad in pathological cell migration. J Hematol Oncol 10, 50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0418-y
P. Moreno-Layseca, C.H. Streuli, Signalling pathways linking integrins with cell cycle progression. Matrix Biol. 34, 144–153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.011
D.-B. Kong, F. Chen, N. Sima, Focal adhesion kinases crucially regulate TGFβ-induced migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via Src kinase and E-cadherin. Onco. Targets Ther. 10, 1783–1792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s122463
J.N. Skhinas, T.R. Cox, The interplay between extracellular matrix remodelling and kinase signalling in cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Adh. Migr. 12, 529–537 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2017.1405208
G. Gonzalez-Avila, B. Sommer, D.A. Mendoza-Posada, C. Ramos, A.A. Garcia-Hernandez, R. Falfan-Valencia, Corrigendum to “Matrix metalloproteinases participation in the metastatic process and their diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer”. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 137, 57–83, Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 138, 172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.04.017
Q. Xiao, G. Ge, Lysyl oxidase, extracellular matrix remodeling and cancer metastasis. Cancer Microenviron. 5, 261–273 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0105-z
B. Fogelgren, N. Polgár, K.M. Szauter, Z. Ujfaludi, R. Laczkó, K.S.K. Fong, K. Csiszar, Cellular fibronectin binds to lysyl oxidase with high affinity and is critical for its proteolytic activation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 24690–24697 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M412979200
M. Gadiya, G. Chakraborty, Signaling by discoidin domain receptor 1 in cancer metastasis. Cell Adh. Migr. 12, 315–323 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2018.1520556
C.A.S. Corsa, A. Brenot, W.R. Grither, S. Van Hove, A.J. Loza, K. Zhang, S.M. Ponik, Y. Liu, D.G. DeNardo, K.W. Eliceiri, P.J. Keely, G.D. Longmore, The action of discoidin domain receptor 2 in basal tumor cells and stromal cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for breast cancer metastasis. Cell Rep. 15, 2510–2523 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.033
Q. Chen, J. Massagué, Molecular pathways: VCAM-1 as a potential therapeutic target in metastasis, Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 5520–5525 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2904
R. Sharma, R. Sharma, T.P. Khaket, C. Dutta, B. Chakraborty, T.K. Mukherjee, Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell. Oncol. 40, 199–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0324-x
T. Liu, C. Han, S. Wang, P. Fang, Z. Ma, L. Xu, R. Yin, Cancer-associated fibroblasts: an emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 12, 86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0770-1
J. Kim, J.-S. Bae, Tumor-associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor microenvironment. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 6058147 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6058147
A. Gratchev, TGF-β signalling in tumour associated macrophages. Immunobiology 222, 75–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2015.11.016
A. Mantovani, F. Marchesi, A. Malesci, L. Laghi, P. Allavena, Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14, 399–416 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217
I. Jang, K.A. Beningo, Integrins, CAFs and mechanical forces in the progression of cancer. Cancers 11, 721 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050721
L.V. Ireland, A. Mielgo, Macrophages and fibroblasts, key players in cancer chemoresistance. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 6, 131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00131
Y. Lin, J. Xu, H. Lan, Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 12, 76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0760-3
C. Bonnans, J. Chou, Z. Werb, Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 786–801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3904
B.D. Robinson, G.L. Sica, Y.-F. Liu, T.E. Rohan, F.B. Gertler, J.S. Condeelis, J.G. Jones, Tumor microenvironment of metastasis in human breast carcinoma: a potential prognostic marker linked to hematogenous dissemination. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 2433–2441 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2179
B. Rizeq, M.I. Malki, The role of CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in breast cancer progression. Cancers 12, 1036 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041036
R. Singh, N. Kapur, H. Mir, N. Singh, J.W. Lillard Jr., S. Singh, CXCR6-CXCL16 axis promotes prostate cancer by mediating cytoskeleton rearrangement via Ezrin activation and αvβ3 integrin clustering. Oncotarget 7, 7343–7353 (2016). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6944
R.B. Troyanovsky, J. Klingelhöfer, S.M. Troyanovsky, α-Catenin contributes to the strength of E-cadherin-p120 interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 22, 4247–4255 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0250
N.A. Gloushankova, S.N. Rubtsova, I.Y. Zhitnyak, Cadherin-mediated cell-cell interactions in normal and cancer cells. Tissue Barriers 5, e1356900 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/21688370.2017.1356900
V. Gkretsi, T. Stylianopoulos, Cell adhesion and matrix stiffness: Coordinating cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Front. Oncol. 8, 145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00145
S. Lamouille, J. Xu, R. Derynck, Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 178–196 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3758
M. Grooteclaes, Q. Deveraux, J. Hildebrand, Q. Zhang, R.H. Goodman, S.M. Frisch, C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 4568–4573 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0830998100
G. Cai, D. Wu, Z. Wang, Z. Xu, K.-B. Wong, C.-F. Ng, F.L. Chan, S. Yu, Collapsin response mediator protein-1 (CRMP1) acts as an invasion and metastasis suppressor of prostate cancer via its suppression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and remodeling of actin cytoskeleton organization. Oncogene 36, 546–558 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.227
W.S. Byun, W.K. Kim, H.J. Han, H.-J. Chung, K. Jang, H.S. Kim, S. Kim, D. Kim, E.S. Bae, S. Park, J. Lee, H.-G. Park, S.K. Lee, Targeting histone methyltransferase DOT1L by a novel psammaplin A analog inhibits growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 15, 140–152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2019.09.005
M.-H. Cho, J.-H. Park, H.-J. Choi, M.-K. Park, H.-Y. Won, Y.-J. Park, C.H. Lee, S.-H. Oh, Y.-S. Song, H.S. Kim, Y.-H. Oh, J.-Y. Lee, G. Kong, DOT1L cooperates with the c-Myc-p300 complex to epigenetically derepress CDH1 transcription factors in breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 6, 7821 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8821
J. Park, D.-H. Kim, S.R. Shah, H.-N. Kim, P. Kshitiz, A. Kim, A. Quiñones-Hinojosa, Levchenko, Switch-like enhancement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by YAP through feedback regulation of WT1 and Rho-family GTPases. Nat. Commun. 10, 2797 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10729-5
P. Potdar, N. Lotey, Role of circulating tumor cells in future diagnosis and therapy of cancer. J. Cancer Metast. Treat. 1, 44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4103/2394-4722.158803
C. Agnoletto, L. Minotti, L. Brulle-Soumare, L. Pasquali, M. Galasso, F. Corrà, F. Baldassari, J.-G. Judde, S. Cairo, S. Volinia, Heterogeneous expression of EPCAM in human circulating tumour cells from patient-derived xenografts. Biomark Res. 6, 31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-018-0145-8
J.C.M. Wan, C. Massie, J. Garcia-Corbacho, F. Mouliere, J.D. Brenton, C. Caldas, S. Pacey, R. Baird, N. Rosenfeld, Liquid biopsies come of age: towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 223–238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.7
X.-L. Lou, J. Sun, S.-Q. Gong, X.-F. Yu, R. Gong, H. Deng, Interaction between circulating cancer cells and platelets: clinical implication. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 27, 450–460 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.04.10
L. Zhang, L.D. Ridgway, M.D. Wetzel, J. Ngo, W. Yin, D. Kumar, J.C. Goodman, M.D. Groves, D. Marchetti, The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 5, 180ra48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3005109
H. Wang, N.H. Stoecklein, P.P. Lin, O. Gires, Circulating and disseminated tumor cells: diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets in motion. Oncotarget 8, 1884–1912 (2017). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12242
W.-C. Wang, X.-F. Zhang, J. Peng, X.-F. Li, A.-L. Wang, Y.-Q. Bie, L.-H. Shi, M.-B. Lin, X.-F. Zhang, Survival mechanisms and influence factors of circulating tumor cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 6304701 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6304701
H. Peinado, H. Zhang, I.R. Matei, B. Costa-Silva, A. Hoshino, G. Rodrigues, B. Psaila, R.N. Kaplan, J.F. Bromberg, Y. Kang, M.J. Bissell, T.R. Cox, A.J. Giaccia, J.T. Erler, S. Hiratsuka, C.M. Ghajar, D. Lyden, Pre-metastatic niches: organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 302–317 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.6
C.-M. Zeng, Z. Chen, L. Fu, Frizzled receptors as potential therapeutic targets in human cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1543 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051543
Y. Zhang, M. Xia, K. Jin, S. Wang, H. Wei, C. Fan, Y. Wu, X. Li, X. Li, G. Li, Z. Zeng, W. Xiong, Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Cancer 17, 45 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0796-y
W. Chen, A.D. Hoffmann, H. Liu, X. Liu, Organotropism: new insights into molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-018-0047-0
X. Jin, Z. Demere, K. Nair, A. Ali, G.B. Ferraro, T. Natoli, A. Deik, L. Petronio, A.A. Tang, C. Zhu, L. Wang, D. Rosenberg, V. Mangena, J. Roth, K. Chung, R.K. Jain, C.B. Clish, M.G. Vander Heiden, T.R. Golub, A metastasis map of human cancer cell lines. Nature 588, 331–336 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2969-2
P.S. Steeg, Targeting metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 201–218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.25
V. Sopik, S.A. Narod, The relationship between tumour size, nodal status and distant metastases: on the origins of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 170, 647–656 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4796-9
M. Kim, S.H. Kizilbash, J.K. Laramy, G. Gampa, K.E. Parrish, J.N. Sarkaria, W.F. Elmquist, Barriers to effective drug treatment for brain metastases: A multifactorial problem in the delivery of precision medicine. Pharm. Res. 35, 177 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-018-2455-9
T.-X. Xie, F.-J. Huang, K.D. Aldape, S.-H. Kang, M. Liu, J.E. Gershenwald, K. Xie, R. Sawaya, S. Huang, Activation of stat3 in human melanoma promotes brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 66, 3188–3196 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2674
M. Yousefi, T. Bahrami, A. Salmaninejad, R. Nosrati, P. Ghaffari, S.H. Ghaffari, Lung cancer-associated brain metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic options. Cell. Oncol. 40, 419–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0345-5
W. Jacot, M.-C. Gerlotto-Borne, S. Thezenas, S. Pouderoux, S. Poujol, M. About, G. Romieu, Carmustine and methotrexate in combination after whole brain radiation therapy in breast cancer patients presenting with brain metastases: a retrospective study. BMC Cancer 10, 257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-257
M.G. Ewend, S. Brem, M. Gilbert, R. Goodkin, P.L. Penar, M. Varia, S. Cush, L.A. Carey, Treatment of single brain metastasis with resection, intracavity carmustine polymer wafers, and radiation therapy is safe and provides excellent local control. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 3637–3641 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2095
U. Bottoni, P. Bonaccorsi, V. Devirgiliis, V. Panasiti, R.G. Borroni, G. Trasimeni, R. Clerico, S. Calvieri, Complete remission of brain metastases in three patients with stage IV melanoma treated with BOLD and G-CSF. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 35, 507–513 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyi141
U. Herrlinger, T. Tzaridis, F. Mack, J.P. Steinbach, U. Schlegel, M. Sabel, P. Hau, R.-D. Kortmann, D. Krex, O. Grauer, R. Goldbrunner, O. Schnell, O. Bähr, M. Uhl, C. Seidel, G. Tabatabai, T. Kowalski, F. Ringel, F. Schmidt-Graf, B. Suchorska, S. Brehmer, A. Weyerbrock, M. Renovanz, L. Bullinger, N. Galldiks, P. Vajkoczy, M. Misch, H. Vatter, M. Stuplich, N. Schäfer, S. Kebir, J. Weller, C. Schaub, W. Stummer, J.-C. Tonn, M. Simon, V.C. Keil, M. Nelles, H. Urbach, M. Coenen, W. Wick, M. Weller, R. Fimmers, M. Schmid, E. Hattingen, T. Pietsch, C. Coch, M. Glas, Neurooncology Working Group of the German Cancer Society, Lomustine-temozolomide combination therapy versus standard temozolomide therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CeTeG/NOA-09): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 393, 678–688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31791-4
L. Abrey, Temozolomide for treating brain metastases. Sem. Oncol. 28, 34–42 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90069-7
M. Preusser, A.S. Berghoff, D. Schadendorf, N.U. Lin, R. Stupp, Brain metastasis: opportunity for drug development? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 25, 786–794 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e328359320d
M. Esposito, T. Guise, Y. Kang, The biology of bone metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 8, a031252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a031252
L.A. Kingsley, P.G.J. Fournier, J.M. Chirgwin, T.A. Guise, Molecular biology of bone metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 6, 2609–2617 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0234
S. Wang, G.-X. Li, C.-C. Tan, R. He, L.-J. Kang, J.-T. Lu, X.-Q. Li, Q.-S. Wang, P.-F. Liu, Q.-L. Zhai, Y.-M. Feng, FOXF2 reprograms breast cancer cells into bone metastasis seeds. Nat. Commun. 10, 2707 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10379-7
T.M. Dando, L.R. Wiseman, Clodronate: a review of its use in the prevention of bone metastases and the management of skeletal complications associated with bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. Drugs Aging 21, 949–962 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2165/00002512-200421140-00005
Z. Wang, L. Lei, X.-J. Cai, L.Y. Chen, M. Yuan, G. Yang, P. Huang, X. Wang, A preliminary study of pamidronic acid downregulation of angiogenic factors IGF-1/PECAM-1 expression in circulating level in bone metastatic breast cancer patients. Onco. Targets. Ther. 9, 3147–3152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S103624
B. Devitt, S.-A. McLachlan, Use of ibandronate in the prevention of skeletal events in metastatic breast cancer. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 4, 453–458 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s1966
P.-H. Chiang, H.-C. Wang, Y.-L. Lai, S.-C. Chen, W. Yen-Hwa, C.-K. Kok, Y.-C. Ou, J.-S. Huang, T.-C. Huang, T.-Y. Chao, Zoledronic acid treatment for cancerous bone metastases: a phase IV study in Taiwan. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 9, 653–659 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.126471
O. Sartor, Overview of samarium sm 153 lexidronam in the treatment of painful metastatic bone disease. Rev. Urol. 6 (Suppl 10), S3–S12 (2004). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16985930. Accessed 23 Apr 2021
W.C. Dougall, I. Holen, E. González Suárez, Targeting RANKL in metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 3, 519 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bonekey.2014.14
Y. Nakai, K. Okamoto, A. Terashima, S. Ehata, J. Nishida, T. Imamura, T. Ono, H. Takayanagi, Efficacy of an orally active small-molecule inhibitor of RANKL in bone metastasis. Bone Res. 7, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-018-0036-5
C. Khanna, X. Wan, S. Bose, R. Cassaday, O. Olomu, A. Mendoza, C. Yeung, R. Gorlick, S.M. Hewitt, L.J. Helman, The membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma metastasis. Nat. Med. 10, 182–186 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm982
A. Tamburrini, A. Majorino, S. Duggan, S. Jogai, A. Alzetani, A record-breaking lung metastasis from renal cell carcinoma 37 years after nephrectomy. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, rjx205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjx205
L. Jin, B. Han, E. Siegel, Y. Cui, A. Giuliano, X. Cui, Breast cancer lung metastasis: Molecular biology and therapeutic implications. Cancer Biol. Ther. 19, 858–868 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1456599
M. Yousefi, R. Nosrati, A. Salmaninejad, S. Dehghani, A. Shahryari, A. Saberi, Organ-specific metastasis of breast cancer: molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying lung metastasis. Cell. Oncol. 41, 123–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0376-6
G.P. Gupta, J. Massagué, Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127, 679–695 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001
P. Tomasini, J. Egea, M. Souquet-Bressand, L. Greillier, F. Barlesi, Alectinib in the treatment of ALK-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: clinical trial evidence and experience with a focus on brain metastases, Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 13, 1753466619831906 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1753466619831906
M.A. Socinski, R.M. Jotte, F. Cappuzzo, F. Orlandi, D. Stroyakovskiy, N. Nogami, D. Rodríguez-Abreu, D. Moro-Sibilot, C.A. Thomas, F. Barlesi, G. Finley, C. Kelsch, A. Lee, S. Coleman, Y. Deng, Y. Shen, M. Kowanetz, A. Lopez-Chavez, A. Sandler, M. Reck, IMpower150 Study Group, Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 2288–2301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1716948
A.V. Balar, M.D. Galsky, J.E. Rosenberg, T. Powles, D.P. Petrylak, J. Bellmunt, Y. Loriot, A. Necchi, J. Hoffman-Censits, J.L. Perez-Gracia, N.A. Dawson, M.S. van der Heijden, R. Dreicer, S. Srinivas, M.M. Retz, R.W. Joseph, A. Drakaki, U.N. Vaishampayan, S.S. Sridhar, D.I. Quinn, I. Durán, D.R. Shaffer, B.J. Eigl, P.D. Grivas, E.Y. Yu, S. Li, E.E. Kadel III, Z. Boyd, R. Bourgon, P.S. Hegde, S. Mariathasan, A. Thåström, O.O. Abidoye, G.D. Fine, D.F. Bajorin, IMvigor210 Study Group, Atezolizumab as first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 389, 67–76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32455-2
R. Saleh, R.Z. Taha, V. Sasidharan Nair, N.M. Alajez, E. Elkord, PD-L1 Blockade by atezolizumab downregulates signaling pathways associated with tumor growth, metastasis, and hypoxia in human triple negative breast cancer. Cancers 11, (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081050
J. Ma, D.J. Waxman, Combination of antiangiogenesis with chemotherapy for more effective cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 3670–3684 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-08-0715
M. Vocka, D. Langer, V. Fryba, J. Petrtyl, T. Hanus, M. Kalousova, T. Zima, L. Petruzelka, Novel serum markers HSP60, CHI3L1, and IGFBP-2 in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 18, 6284–6292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10925
O. Golubnitschaja, K.C. Sridhar, Liver metastatic disease: new concepts and biomarker panels to improve individual outcomes. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 33, 743–755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9816-8
D.G. Power, N.E. Kemeny, The role of floxuridine in metastatic liver disease. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 1015–1025 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0709
D. Melisi, R. Garcia-Carbonero, T. Macarulla, D. Pezet, G. Deplanque, M. Fuchs, J. Trojan, H. Oettle, M. Kozloff, A. Cleverly, C. Smith, S.T. Estrem, I. Gueorguieva, M.M.F. Lahn, A. Blunt, K.A. Benhadji, J. Tabernero, Galunisertib plus gemcitabine vs. gemcitabine for first-line treatment of patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 119, 1208–1214 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0246-z
J. Strauss, C.R. Heery, J. Schlom, R.A. Madan, L. Cao, Z. Kang, E. Lamping, J.L. Marté, R.N. Donahue, I. Grenga, L. Cordes, O. Christensen, L. Mahnke, C. Helwig, J.L. Gulley, Phase I Trial of M7824 (MSB0011359C), a bifunctional fusion protein targeting PD-L1 and TGFβ, in advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 1287–1295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2653
M. Elbaz, M. Ehab, Profile of palbociclib in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Target Ther. 8, 83–91 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2147/bctt.s83146
K.J. Frankowski, C. Wang, S. Patnaik, F.J. Schoenen, N. Southall, D. Li, Y. Teper, W. Sun, I. Kandela, D. Hu, C. Dextras, Z. Knotts, Y. Bian, J. Norton, S. Titus, M.A. Lewandowska, Y. Wen, K.I. Farley, L.M. Griner, J. Sultan, Z. Meng, M. Zhou, T. Vilimas, A.S. Powers, S. Kozlov, K. Nagashima, H.S. Quadri, M. Fang, C. Long, O. Khanolkar, W. Chen, J. Kang, H. Huang, E. Chow, E. Goldberg, C. Feldman, R. Xi, H.R. Kim, G. Sahagian, S.J. Baserga, A. Mazar, M. Ferrer, W. Zheng, A. Shilatifard, J. Aubé, U. Rudloff, J.J. Marugan, S. Huang, Metarrestin, a perinucleolar compartment inhibitor, effectively suppresses metastasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 10, 441 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aap8307
L. Malorni, G. Curigliano, A.M. Minisini, S. Cinieri, C.A. Tondini, K. D’Hollander, G. Arpino, A. Bernardo, A. Martignetti, C. Criscitiello, F. Puglisi, M. Pestrin, G. Sanna, E. Moretti, E. Risi, C. Biagioni, A. McCartney, L. Boni, M. Buyse, I. Migliaccio, L. Biganzoli, A. Di Leo, Palbociclib as single agent or in combination with the endocrine therapy received before disease progression for estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: TREnd trial. Ann. Oncol. 29, 1748–1754 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy214
Y. Suhail, M.P. Cain, K. Vanaja, P.A. Kurywchak, A. Levchenko, R. Kalluri, Kshitiz, Systems biology of cancer metastasis. Cell Systems 9, 109–127 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2019.07.003
Z.A. Yochum, J. Cades, L. Mazzacurati, N.M. Neumann, S.K. Khetarpal, S. Chatterjee, H. Wang, M.A. Attar, E.H.-B. Huang, S.N. Chatley, K. Nugent, A. Somasundaram, J.A. Engh, A.J. Ewald, Y.-J. Cho, C.M. Rudin, P.T. Tran, T.F. Burns, A first-in-class TWIST1 inhibitor with activity in oncogene-driven lung cancer, Mol. Cancer Res. 15, 1764–1776 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0298
L.F. Vistain, N. Yamamoto, R. Rathore, P. Cha, T.J. Meade, Targeted inhibition of snail activity in breast cancer cells by using a Co(III)-Ebox conjugate. Chem. Biochem. 16, 2065–2072 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201500289
J. Sakata, F. Utsumi, S. Suzuki, K. Niimi, E. Yamamoto, K. Shibata, T. Senga, F. Kikkawa, H. Kajiyama, Inhibition of ZEB1 leads to inversion of metastatic characteristics and restoration of paclitaxel sensitivity of chronic chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 8, 99482–99494 (2017). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20107
Q. Du, X. Zhang, X. Zhang, M. Wei, H. Xu, S. Wang, Propofol inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of MCF-7 cells by suppressing miR-21 expression, Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 1265–1271 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1594000
C. Bartholomeusz, X. Xie, M.K. Pitner, K. Kondo, A. Dadbin, J. Lee, H. Saso, P.D. Smith, K.N. Dalby, N.T. Ueno, MEK inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) prevents lung metastasis in a triple-negative breast cancer xenograft model. Mol. Cancer Therap. 14, 2773–2781 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-15-0243
L.H. El Touny, A. Vieira, A. Mendoza, C. Khanna, M.J. Hoenerhoff, J.E. Green, Combined SFK/MEK inhibition prevents metastatic outgrowth of dormant tumor cells. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 156–168 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI70259
J. Chen, T. Deng, X. Li, W. Cai, MiR-193b inhibits the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by targeting IGF1R, Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 2058–2064 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1620251
D. Melisi, S. Ishiyama, G.M. Sclabas, J.B. Fleming, Q. Xia, G. Tortora, J.L. Abbruzzese, P.J. Chiao, LY2109761, a novel transforming growth factor beta receptor type I and type II dual inhibitor, as a therapeutic approach to suppressing pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7, 829–840 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0337
A. Bandyopadhyay, J.K. Agyin, L. Wang, Y. Tang, X. Lei, B.M. Story, J.E. Cornell, B.H. Pollock, G.R. Mundy, L.-Z. Sun, Inhibition of pulmonary and skeletal metastasis by a transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 66, 6714–6721 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-3565
R. Ge, V. Rajeev, P. Ray, E. Lattime, S. Rittling, S. Medicherla, A. Protter, A. Murphy, J. Chakravarty, S. Dugar, G. Schreiner, N. Barnard, M. Reiss, Inhibition of growth and metastasis of mouse mammary carcinoma by selective inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase in vivo, Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 4315–4330 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0162
S. Biswas, J.S. Nyman, J. Alvarez, A. Chakrabarti, A. Ayres, J. Sterling, J. Edwards, T. Rana, R. Johnson, D.S. Perrien, S. Lonning, Y. Shyr, L.M. Matrisian, G.R. Mundy, Anti-transforming growth factor ß antibody treatment rescues bone loss and prevents breast cancer metastasis to bone. PLoS One 6, e27090 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027090
C.-Y. Park, D.-K. Kim, Y.Y. Sheen, EW-7203, a novel small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) type I receptor/activin receptor-like kinase-5, blocks TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Sci. 102, 1889–1896 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02014.x
C.-Y. Park, J.-Y. Son, C.H. Jin, J.-S. Nam, D.-K. Kim, Y.Y. Sheen, EW-7195, a novel inhibitor of ALK5 kinase inhibits EMT and breast cancer metastasis to lung. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 2642–2653 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.07.007
F. Zhang, D.R. Braun, G.E. Ananiev, F. Michael Hoffmann, I.-W. Tsai, S.R. Rajski, T.S. Bugni, Biemamides A–E, inhibitors of the TGF-β pathway that block the epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Org. Lett. 20, 5529–5532 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01871
L. Di, L.-J. Liu, Y.-M. Yan, R. Fu, Y. Li, Y. Xu, Y.-X. Cheng, Z.-Q. Wu, Discovery of a natural small-molecule compound that suppresses tumor EMT, stemness and metastasis by inhibiting TGFβ/BMP signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38, 134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1130-2
V. Ramesh, T. Brabletz, P. Ceppi, Targeting EMT in cancer with repurposed metabolic inhibitors. Trends Cancer Res. 6, 942–950 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.06.005
H. Li, Y. Chen, N. Xu, M. Yu, X. Tu, Z. Chen, M. Lin, B. Xie, J. Fu, L. Han, AMD3100 inhibits brain-specific metastasis in lung cancer via suppressing the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and protecting blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Transl. Res. 9, 5259–5274 (2017). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29312481. Accessed 23 Apr 2021
W.-B. Zhu, Z.-F. Zhao, X. Zhou, AMD3100 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell invasion, and metastasis in the liver and the lung through blocking the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 11746–11759 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27831
B. Devapatla, A. Sharma, S. Woo, CXCR2 inhibition combined with Sorafenib improved antitumor and antiangiogenic response in preclinical models of ovarian cancer. PLoS One 10, e0139237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139237
X. Yang, J. Di, Y. Zhang, S. Zhang, J. Lu, J. Liu, W. Shi, The Rho-kinase inhibitor inhibits proliferation and metastasis of small cell lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 66, 221–227 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2011.11.011
H. Ying, S.L. Biroc, W.-W. Li, B. Alicke, J.-A. Xuan, R. Pagila, Y. Ohashi, T. Okada, Y. Kamata, H. Dinter, The Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil inhibits tumor progression in human and rat tumor models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 2158–2164 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0440
T.F. Borin, A.S. Arbab, G.B. Gelaleti, L.C. Ferreira, M.G. Moschetta, B.V. Jardim-Perassi, A.S.M. Iskander, N.R.S. Varma, A. Shankar, V.B. Coimbra, V.A. Fabri, J.G. de Oliveira, D.A.P. de CZuccari, Melatonin decreases breast cancer metastasis by modulating Rho-associated kinase protein-1 expression. J. Pineal Res. 60, 3–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12270
S. Liu, R.H. Goldstein, E.M. Scepansky, M. Rosenblatt, Inhibition of rho-associated kinase signaling prevents breast cancer metastasis to human bone. Cancer Res. 69, 8742–8751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1541
E. Koedoot, M. Fokkelman, V.-M. Rogkoti, M. Smid, I. van de Sandt, H. de Bont, C. Pont, J.E. Klip, S. Wink, M.A. Timmermans, E.A.C. Wiemer, P. Stoilov, J.A. Foekens, S.E. Le Dévédec, J.W.M. Martens, B. van de Water, Uncovering the signaling landscape controlling breast cancer cell migration identifies novel metastasis driver genes. Nat. Commun. 10, 2983 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11020-3
R. Kanteti, S.K. Batra, F.E. Lennon, R. Salgia, FAK and paxillin, two potential targets in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 7, 31586–31601 (2016). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8040
B.Y. Lee, P. Timpson, L.G. Horvath, R.J. Daly, FAK signaling in human cancer as a target for therapeutics. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 146, 132–149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.10.001
A. Winer, M. Janosky, B. Harrison, J. Zhong, D. Moussai, P. Siyah, N. Schatz-Siemers, J. Zeng, S. Adams, P. Mignatti, Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by presurgical treatment with an oral matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor: A preclinical proof-of-principle study. Mol. Cancer Ther. 15, 2370–2377 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0194
Y. Lyu, Q. Xiao, L. Yin, L. Yang, W. He, Potent delivery of an MMP inhibitor to the tumor microenvironment with thermosensitive liposomes for the suppression of metastasis and angiogenesis, Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 4, 26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-019-0054-9
R.D. Bonfil, A. Sabbota, S. Nabha, M.M. Bernardo, Z. Dong, H. Meng, H. Yamamoto, S.R. Chinni, I.T. Lim, M. Chang, L.C. Filetti, S. Mobashery, M.L. Cher, R. Fridman, Inhibition of human prostate cancer growth, osteolysis and angiogenesis in a bone metastasis model by a novel mechanism-based selective gelatinase inhibitor. Int. J. Cancer. 118, 2721–2726 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21645
W.R. Grither, G.D. Longmore, Inhibition of tumor–microenvironment interaction and tumor invasion by small-molecule allosteric inhibitor of DDR2 extracellular domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, E7786–E7794 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1805020115
X. Hou, H. Du, X. Quan, L. Shi, Q. Zhang, Y. Wu, Y. Liu, J. Xiao, Y. Li, L. Lu, X. Ai, M. Zhan, S. Yuan, L. Sun, Silibinin inhibits NSCLC metastasis by targeting the EGFR/LOX pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 21 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00021
J. Chang, M.C. Lucas, L.E. Leonte, M. Garcia-Montolio, L.B. Singh, A.D. Findlay, M. Deodhar, J.S. Foot, W. Jarolimek, P. Timpson, J.T. Erler, T.R. Cox, Pre-clinical evaluation of small molecule LOXL2 inhibitors in breast cancer. Oncotarget 8, 26066–26078 (2017). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15257
A. Bondareva, C.M. Downey, F. Ayres, W. Liu, S.K. Boyd, B. Hallgrimsson, F.R. Jirik, The lysyl oxidase inhibitor, β-aminopropionitrile, diminishes the metastatic colonization potential of circulating breast cancer cells. PLoS One 4, e5620 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005620
T.L.M. Ten Hagen, A.L.B. Seynhaeve, G.A. de Wiel-Ambagtsheer, E.A. de Bruijn, S.T. van Tiel, C. Ruegg, M. Meyring, M. Grell, S.L. Goodman, A.M.M. Eggermont, The αVβ3/αVβ5 integrin inhibitor cilengitide augments tumor response to melphalan isolated limb perfusion in a sarcoma model. Int. J. Cancer. 132, 2694–2704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27940
K.B. Kim, V. Prieto, R.W. Joseph, A.H. Diwan, G.E. Gallick, N.E. Papadopoulos, A.Y. Bedikian, L.H. Camacho, P. Hwu, C.S. Ng, W. Wei, M.M. Johnson, S.M. Wittemer, A. Vardeleon, A. Reckeweg, A.D. Colevas, A randomized phase II study of cilengitide (EMD 121974) in patients with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 22, 294–301 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1097/CMR.0b013e32835312e4
J. Vansteenkiste, F. Barlesi, C.F. Waller, J. Bennouna, C. Gridelli, E. Goekkurt, D. Verhoeven, A. Szczesna, M. Feurer, J. Milanowski, P. Germonpre, H. Lena, D. Atanackovic, M. Krzakowski, C. Hicking, J. Straub, M. Picard, W. Schuette, K. O’Byrne, Cilengitide combined with cetuximab and platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients: results of an open-label, randomized, controlled phase II study (CERTO). Ann. Oncol. 26, 1734–1740 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv219
C. Scaringi, G. Minniti, P. Caporello, R.M. Enrici, Integrin inhibitor cilengitide for the treatment of glioblastoma: a brief overview of current clinical results. Anticancer Res. 32, 4213–4223 (2012). https://ar.iiarjournals.org/content/32/10/4213.long
A. Gilam, J. Conde, D. Weissglas-Volkov, N. Oliva, E. Friedman, N. Artzi, N. Shomron, Local microRNA delivery targets Palladin and prevents metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 7, 12868 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12868
L.-X. Yan, Y.-H. Liu, J.-W. Xiang, Q.-N. Wu, L.-B. Xu, X.-L. Luo, X.-L. Zhu, C. Liu, F.-P. Xu, D.-L. Luo, P. Mei, J. Xu, K.-P. Zhang, J. Chen, PIK3R1 targeting by miR-21 suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by reducing PI3K/AKT signaling and reversing EMT, and predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 48, 471–484 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3287
G. Oshima, N. Guo, C. He, M.E. Stack, C. Poon, A. Uppal, S.C. Wightman, A. Parekh, K.B. Skowron, M.C. Posner, W. Lin, N.N. Khodarev, R.R. Weichselbaum, In vivo delivery and therapeutic effects of a microRNA on colorectal liver metastases. Mol. Ther. 25, 1588–1595 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.04.005
D. Dettori, F. Orso, E. Penna, D. Baruffaldi, S. Brundu, F. Maione, E. Turco, E. Giraudo, D. Taverna, Therapeutic silencing of miR-214 inhibits tumor progression in multiple mouse models. Mol. Ther. 26, 2008–2018 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.05.020
Y. Hara, R. Torii, S. Ueda, E. Kurimoto, E. Ueda, H. Okura, Y. Tatano, H. Yagi, Y. Ohno, T. Tanaka, K. Masuko, T. Masuko, Inhibition of tumor formation and metastasis by a monoclonal antibody against lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1. Cancer Sci. 109, 3171–3182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13755
W. Leconet, M. Chentouf, S. du Manoir, C. Chevalier, A. Sirvent, I. Aït-Arsa, M. Busson, M. Jarlier, N. Radosevic-Robin, C. Theillet, D. Chalbos, J.-M. Pasquet, A. Pèlegrin, C. Larbouret, B. Robert, Therapeutic activity of anti-AXL antibody against triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenografts and metastasis, Clin. Cancer Res. 23, 2806–2816 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1316
K. Jin, N.B. Pandey, A.S. Popel, Simultaneous blockade of IL-6 and CCL5 signaling for synergistic inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 20, 54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-018-0981-3
A.-M. Georgoudaki, K.E. Prokopec, V.F. Boura, E. Hellqvist, S. Sohn, J. Östling, R. Dahan, R.A. Harris, M. Rantalainen, D. Klevebring, M. Sund, S.E. Brage, J. Fuxe, C. Rolny, F. Li, J.V. Ravetch, M.C.I. Karlsson, Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages by antibody targeting inhibits cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Rep. 15, 2000–2011 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.084
S. Mochizuki, M. Shimoda, H. Abe, Y. Miyamae, J. Kuramoto, N. Aramaki-Hattori, K. Ishii, H. Ueno, A. Miyakoshi, K. Kojoh, Y. Okada, Selective inhibition of ADAM28 suppresses lung carcinoma cell growth and metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 17, 2427–2438 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-1198
Y. Kato, A. Kunita, S. Abe, S. Ogasawara, Y. Fujii, H. Oki, M. Fukayama, Y. Nishioka, M.K. Kaneko, The chimeric antibody chLpMab-7 targeting human podoplanin suppresses pulmonary metastasis via ADCC and CDC rather than via its neutralizing activity. Oncotarget 6, 36003–36018 (2015). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5339
J. Klingelhöfer, B. Grum-Schwensen, M.K. Beck, R.S.P. Knudsen, M. Grigorian, E. Lukanidin, N. Ambartsumian, Anti-S100A4 antibody suppresses metastasis formation by blocking stroma cell invasion. Neoplasia 14, 1260–1268 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.121554
A. Chiechi, D.L. Waning, K.R. Stayrook, J.T. Buijs, T.A. Guise, K.S. Mohammad, Role of TGF- in breast cancer bone metastases. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 4, 15–30 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2013.410A4003
S. Milette, J.K. Sicklick, A.M. Lowy, P. Brodt, Molecular pathways: targeting the microenvironment of liver metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 23, 6390–6399 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1636
M. Singh, C. Venugopal, T. Tokar, N. McFarlane, M.K. Subapanditha, M. Qazi, D. Bakhshinyan, P. Vora, N.K. Murty, I. Jurisica, S.K. Singh, Therapeutic targeting of the premetastatic stage in human lung-to-brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 78, 5124–5134 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1022
A. Bettaieb, C. Paul, S. Plenchette, J. Shan, L. Chouchane, F. Ghiringhelli, Precision medicine in breast cancer: reality or utopia? J. Transl. Med. 15, 139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1239-z
Y.-Z. Jiang, Y. Liu, Y. Xiao, X. Hu, L. Jiang, W.-J. Zuo, D. Ma, J. Ding, X. Zhu, J. Zou, C. Verschraegen, D.G. Stover, V. Kaklamani, Z.-H. Wang, Z.-M. Shao, Molecular subtyping and genomic profiling expand precision medicine in refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the FUTURE trial. Cell Res. 31, 178–186 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0375-9
J. Verigos, A. Magklara, Revealing the complexity of breast cancer by next generation sequencing. Cancers 7, 2183–2200 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7040885
Q. Tan, J. Cui, J. Huang, Z. Ding, H. Lin, X. Niu, Z. Li, G. Wang, Q. Luo, S. Lu, Genomic alteration during metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 38, 469–486 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1159/000438644
V. Izzi, M.N. Davis, A. Naba, Pan-cancer analysis of the genomic alterations and mutations of the matrisome. Cancers 12, 2046 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082046
F. Chen, Y. Zhang, S. Varambally, C.J. Creighton, Molecular correlates of metastasis by systematic pan- cancer analysis across The Cancer Genome Atlas, Mol. Cancer Res. 17, 476–487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0601
P. Priestley, J. Baber, M.P. Lolkema, N. Steeghs, E. de Bruijn, C. Shale, K. Duyvesteyn, S. Haidari, A. van Hoeck, W. Onstenk, P. Roepman, M. Voda, H.J. Bloemendal, V.C.G. Tjan-Heijnen, C.M.L. van Herpen, M. Labots, P.O. Witteveen, E.F. Smit, S. Sleijfer, E.E. Voest, E. Cuppen, Pan-cancer whole-genome analyses of metastatic solid tumours. Nature 575, 210–216 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1689-y
S. Mishra, C.D. Kaddi, M.D. Wang, Pan-cancer analysis for studying cancer stage using protein and gene expression data. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2016, 2440–2443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2016.7591223
K. Pinker, J. Chin, A.N. Melsaether, E.A. Morris, L. Moy, Precision medicine and radiogenomics in breast cancer: New approaches toward diagnosis and treatment. Radiology 287, 732–747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018172171
S.A. Eschrich, J. Pramana, H. Zhang, H. Zhao, D. Boulware, J.-H. Lee, G. Bloom, C. Rocha-Lima, S. Kelley, D.P. Calvin, T.J. Yeatman, A.C. Begg, J.F. Torres-Roca, A gene expression model of intrinsic tumor radiosensitivity: prediction of response and prognosis after chemoradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 75, 489–496 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.014
J. Meehan, M. Gray, C. Martínez-Pérez, C. Kay, L.Y. Pang, J.A. Fraser, A.V. Poole, I.H. Kunkler, S.P. Langdon, D. Argyle, A.K. Turnbull, Precision medicine and the role of biomarkers of radiotherapy response in breastcCancer. Front. Oncol. 10, 628 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00628
Acknowledgements
BK is supported by a doctoral fellowship provided by Pondicherry University, India. The authors acknowledge the Centre for Bioinformatics, Pondicherry University, India for providing the computational facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, B., Coumar, M.S. Deciphering molecular mechanisms of metastasis: novel insights into targets and therapeutics. Cell Oncol. 44, 751–775 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00611-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00611-2