Abstract
Purpose
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which has a male predominance, lacks effective therapeutic options. Previously, the cardiac glycoside analogue bufalin has been found to inhibit HBV infection and HCC development. As yet, however, its molecular role in HBV-associated HCC has remained obscure.
Methods
Colony formation and soft agar assays, xenograft and orthotopic mouse models and HBV X protein (HBx) transgenic mice with exposure to diethylnitrosamine were used to evaluate the effect of bufalin on HBV-associated HCC growth and tumorigenicity. HBx-induced oncogenic signaling regulated by bufalin was assessed using PCR array, chromatin immunoprecipitation, site-directed mutagenesis, luciferase reporter, transcription and protein expression assays. Synergistic HCC therapeutic effects were examined using combinations of bufalin and sorafenib.
Results
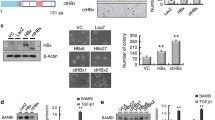
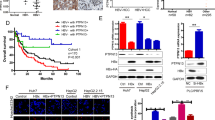
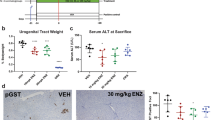
We found that bufalin exerted a more profound effect on inhibiting the proliferation of HBV-associated HCC cells than of non HBV-associated HCC cells. Bufalin significantly inhibited HBx-induced malignant transfromation in vitro and tumorigenicity in vivo. Androgen receptor (AR) signaling was found to be a target of bufalin resistance to HBV-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. We also found that bufalin induced both AR dephosphorylation and cell cycle-related kinase (CCRK) degradation to inhibit β-catenin/TCF signaling, which subsequently led to cell cycle arrest via cyclin D1 down-regulation and p21 up-regulation, resulting in HCC regression. Furthermore, we found that bufalin reduced > 60% diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in HBx transgenic mice, and improved the sensitivity of refractory HBV-associated HCC cells to sorafenib treatment.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that bufalin acts as a potential anti-HCC therapeutic candidate to block HBx-induced AR/CCRK/β-catenin signaling by targeting AR and CCRK, which may provide a novel strategy for the treatment of HBV-associated HCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66, 7–30 (2016)
C. Trepo, H.L. Chan, A. Lok, Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 384, 2053–2063 (2014)
C. Ye, X. Zhang, X. Chen, Q. Cao, X. Zhang, Y. Zhou, W. Li, L. Hong, H. Xie, X. Liu, H. Cao, Y.J. Wang, B. Kang, Multiple novel hepatocellular carcinoma signature genes are commonly controlled by the master pluripotency factor OCT4. Cell Oncol 43, 279–295 (2020)
T.W. Wu, H.H. Lin, L.Y. Wang, Chronic hepatitis B infection in adolescents who received primary infantile vaccination. Hepatology 57, 37–45 (2013)
P. Revill, B. Testoni, S. Locarnini, F. Zoulim, Global strategies are required to cure and eliminate HBV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13, 239–248 (2016)
I.F. Hung, R.T. Poon, C.L. Lai, J. Fung, S.T. Fan, M.F. Yuen, Recurrence of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with high viral load at the time of resection. Am J Gastroenterol 103, 1663–1673 (2008)
M. Kudo, R.S. Finn, S. Qin, K.H. Han, K. Ikeda, F. Piscaglia, A. Baron, J.W. Park, G. Han, J. Jassem, J.F. Blanc, A. Vogel, D. Komov, T.R.J. Evans, C. Lopez, C. Dutcus, M. Guo, K. Saito, S. Kraljevic, T. Tamai, M. Ren, A.L. Cheng, Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 391, 1163–1173 (2018)
J. Bruix, J.L. Raoul, M. Sherman, V. Mazzaferro, L. Bolondi, A. Craxi, P.R. Galle, A. Santoro, M. Beaugrand, A. Sangiovanni, C. Porta, G. Gerken, J.A. Marrero, A. Nadel, M. Shan, M. Moscovici, D. Voliotis, J.M. Llovet, Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Subanalyses of a phase III trial. J Hepatol 57, 821–829 (2012)
H.B. El-Serag, Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 142, 1264–1273 e1261 (2012)
H. Zhang, X.X. Li, Y. Yang, Y. Zhang, H.Y. Wang, X.F.S. Zheng, Significance and mechanism of androgen receptor overexpression and androgen receptor/mechanistic target of rapamycin cross-talk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67, 2271–2286 (2018)
Y. Murakami, K. Saigo, H. Takashima, M. Minami, T. Okanoue, C. Brechot, P. Paterlini-Brechot, Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 54, 1162–1168 (2005)
W.K. Sung, H. Zheng, S. Li, R. Chen, X. Liu, Y. Li, N.P. Lee, W.H. Lee, P.N. Ariyaratne, C. Tennakoon, F.H. Mulawadi, K.F. Wong, A.M. Liu, R.T. Poon, S.T. Fan, K.L. Chan, Z. Gong, Y. Hu, Z. Lin, G. Wang, Q. Zhang, T.D. Barber, W.C. Chou, A. Aggarwal, K. Hao, W. Zhou, C. Zhang, J. Hardwick, C. Buser, J. Xu, Z. Kan, H. Dai, M. Mao, C. Reinhard, J. Wang, J.M. Luk, Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 44, 765–769 (2012)
A.B. Rogers, E.J. Theve, Y. Feng, R.C. Fry, K. Taghizadeh, K.M. Clapp, C. Boussahmain, K.S. Cormier, J.G. Fox, Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with liver-gender disruption in male mice. Cancer Res 67, 11536–11546 (2007)
P. Huang, B. Zhuang, H. Zhang, H. Yan, Z. Xiao, W. Li, J. Zhang, Q. Tang, K. Hu, H.P. Koeffler, J. Wang, D. Yin, Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) is responsible for resistance to targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: Ex vivo culture evidence. Clin Cancer Res 21, 4420–4430 (2015)
C. Neuveut, Y. Wei, M.A. Buendia, Mechanisms of HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol 52, 594–604 (2010)
W.J. Yang, C.J. Chang, S.H. Yeh, W.H. Lin, S.H. Wang, T.F. Tsai, D.S. Chen, P.J. Chen, Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances the transcriptional activity of the androgen receptor through c-Src and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta kinase pathways. Hepatology 49, 1515–1524 (2009)
C.M. Chiu, S.H. Yeh, P.J. Chen, T.J. Kuo, C.J. Chang, P.J. Chen, W.J. Yang, D.S. Chen, Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances androgen receptor-responsive gene expression depending on androgen level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, 2571–2578 (2007)
Z. Yu, Y.Q. Gao, H. Feng, Y.Y. Lee, M.S. Li, Y. Tian, M.Y. Go, D.Y. Yu, Y.S. Cheung, P.B. Lai, J. Yu, V.W. Wong, J.J. Sung, H.L. Chan, A.S. Cheng, Cell cycle-related kinase mediates viral-host signalling to promote hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut 63, 1793–1804 (2014)
M.R. Romero, T. Efferth, M.A. Serrano, B. Castano, R.I. Macias, O. Briz, J.J. Marin, Effect of artemisinin/artesunate as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus production in an "in vitro" replicative system. Antivir Res 68, 75–83 (2005)
S.H. Wu, D.T. Bau, Y.T. Hsiao, K.W. Lu, T.C. Hsia, J.C. Lien, Y.C. Ko, W.H. Hsu, S.T. Yang, Y.P. Huang, J.G. Chung, Bufalin induces apoptosis in vitro and has antitumor activity against human lung cancer xenografts in vivo. Environ Toxicol 32, 1305–1317 (2017)
Y. Feng, Y. Chen, Y. Meng, Q. Cao, Q. Liu, C. Ling, C. Wang, Bufalin suppresses migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells elicited by poly (I:C) therapy. Oncoimmunology 7, e1426434 (2018)
X. Cui, Y. Inagaki, H. Xu, D. Wang, F. Qi, N. Kokudo, D. Fang, W. Tang, Anti-hepatitis B virus activities of cinobufacini and its active components bufalin and cinobufagin in HepG2.2.15 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 33, 1728–1732 (2010)
J.Q. Gai, X. Sheng, J.M. Qin, K. Sun, W. Zhao, L. Ni, The effect and mechanism of bufalin on regulating hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 48, 338–348 (2016)
Q. Miao, L.L. Bi, X. Li, S. Miao, J. Zhang, S. Zhang, Q. Yang, Y.H. Xie, J. Zhang, S.W. Wang, Anticancer effects of bufalin on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells: Roles of apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Mol Sci 14, 1370–1382 (2013)
Y. Wang, D.M. Lonard, Y. Yu, D.C. Chow, T.G. Palzkill, J. Wang, R. Qi, A.J. Matzuk, X. Song, F. Madoux, P. Hodder, P. Chase, P.R. Griffin, S. Zhou, L. Liao, J. Xu, B.W. O'Malley, Bufalin is a potent small-molecule inhibitor of the steroid receptor coactivators SRC-3 and SRC-1. Cancer Res 74, 1506–1517 (2014)
Y. Zhang, Y. Dong, M.W. Melkus, S. Yin, S.N. Tang, P. Jiang, K. Pramanik, W. Wu, S. Kim, M. Ye, H. Hu, J. Lu, C. Jiang, Role of P53-senescence induction in suppression of LNCaP prostate Cancer growth by Cardiotonic compound Bufalin. Mol Cancer Ther 17, 2341–2352 (2018)
T.I. Lee, S.E. Johnstone, R.A. Young, Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nat Protoc 1, 729–748 (2006)
D.Y. Yu, H.B. Moon, J.K. Son, S. Jeong, S.L. Yu, H. Yoon, Y.M. Han, C.S. Lee, J.S. Park, C.H. Lee, B.H. Hyun, S. Murakami, K.K. Lee, Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice expressing the hepatitis B virus X-protein. J Hepatol 31, 123–132 (1999)
H. Li, H. Zhou, D. Wang, J. Qiu, Y. Zhou, X. Li, M.G. Rosenfeld, S. Ding, X.D. Fu, Versatile pathway-centric approach based on high-throughput sequencing to anticancer drug discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109, 4609–4614 (2012)
S. Chen, S. Gulla, C. Cai, S.P. Balk, Androgen receptor serine 81 phosphorylation mediates chromatin binding and transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem 287, 8571–8583 (2012)
B.W. Benham-Pyle, B.L. Pruitt, W.J. Nelson, Cell adhesion. Mechanical strain induces E-cadherin-dependent Yap1 and beta-catenin activation to drive cell cycle entry. Science 348, 1024–1027 (2015)
H. Feng, A.S. Cheng, D.P. Tsang, M.S. Li, M.Y. Go, Y.S. Cheung, G.J. Zhao, S.S. Ng, M.C. Lin, J. Yu, P.B. Lai, K.F. To, J.J. Sung, Cell cycle-related kinase is a direct androgen receptor-regulated gene that drives beta-catenin/T cell factor-dependent hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 121, 3159–3175 (2011)
H. Feng, Z. Yu, Y. Tian, Y.Y. Lee, M.S. Li, M.Y. Go, Y.S. Cheung, P.B. Lai, A.M. Chan, K.F. To, H.L. Chan, J.J. Sung, A.S. Cheng, A CCRK-EZH2 epigenetic circuitry drives hepatocarcinogenesis and associates with tumor recurrence and poor survival of patients. J Hepatol 62, 1100–1111 (2015)
C.M. Kim, K. Koike, I. Saito, T. Miyamura, G. Jay, HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 351, 317–320 (1991)
S. Wilhelm, C. Carter, M. Lynch, T. Lowinger, J. Dumas, R.A. Smith, B. Schwartz, R. Simantov, S. Kelley, Discovery and development of sorafenib: A multikinase inhibitor for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5, 835–844 (2006)
J.M. Llovet, J. Zucman-Rossi, E. Pikarsky, B. Sangro, M. Schwartz, M. Sherman, G. Gores, Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2, 16018 (2016)
Z. Meng, C.R. Garrett, Y. Shen, L. Liu, P. Yang, Y. Huo, Q. Zhao, A.R. Spelman, C.S. Ng, D.Z. Chang, L. Cohen, Prospective randomised evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine combined with chemotherapy: A randomised phase II study of wild toad extract plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer 107, 411–416 (2012)
D.Z. Qiu, Z.J. Zhang, W.Z. Wu, Y.K. Yang, Bufalin, a component in Chansu, inhibits proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 13, 185 (2013)
S.H. Wang, S.H. Yeh, P.J. Chen, The driving circuit of HBx and androgen receptor in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut 63, 1688–1689 (2014)
M.W. Yu, S.W. Cheng, M.W. Lin, S.Y. Yang, Y.F. Liaw, H.C. Chang, T.J. Hsiao, S.M. Lin, S.D. Lee, P.J. Chen, C.J. Liu, C.J. Chen, Androgen-receptor gene CAG repeats, plasma testosterone levels, and risk of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 92, 2023–2028 (2000)
M.W. Yu, Y.C. Yang, S.Y. Yang, S.W. Cheng, Y.F. Liaw, S.M. Lin, C.J. Chen, Hormonal markers and hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A nested case-control study among men. J Natl Cancer Inst 93, 1644–1651 (2001)
H. Sun, W. Yang, Y. Tian, X. Zeng, J. Zhou, M.T.S. Mok, W. Tang, Y. Feng, L. Xu, A.W.H. Chan, J.H. Tong, Y.S. Cheung, P.B.S. Lai, H.K.S. Wang, S.W. Tsang, K.L. Chow, M. Hu, R. Liu, L. Huang, B. Yang, P. Yang, K.F. To, J.J.Y. Sung, G.L.H. Wong, V.W.S. Wong, A.S.L. Cheng, An inflammatory-CCRK circuitry drives mTORC1-dependent metabolic and immunosuppressive reprogramming in obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun 9, 5214 (2018)
M.D. Thompson, S.P. Monga, WNT/beta-catenin signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology 45, 1298–1305 (2007)
M. Ruiz de Galarreta, E. Bresnahan, P. Molina-Sanchez, K.E. Lindblad, B. Maier, D. Sia, M. Puigvehi, V. Miguela, M. Casanova-Acebes, M. Dhainaut, C. Villacorta-Martin, A.D. Singhi, A. Moghe, J. von Felden, L. Tal Grinspan, S. Wang, A.O. Kamphorst, S.P. Monga, B.D. Brown, A. Villanueva, J.M. Llovet, M. Merad, A. Lujambio, beta-catenin activation promotes immune escape and resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Discov 9, 1124–1141 (2019)
F. Qi, A. Li, Y. Inagaki, N. Kokudo, S. Tamura, M. Nakata, W. Tang, Antitumor activity of extracts and compounds from the skin of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Int Immunopharmacol 11, 342–349 (2011)
D. Wu, W.Y. Zhou, X.T. Lin, L. Fang, C.M. Xie, Bufalin induces apoptosis via mitochondrial ROS-mediated caspase-3 activation in HCT-116 and SW620 human colon cancer cells. Drug Chem Toxicol 42, 444–450 (2019)
H. Huang, W. Zhang, Bufalin induced apoptosis of bladder carcinoma cells through the inactivation of Na+K+-ATPase. Oncol Lett 16, 3826–3832 (2018)
W. Gu, L. Liu, F.F. Fang, F. Huang, B.B. Cheng, B. Li, Reversal effect of bufalin on multidrug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402/5-FU cells. Oncol Rep 31, 216–222 (2014)
Z. Yu, H. Feng, X. Sun, Y. Zhuo, M. Li, Z. Zhou, L. Huang, Y. Jiang, X. Zhu, X. Zhang, F. Le, C. Zheng, A.S. Cheng, Y. Gao, Bufalin suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting beta-catenin/TCF signaling via cell cycle-related kinase. Sci Rep 8, 3891 (2018)
D. Witt-Kehati, A. Fridkin, M.B. Alaluf, R. Zemel, A. Shlomai, Inhibition of pMAPK14 overcomes resistance to Sorafenib in hepatoma cells with hepatitis B virus. Transl Oncol 11, 511–517 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81774240, 81874436, 81673935, 81673938, 81672789, 81603589, 81774256 and 81673767), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (H2017013), the Chenguang Program from Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (15CG48), the Shanghai Rising-star Program (17QA1403900), the Training plan of outstanding young medical talents, Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (2017YQ021), the Talent Youth Supporting project sponsored by the Chinese Medicine Association (QNRC2-C14), the Training Plan for Excellent Academic Leaders of Shanghai Health System (2017BR007), the Science Research Project of Thirteen Five-year Plan (2018ZX10725504), the Shanghai science and Technology Commission support project (16401970600), Siming Scholar from Shanghai Shuguang Hospital (SGXZ-201904), and the Chinese medicine preponderant disease breeding project (zybz-2017004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: Z.Y., X.H.S., Y.Q.G.; acquisition of data: Z.Y., H.F., Y.H.Z., M.L., X.J.Z.; analysis and interpretation of data: L.Y.H., X.Z., Z.H.Z., C.Z.; drafting of the manuscript: Z.Y., H.F.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: X.H.S., Y.Q.G.; statistical analysis: Y.J., F.L.; administrative, technical or material support: D.-Y.Y., A.S.L.C.; study supervision: Z.Y., X.H.S., Y.Q.G.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors declare any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 407 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Feng, H., Zhuo, Y. et al. Bufalin inhibits hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma development through androgen receptor dephosphorylation and cell cycle-related kinase degradation. Cell Oncol. 43, 1129–1145 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00546-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00546-0