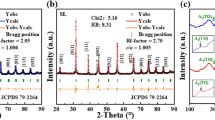
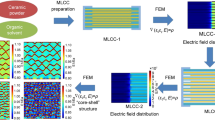
Abstract
Insulation resistance (IR) degradation in BaTiO3 is a key issue for developing miniaturized multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) with high capacity. Despite rapid progress in BaTiO3-based MLCCs, the mechanism of IR degradation is still controversial. In this study, we demonstrate the Al doping effect on IR degradation behavior of BaTiO3 MLCCs by electrical measurements and scanning Kelvin probe microscopy (SKPM). As the Al doping concentration in BaTiO3 increases, IR degradation of MLCCs seems to be suppressed from electrical characterization results. However, SKPM results reveal that the conductive regions near the cathode become lager with Al doping after IR degradation. The formation of conducting regions is attributed to the migration of oxygen vacancies, which is the origin of IR degradation in BaTiO3, in dielectric layers. These results imply that acceptor doping in BaTiO3 solely cannot suppress the IR degradation in MLCC even though less asymmetric IR characteristics and IR degradation in MLCCs with higher Al doping concentration are observed from electrical characterization. Our results strongly suggest that observing the surface potential distribution in IR degraded dielectric layers using SKPM is an effective method to unravel the mechanism of IR degradation in MLCCs.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, C.-H., Park, K.-J., Yoon, Y.-J., Sinn, D.-S., Kim, Y.-T., Hur, K.-H.: Effects of milling condition on the formation of core–shell structure in BaTiO3 grains. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 2589 (2008)
Sakabe, Y.: Multilayer ceramic capacitors. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2, 584 (1997)
Tian, Z., Wang, X., Lee, S., Hur, K.H., Li, L.: Microstructure evolution and dielectric properties of ultrafine grained BaTiO3‐based ceramics by two‐step sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1119 (2011)
Kishi, H., Mizuno, Y., Chazono, H.: Base-metal electrode-multilayer ceramic capacitors: past, present and future perspectives. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1 (2003)
Gong, H., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Tian, Z., Li, L.: Electrical and reliability characteristics of Mn-doped nano BaTiO3-based ceramics for ultrathin multilayer ceramic capacitor application. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 114119 (2012)
Ayvazian, T., Bersuker, G., Lingley, Z.R., Brodie, M.J., Foran, B.J.: Conductive paths through polycrystalline BaTiO3: scanning probe microscopy study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 072904 (2016)
Sakabe, Y., Reynolds, T.: Base-metal electrode capacitors. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 81, 24 (2002)
Randall, C.A.: Scientific and engineering issues of the state-of-the-art and future multilayer capacitors. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 109, S2 (2001)
Okamoto, T., Kitagawa, S., Inoue, N., Ando, A.: Electric field concentration in the vicinity of the interface between anode and degraded BaTiO3-based ceramics in multilayer ceramic capacitor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 072905 (2011)
Suzuki, K., Okamoto, T., Kondo, H., Tanaka, N., Ando, A.: Insulation degradation behavior of multilayer ceramic capacitors clarified by Kelvin probe force microscopy under ultra-high vacuum. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 064103 (2013)
Choi, Y.-K., Hoshina, T., Takeda, H., Teranishi, T., Tsurumi, T.: Effects of oxygen vacancies and grain sizes on the dielectric response of BaTiO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 212907 (2010)
Yoon, S.-H., Park, J.-S., Kim, S.-H., Kim, D.-Y.: Thermally stimulated depolarization current analysis for the dielectric aging of Mn and V-codoped BaTiO3 multi layer ceramic capacitor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 042901 (2013)
Yoon, S.-H., Kim, S.-H., Kim, D.-Y.: Correlation between I (current)-V (voltage) characteristics and thermally stimulated depolarization current of Mn-doped BaTiO3 multilayer ceramic capacitor. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 074102 (2013)
Yoon, S.-H., Kim, M.-Y.: Dielectric nonlinear behavior of (Ba0.95Ca0.05)(Ti0.83Zr0.17)O3‐based multi‐layer ceramic capacitor. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 1544 (2018)
Yoo, H.-I., Oh, T.-S., Kwon, H.-S., Shin, D.-K., Lee, J.-S.: Electrical conductivity–defect structure correlation of variable-valence and fixed-valence acceptor-doped BaTiO3 in quenched state. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3115 (2009)
Baiatu, T., Waser, R., Härdtl, K.: dc electrical degradation of Perovskite‐type Titanates: III, a model of the mechanism. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1663 (1990)
Chazono, H., Kishi, H.: DC-electrical degradation of the BT-based material for multilayer ceramic capacitor with Ni internal electrode: impedance analysis and microstructure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 5624 (2001)
Nakano, M., Saito, A., Wada, N.: Changes in the electrical conduction mechanism with the electrical degradation of BaTiO3-based ceramics. Key Eng. Mater. 388, 201 (2009)
Duiker, H.M., Beale, P.D., Scott, J.F., de Araujo, C.A.P., Melnick, B.M., Cuchiaro, J.D., McMillan, L.D.: Fatigue and switching in ferroelectric memories: theory and experiment. J. Appl. Phys. 68, 5783 (1990)
Kwon, H.-S., Yoon, S.-H., Yoo, H.-I.: Insulation-resistance degradation kinetics of bulk BaTi1−ξAξO3−Δ and defect-chemical origin of acceptor-type(A) and doping-level(ξ) effect. J. Appl. Phys. 120, 044101 (2016)
Lee, C.-E., Yoo, H.-I.: Ba/Ti ratio effect on oxygen re-equilibration kinetics of donor-doped BaTiO3. Solid State Ion. 179, 338 (2008)
Shao, G., Glaz, M.S., Ma, F., Ju, H., Ginger, D.S.: Intensity-modulated scanning Kelvin probe microscopy for probing recombination in organic photovoltaics. ACS Nano 8, 10 (2014)
Hu, Y., Pecunia, V., Jiang, L., Di, C.-A., Gao, X., Sirringhaus, H.: Scanning Kelvin probe microscopy investigation of the role of minority carriers on the switching characteristics of organic field‐effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 28, 4713 (2016)
Li, J.B., Chawla, V., Clemens, B.M.: Investigating the role of grain boundaries in CZTS and CZTSSe thin film solar cells with scanning probe microscopy. Adv. Mater. 24, 720 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Samsung Electro-Mechanics Co. Ltd. and the Future Material Discovery (2016M3D1A1027666) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). Jun Min Suh acknowledges the Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (2015H1A2A1033701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, K., Lee, T.H., Suh, J.M. et al. Direct Observation of Surface Potential Distribution in Insulation Resistance Degraded Acceptor-Doped BaTiO3 Multilayered Ceramic Capacitors. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 629–635 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0066-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0066-6