Abstract
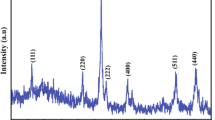
In this study, various concentrations of Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized using the sol–gel method. A variety of characterization techniques as ultra-violet visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) were employed to analyze the prepared nanopowders. XRD measurement confirmed the substitution of Fe ion without disturbing the tetragonal crystal system of TiO2. The crystallite size was found to decrease and lattice strain increases upon doping estimated by Williamson Hall plot. Furthermore, the average grain size calculated by FESEM found was between 10 and 30 nm for pure and doped TiO2. UV–Vis spectroscopy showed an increase in absorption accompanied red shift and increase in band gap energies from 3.36 to 3.62 eV with the addition of Fe. The FTIR spectroscopy was employed to confirm the presence of functional groups in the fabricated nanopowders. Upon mixing the saturation magnetization (Ms) varying from (2.12 to 1.51)10−2 emu/g was observed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dietl, T., Tomasz, H., Ohno, F., Matsukura, J.Cibert, Ferrand, D.: Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019 (2000)
Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B., Coey, J.M.D.: Thin films: unexpected magnetism in a dielectric oxide. Nature 430, 630 (2004)
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Yu Chtchelkanova, A., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488 (2001)
Chambers, S.A., Farrow, R.F.C.: New possibilities for ferromagnetic semiconductors. MRS Bull. 28, 729 (2003)
Bryan, J.D., Gamelin, D.R.: Doped semiconductor nanocrystals: synthesis, characterization, physical properties, and applications. Prog. Inorg. Chem. 54(47), 47–126 (2005)
Zhao, Z.W., Tay, B.K., Chen, J.S., Hu, J.F., Lim, B.C., Li, G.P.: Large magnetic moment observed in Co-doped ZnO nanocluster-assembled thin films at room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 152502 (2007)
Calle, A.M., Sanchez, L.C., Arboleda, J.D., Beltran, J.J., Barrero, C.A., Osorio, J., Nomura, K.: Mixtures of iron and anatase TiO2 by mechanical alloying. Microelectron. J. 39, 1322 (2008)
Fujishima, A., Rao, T.N., Tryk, D.A.: Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 1, 1 (2000)
Reddy, B.M., Ganesh, I., Khan, A.: Stabilization of nanosized titania-anatase for high temperature catalytic applications. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 223, 295 (2004)
Yu, J., Xiang, Q., Zhou, M.: Preparation, characterization and visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped titania nanorods and first-principles study for electronic structures. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 90, 595 (2009)
Yuji, M., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki, M., Ahmet, P., Chikyow, T., Koshihara, S., Koinuma, H.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science 291, 854 (2001)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Prellier, W., Hassini, A., Ruyter, A., Gervais, F.: Ferromagnetism in transition-metal-doped TiO2 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 70, 195204 (2004)
Chen, J., Rulis, P., Ouyang, L., Satpathy, S., Ching, W.Y.: Vacancy-enhanced ferromagnetism in Fe-doped rutile TiO2. Phys. Rev. B 74, 235207 (2006)
Coey, J.M.D., Douvalis, A.P., Fitzgerald, C.B., Venkatesan, M.: Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1332 (2004)
Dhanapandian, S., Arunachalam, A., Manoharan, C.: Highly oriented and physical properties of sprayed anatase Sn-doped TiO2 thin films with an enhanced antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 387 (2016)
Mugundan, S., Rajamannan, B., Virothagiri, G., Shanmugam, N., Gobi, R., Praveen, P.: Synthesis and characterization of undoped and cobalt-doped TiO2 nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 449 (2015)
Jianping, X., Shi, S., Li, L., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Wang, J., Lv, L., Zhang, F., Zhong, W.: Structural, optical, and ferromagnetic properties of Co-doped TiO2 films annealed in vacuum. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 053910 (2010)
Rumaiz, A.K., Bakhtyar, A., Ceylan, A., Boggs, M., Beebe, T., Ismat, S.: Shah, Experimental studies on vacancy induced ferromagnetism in undoped TiO2. Solid State Commun. 144, 334 (2007)
Grecu, M.N., Constantinescu, S., Tărăbăşanu-Mihăilă, D., Ghica, D., Bibicu, I.: Spin dynamics in 57Fe-doped TiO2 anatase nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 248, 2927 (2011)
Grecu, M.N., Macovei, D., Ghica, D., Logofatu, C., Valsan, S., Apostol, N.G., Lungu, G.A., Negrea, R.F., Piticescu, R.R.: Co environment and magnetic defects in anatase CoxTi1−xO2 nanopowders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 161909 (2013)
Dinkar, V.A., Shridhar, S.J.: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic applications of Zn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by sol–gel method. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 965 (2016)
Pereira, L.C.J., Nunes, M.R., Monteiro, O.C., Silvestre, A.J.: Magnetic properties of Co-doped TiO2 anatase nanopowders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222502 (2008)
Kaspar, T.C., Droubay, T., Heald, S.M., Engelhard, M.H., Nachimuthu, P., Chambers, S.A.: Hidden ferromagnetic secondary phases in cobalt-doped ZnO epitaxial thin films. Phys. Rev. B 77, 201303 (2008)
Rao, B.K., Jena, P.: Giant magnetic moments of nitrogen-doped Mn clusters and their relevance to ferromagnetism in Mn-doped GaN. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 185504 (2002)
Zhang, Y., Shen, Y., Gu, F., Wu, M., Xie, Y., Zhang, J.: Influence of Fe ions in characteristics and optical properties of mesoporous titanium oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 85 (2009)
Hiromi, Y., Harada, M., Misaka, J., Takeuchi, M., Neppolian, B., Anpo, M.: Photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds diluted in water using visible light-responsive metal ion-implanted TiO2 catalysts: Fe ion-implanted TiO2. Catal.Today 84, 191 (2003)
Dholam, R., Patel, N., Adami, M., Miotello, A.: Hydrogen production by photocatalytic water-splitting using Cr- or Fe-doped TiO2 composite thin films photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34, 5337 (2009)
Calle, A.M., Sanchez, L.C., Arboleda, J.D., Beltran, J.J., Barrero, C.A., Osorio, J., Nomura, K.: Mixtures of iron and anatase TiO2 by mechanical alloying. Microelectron. J. 39, 1322 (2008)
Ikram, M., Niaz, N.A., Khalid, N.R., Ramzan, M., Imran, M., Ali, S.: Tetra blended based hybrid bulk heterojunction solar cells. J. Ovonic Res. 10, 257 (2014)
Ali, A., Zafar, H., Zia, M., Haq, I., Rehman Phull, A., Ali, J.S., Hussain, A.: Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 9, 49 (2016)
Reyes-Coronado, D., Rodríguez-Gattorno, G., Espinosa-Pesqueira, M.E., Cab, C., de Coss, R., Oskam, G.: Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology 19, 145605 (2008)
Zhang, Y.H., Reller, A.: Nanocrystalline iron-doped mesoporous titania and its phase transition. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 2537 (2001)
Jiefang, Z., Zheng, W., He, B., Zhang, J., Anpo, M.: Characterization of Fe–TiO2 photocatalysts synthesized by hydrothermal method and their photocatalytic reactivity for photodegradation of XRG dye diluted in water. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 216, 35 (2004)
Wang, C., Böttcher, C., Bahnemann, D.W., Dohrmann, J.K.: A comparative study of nanometer sized Fe(III)-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and activity. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 2322 (2003)
Masanori, H., Joji, T., Inagaki, M., Iwata, H.: Direct formation of iron(III)-doped titanium oxide (anatase) by thermal hydrolysis and its structural property. J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 87, 35 (2008)
Alexandrescu, R., Birjega, R., Popovici, E., Soare, I., Gavrila-Florescu, L., Voicu, I., Sandu, I., Dumitrache, F., Prodan, G., Vasile, E., Figgemeier, E.: Structural investigations on TiO2 and Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by laser pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 515, 8438 (2007)
Zhang, X., Zhou, M., Lei, L.: Co-deposition of photocatalytic Fe doped TiO2 coatings by MOCVD. Catal. Commun. 7, 427 (2006)
Song, L., Liu, X., Chen, Y., Jiang, R.: A novel preparation of highly active iron-doped titania photocatalysts with a p–n junction semiconductor structure. J. Alloys Compounds. 506, 877 (2010)
Ranjit KT, Viswanathan B (1997) J Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 108: 79
Cernea, M., Valsangiacom, C., Trusca, R., Vasiliu, F.: Synthesis of iron-doped anatase-TiO2 powders by a particulate sol–gel route. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9, 2648 (2007)
Dholam, R., Patel, N., Adami, M., Miotello, A.: Hydrogen production by photocatalytic water-splitting using Cr- or Fe-doped TiO2 composite thin films photocatalyst. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34, 5337 (2009)
Reyes-Rojasa, A., Esparza-Poncea, H., De la Torre, S.D., Torres-Moye, E.: Compressive strain-dependent bending strength property of Al2O3–ZrO2 (1.5 mol% Y2O3) composites performance by HIP. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 756 (2009)
KantiKole, A., Kumbhakar, P.: Cubic-to-hexagonal phase transition and optical properties of chemically synthesized ZnS nanocrystals. Results Phys. 2, 150 (2012)
Ghosh, A., Kumari, N., Tewari, S., Bhattacharjee, A.: Structural and optical properties of pure and Al doped ZnO nanocrystalsIndian. J. Phys. 87, 1099 (2013)
Williamson, G.K., Hall, W.H.: X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolframL’elargissement des raies de rayons x obtenues des limailles d’aluminium et de tungsteneDie verbreiterung der roentgeninterferenzlinien von aluminium- und wolframspaenen. Acta Metall. 1, 22 (1953)
Nafees, M., Liaqut, W., Ali, S., Shafique, M.A.: Synthesis of ZnO/Al: ZnO nanomaterial: structural and band gap variation in ZnO nanomaterial by Al doping. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 49 (2013)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Pellier, W.: Distribution of dopant in Fe:TiO2 and Ni:TiO2 thin films. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 281, 347 (2004)
Thu, D.X., Trung, V.Q., Nghia, N.M., Khang, N.C., Lam, T.D.: Effects of Fe doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Electr. Mater. 45, 11 (2016)
Zhang, Yu-Hong, Reller, Armin: Nanocrystalline iron-doped mesoporous titania and its phase transition. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 2537 (2001)
Nasralla, N., Yeganeh, M., Astuti, Y., Piticharoenphun, S., Shahtahmasebi, N., Kompany, A., Karimipour, M., Mendis, B.G., Poolton, N.R.J., Šiller, L.: Structural and spectroscopic study of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Sci. Iranica 20, 1018 (2013)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Prellier, W.: Distribution of dopant in Fe:TiO2 and Ni:TiO2 thin films. J. Magn. Mag. Mater. 281, 347–352 (2004)
Cernea, M., Valsangiacom, C., Truscaa, R., Vasiliu, F.: Synthesis of iron-doped anatase-TiO2 powders by a particulate sol-gel route. J. Optoelectr. Adv. Mater. 9, 2648 (2007)
Hung, W.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Chu, H., Tseng, T.-K.: Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 and Fe/TiO2 nanoparticles and their performance for photocatalytic degradation of 1, 2-dichloroethane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 2205–2213 (2008)
Luu, C.L., Nguyen, Q.T., Ho, S.T., Tseng, T.-K.: Synthesis and characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 photocatalyst by the sol–gel method. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 1, 015008 (2010)
da Santos, R.S., Faria, G.A., Giles, C., Leite, C.A.P., de Barbosa, H.S., Arruda, M.A.Z., Longo, C.: Iron insertion and hematite segregation on Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles obtained from sol–gel and hydrothermal method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 5555 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC) Pakistan, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahid, R., Manzoor, M., Rafiq, A. et al. Influence of Iron Doping on Structural, Optical and Magnetic Properties of TiO2 Nanoparticles. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 587–593 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0060-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0060-z