Abstract
Background
Genetic variations in cancer patients may serve as important prognostic indicators of clinical outcome. The GNAS1 T393C single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) diversely correlates with the clinical outcome in cancer. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential prognostic value of T393C-SNP in complete resected only surgically treated esophageal cancer (EC).
Methods
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leucocytes of 190 patients who underwent only complete surgical resection for EC. T393C-SNP was correlated with clinic-pathological parameters, tumor cell dissemination in bone marrow (DTC) and clinical outcome.
Results
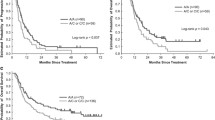
T-allele carriers had more advanced disease due to presence of lymph node metastasis (P < 0.0001) and DTC (P = 0.01) and higher recurrence rate (P = 0.01) compared to CC genotype. The disease-free (P < 0.001) and overall survival (P < 0.001) was better in CC compared to TT and TC patients. In the multivariate Cox regression disease-stage adjusted analysis the T393C-SNP was identified as a strong independent prognostic factor for recurrence (hazard ratio 1.8, P = 0.01) and survival (hazard ratio 2.5, P < 0.001) in EC patients.
Conclusion
Determination of T393C-SNP preoperatively will allow allocation of EC patients into different risk profiles which may help to stratify patients eligible for neoadjuvant and or adjuvant therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
R.A. Malthaner, R.K. Wong, R.B. Rumble, L. Zuraw, Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for resectable esophageal cancer: a clinical practice guideline. BMC Cancer 4, 67 (2004)
R.A. Malthaner, R.K. Wong, R.B. Rumble, L. Zuraw, Neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy for resectable esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2, 35 (2004)
C.G. Peyre, J.A. Hagen, S.R. DeMeester, J.J. Van Lanschot, A. Holscher et al., Predicting systemic disease in patients with esophageal cancer after esophagectomy: a multinational study on the significance of the number of involved lymph nodes. Ann. Surg. 248, 979–985 (2008)
E. Adjadj, M. Schlumberger, F. de Vathaire, Germ-line DNA polymorphisms and susceptibility to differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet Oncol. 10, 181–190 (2009)
D.F. Easton, K.A. Pooley, A.M. Dunning, P.D. Pharoah, D. Thompson et al., Genome-wide association study identifies novel breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature 447, 1087–1093 (2007)
K.W. Hunter, Host genetics and tumour metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 90, 752–755 (2004)
M.R. Koelle, Heterotrimeric G protein signaling: getting inside the cell. Cell 126, 25–27 (2006)
L.S. Weinstein, S. Yu, D.R. Warner, J. Liu, Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr. Rev. 22, 675–705 (2001)
J. Lyons, C.A. Landis, G. Harsh, L. Vallar, K. Grunewald et al., Two G protein oncogenes in human endocrine tumors. Science 249, 655–659 (1990)
A. Lania, G. Mantovani, A. Spada, Genetics of pituitary tumors: focus on G-protein mutations. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 228, 1004–1017 (2003)
Y. Daaka, L.M. Luttrell, R.J. Lefkowitz, Switching of the coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to different G proteins by protein kinase A. Nature 390, 88–91 (1997)
X. Yang, F.Y. Lee Sr., G.S. Wand, Increased expression of Gs(alpha) enhances activation of the adenylyl cyclase signal transduction cascade. Mol. Endocrinol. 11, 1053–1061 (1997)
U.H. Frey, H. Alakus, J. Wohlschlaeger, K.J. Schmitz, G. Winde et al., GNAS1 T393C polymorphism and survival in patients with sporadic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 5071–5077 (2005)
U.H. Frey, A. Eisenhardt, G. Lummen, H. Rubben, K.H. Jockel et al., The T393C polymorphism of the G alpha s gene (GNAS1) is a novel prognostic marker in bladder cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 14, 871–877 (2005)
K. Pantel, C. Alix-Panabieres, S. Riethdorf, Cancer micrometastases. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6, 339–351 (2009)
K. Pantel, R.H. Brakenhoff, B. Brandt, Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 329–340 (2008)
E. Borgen, B. Naume, J.M. Nesland, G. Kvalheim, K. Beiske et al., Standardization of the immunocytochemical detection of cancer cells in BM and blood: I. Establishment of objective criteria for the evaluation of immunostained cells. Cytotherapy 1, 377–388 (1999)
T. Fehm, S. Braun, V. Muller, W. Janni, G. Gebauer et al., A concept for the standardized detection of disseminated tumor cells in bone marrow from patients with primary breast cancer and its clinical implementation. Cancer 107, 885–892 (2006)
U.H. Frey, G. Lummen, T. Jager, K.H. Jockel, K.W. Schmid et al., The GNAS1 T393C polymorphism predicts survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 759–763 (2006)
U.H. Frey, H. Nuckel, L. Sellmann, D. Siemer, R. Kuppers et al., The GNAS1 T393C polymorphism is associated with disease progression and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 5686–5692 (2006)
G.F. Lehnerdt, P. Franz, S. Winterhoff, A. Bankfalvi, S. Grehl et al., The GNAS1 T393C polymorphism predicts survival in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Laryngoscope 118, 2172–2176 (2008)
G.F. Lehnerdt, P. Franz, A. Zaqoul, K.J. Schmitz, S. Grehl et al., Overall and relapse-free survival in oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma are associated with genotypes of T393C polymorphism of the GNAS1 gene. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 1753–1758 (2008)
L.S. Weinstein, J. Liu, A. Sakamoto, T. Xie, M. Chen, Minireview: GNAS: normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology 145, 5459–5464 (2004)
F. Capon, M.H. Allen, M. Ameen, A.D. Burden, D. Tillman et al., A synonymous SNP of the corneodesmosin gene leads to increased mRNA stability and demonstrates association with psoriasis across diverse ethnic groups. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 2361–2368 (2004)
J. Duan, M.S. Wainwright, J.M. Comeron, N. Saitou, A.R. Sanders et al., Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 205–216 (2003)
M.J. Tierney, R.L. Medcalf, Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 2 contains mRNA instability elements within exon 4 of the coding region. Sequence homology to coding region instability determinants in other mRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 13675–13684 (2001)
F. Otterbach, R. Callies, U.H. Frey, K.J. Schmitz, C. Wreczycki et al., The T393C polymorphism in the gene GNAS1 of G protein is associated with survival of patients with invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 105, 311–317 (2007)
K.J. Schmitz, H. Lang, U.H. Frey, G.C. Sotiropoulos, J. Wohlschlaeger et al., GNAS1 T393C polymorphism is associated with clinical course in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Neoplasia 9, 159–165 (2007)
H. Alakus, U. Warnecke-Eberz, E. Bollschweiler, S.P. Monig, D. Vallbohmer et al., GNAS1 T393C polymorphism is associated with histopathological response to neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in esophageal cancer. Pharmacogenomics J. 9, 202–207 (2009)
E.J. Neer, Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell 80, 249–257 (1995)
L.S. Weinstein, T. Xie, Q.H. Zhang, M. Chen, Studies of the regulation and function of the Gs alpha gene Gnas using gene targeting technology. Pharmacol. Ther. 115, 271–291 (2007)
A. Harry, Y. Chen, R. Magnusson, R. Iyengar, G. Weng, Differential regulation of adenylyl cyclases by Galphas. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 19017–19021 (1997)
M. Keiper, M.B. Stope, D. Szatkowski, A. Bohm, K. Tysack et al., Epac- and Ca2+ -controlled activation of Ras and extracellular signal-regulated kinases by Gs-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 46497–46508 (2004)
S. Kiermayer, R.M. Biondi, J. Imig, G. Plotz, J. Haupenthal et al., Epac activation converts cAMP from a proliferative into a differentiation signal in PC12 cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 5639–5648 (2005)
C. Peyssonnaux, A. Eychene, The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: new concepts of activation. Biol. Cell 93, 53–62 (2001)
B.C. Visser, A.P. Venook, M.G. Patti, Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy for esophageal cancer: a critical reappraisal. Surg. Oncol. 12, 1–7 (2003)
J. Zhang, H.Q. Chen, Y.W. Zhang, J.Q. Xiang, Adjuvant chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: a meta-analysis and experience from the Shanghai Cancer Hospital. J. Int. Med. Res. 36, 875–882 (2008)
A. DeMichele, R. Aplenc, J. Botbyl, T. Colligan, L. Wray et al., Drug-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms predict clinical outcome in a node-positive breast cancer cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 5552–5559 (2005)
F. Innocenti, L. Iyer, M.J. Ratain, Pharmacogenetics: a tool for individualizing antineoplastic therapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 39, 315–325 (2000)
F. Innocenti, S.D. Undevia, L. Iyer, P.X. Chen, S. Das et al., Genetic variants in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene predict the risk of severe neutropenia of irinotecan. J. Clin. Oncol. 22, 1382–1388 (2004)
P.E. Huijts, M.P. Vreeswijk, K.H. Kroeze-Jansema, C.E. Jacobi, C. Seynaeve et al., Clinical correlates of low-risk variants in FGFR2, TNRC9, MAP3K1, LSP1 and 8q24 in a Dutch cohort of incident breast cancer cases. Breast Cancer Res. 9, R78 (2007)
P. Kraft, P. Pharoah, S.J. Chanock, D. Albanes, L.N. Kolonel et al., Genetic variation in the HSD17B1 gene and risk of prostate cancer. PLoS Genet. 1, e68 (2005)
U.H. Frey, A. Fritz, S. Rotterdam, K.W. Schmid, A. Potthoff et al., GNAS1 T393C polymorphism and disease progression in patients with malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Med. Res. 15, 422–427 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yogesh K. Vashist and Asad Kutup have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vashist, Y.K., Kutup, A., Musici, S. et al. The GNAS1 T393C single nucleotide polymorphism predicts the natural postoperative course of complete resected esophageal cancer. Cell Oncol. 34, 281–288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-011-0016-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-011-0016-x