Abstract
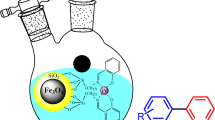
In the present study, the synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@SiO2@MgAl-LDH@Au.Pd were reported and utilized in an efficient and environmentally benign protocol for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and preparation of biphenyl derivatives. The synthesized nanocomposite was studied and identified by various analytical methods such as FT-IR, XRD, EDS, TEM, TGA, FESEM, VSM and XPS. Monitoring the progress of the reduction reaction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol was performed by UV–Vis analysis. According to the results, 4-nitrophenol was successfully converted to the corresponding 4-aminophenol using NaBH4 in the presence of nanocomposite. Furthermore, the application of this magnetic nanocatalyst was also investigated in Suzuki coupling reaction. Consequently, the reactions of different aryl halides with phenylboronic acids led to the formation of corresponding biphenyl products in high-to-excellent yields. The recovery and reusability of Fe3O4@SiO2@MgAl-LDH@Au.Pd disclosed that it can be retrieved and reused for the next run up to 6 times with slight decline in its activity.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilal, M.; Bagheri, A.R.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S.: Environmental occurrence, toxicity concerns, and remediation of recalcitrant nitroaromatic compounds. J. Environ. Manag. 291, 112685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112685
Eichenbaum, G.; Johnson, M.; Kirkland, D.; O’Neill, P.; Stellar, S.; Bielawne, J.; DeWire, R.; Areia, D.; Bryant, S.; Weiner, S.; Desai-Krieger, D.; Guzzie-Peck, P.; Evans, D.C.; Tonelli, A.: Assessment of the genotoxic and carcinogenic risks of p-nitrophenol when it is present as an impurity in a drug product. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 55, 33–42 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2009.05.018
Rappoport, Z.: The Chemistry of Anilines: Part 1. John Wiley, Chichester (2009)
Jain, Z.J.; Gide, P.S.; Kankate, R.S.: Biphenyls and their derivatives as synthetically and pharmacologically important aromatic structural moieties. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S2051–S2066 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.035
Wang, L.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, P.; Tian, X.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Liu, Z.: Nitrogen-bonded ultrasmall palladium clusters over the nitrogen-doped carbon for promoting Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 5, 1396–1403 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00468-5
Mora, M.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Ruiz, J.R.: Heterogeneous Suzuki cross-coupling reactions over palladium/hydrotalcite catalysts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 302, 568–575 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.06.058
Choudhary, H.; Jia, J.; Nishimura, S.; Ebitani, K.: Surfactant-assisted Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction of unreactive chlorobenzene over hydrotalcite-supported palladium catalyst. Asian J. Org. Chem. 6, 274–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.201600606
Karanjit, S.; Kashihara, M.; Nakayama, A.; Shrestha, L.K.; Ariga, K.; Namba, K.: Highly active and reusable hydrotalcite-supported Pd (0) catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions of aryl bromides and chlorides. Tetrahedron 74, 948–954 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2017.12.056
Fan, X.; Zheng, Y.: Biosynthesis of eco-friendly and recyclable Pd/LDHs catalyst using the withered leaves extract for Suzuki coupling reaction. IET Nanobiotechnol. 14, 59–65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0188
Ruiz, J.R.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Mora, M.: Palladium supported on hydrotalcite as a catalyst for the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. Tetrahedron 62, 2922–2926 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2006.01.004
Yu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Cao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Lu, S.; Cao, X.; Gu, H.: One-pot synthesis of Pd/azo-polymer as an efficient catalyst for 4-nitrophenol reduction and Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. Chem. Asian J. 16, 837–844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202100002
Wang, P.; Zhu, H.; Liu, M.; Niu, J.; Yuan, B.; Li, R.; Ma, J.: Stabilizing Pd on the surface of amine-functionalized hollow Fe3O4 spheres: a highly active and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling and hydrogenation reactions. RSC Adv. 4, 28922–28927 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA02130D
Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q.: Tannic Acid: A green and efficient stabilizer of Au, Ag, Cu and Pd nanoparticles for the 4-Nitrophenol Reduction, Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions and click reactions in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 604, 281–291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.015
Baran, N.Z.: Palladium nanoparticles decorated on a novel polyazomethine as a highly productive and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions and 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Organomet. Chem. 899, 120886 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2019.120886
Dong, Z.; Pan, H.; Chen, J.; Fan, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.: Palladium supported on urea-containing porous organic polymers as heterogeneous catalysts for C–C cross coupling reactions and reduction of nitroarenes. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 25, 101317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101317
Sakthivel, C.; Nivetha, A.; Prabha, I.: Evaluation on synthesis and catalytic properties of ZnO enriched MgO nanomaterials using Limonia Acidissima as effective green substrate. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 7081–7091 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06344-6
Lu, F.; Astruc, D.: Nanocatalysts and other nanomaterials for water remediation from organic pollutants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 408, 213180 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213180
Kempasiddaiah, M.; Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Baidya, M.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A.: Efficient and recyclable palladium enriched magnetic nanocatalyst for reduction of toxic environmental pollutants. J. Environ. Sci. 101, 189–204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.015
Manda, A.A.: Synthesis of Bi2O2.75/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite by laser ablation and its application for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06940-0
Farooqi, Z.H.; Begum, R.; Naseem, K.; Wu, W.; Irfan, A.: Zero valent iron nanoparticles as sustainable nanocatalysts for reduction reactions. Catal. Rev. 64, 286–355 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/01614940.2020.1807797
Zhang, K.; Suh, J.M.; Choi, J.W.; Jang, H.W.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Varma, R.S.: Recent advances in the nanocatalyst-assisted NaBH4 reduction of nitroaromatics in water. ACS Omega 4, 483–495 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b03051
Shokouhimehr, M.: Magnetically separable and sustainable nanostructured catalysts for heterogeneous reduction of nitroaromatics. Catalysts 5, 534–560 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5020534
Byun, S.; Song, Y.; Kim, B.M.: Heterogenized bimetallic Pd–Pt–Fe3O4 nanoflakes as extremely robust, magnetically recyclable catalysts for chemoselective nitroarene reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 14637–14647 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05229
Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, Q.; He, M.Y.; Wang, L.: Magnetically recyclable metal–organic framework@Fe3O4 composite-catalyzed facile reduction of nitroarene compounds in aqueous medium. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 32, e4132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4132
Yao, T.; Cui, T.; Fang, X.; Cui, F.; Wu, J.: Preparation of yolk–shell Fex Oy/Pd@ mesoporous SiO2 composites with high stability and their application in catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 5, 5896–5904 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR01470C
Liu, Y.; Lv, M.; Li, L.; Yu, H.; Wu, Q.; Pang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.: Synthesis of a highly active amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2/APTS/Ru magnetic nanocomposite catalyst for hydrogenation reactions. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e4686 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4686
Ayad, M.M.; Amer, W.A.; Kotp, M.G.; Minisy, I.M.; Rehab, A.F.; Kopecký, D.; Fitl, P.: Synthesis of silver-anchored polyaniline-chitosan magnetic nanocomposite: a smart system for catalysis. RSC Adv. 7, 18553–18560 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02575K
Sydnes, M.O.: The Use of palladium on magnetic support as catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. Catalysts 7, 35 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7010035
Jose, D.E.; Kanchana, U.S.; Mathew, T.V.: Recent developments of supported Palladium nanocatalyst and magnetically separable supported Palladium nanocatalysts for Heck cross-coupling reactions. J. Nanoparticle Res. 24, 89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05472-w
Yousefi, V.; Tarhriz, V.; Eyvazi, S.; Dilmaghani, A.: Synthesis and application of magnetic@ layered double hydroxide as an anti-inflammatory drugs nanocarrier. J. Nanobiotechnol. 18, 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-00718-y
Ay, A.N.; Abramova, N.V.; Konuk, D.; Lependina, O.L.; Sokolov, V.I.; Zümreoglu-Karan, B.: Magnetically-recoverable Pd-immobilized layered double hydroxide-iron oxide nanocomposite catalyst for carbon-carbon cross-coupling reactions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 27, 64–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2012.10.020
Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.: Facile synthesis of magnetic recyclable palladium-gold alloy nanoclusters catalysts PdAur/Fe3O4@ LDH and its catalytic applications in Heck reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 878, 84–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2018.10.007
Gao, X.; Niu, L.; Qiao, X.; Feng, W.; Cao, Y.; Bai, G.: Facile preparation of a stable Fe3O4@ LDH@ NiB magnetic core–shell nanocomposite for hydrogenation. Chin. J. Chem. 35, 1149–1156 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201600759
Dinari, M.; Dadkhah, F.: Swift reduction of 4-nitrophenol by easy recoverable magnetite-Ag/layered double hydroxide/starch bionanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 228, 115392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115392
Gu, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, T.; Jehan, R.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X.: Recent advances in layered double hydroxide-based nanomaterials for the removal of radionuclides from aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. 240, 493–505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.136
Islam, S.; Khan, W.: Synthesis of dendritic ligand assisted Zn/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles as a highly active green catalyst for chemoselective oxidation and reduction reaction. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 447–462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04908-6
Mandal, R.; Baranwal, A.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P.: Evolving trends in bio/chemical sensor fabrication incorporating bimetallic nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 117, 546–561 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.039
Sharma, D.; Ledwani, L.; Kumar, N.; Mehrotra, T.; Pervaiz, N.; Kumar, R.: An investigation of physicochemical and biological properties of Rheum emodi-mediated bimetallic Ag–Cu nanoparticles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 275–285 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04641-0
Hossain, S.S.: Bimetallic Pd–Fe supported on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as electrocatalyst for formic acid oxidation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 6543–6556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05192-0
Wang, D.; Villa, A.; Porta, F.; Prati, L.; Su, D.: Bimetallic gold/palladium catalysts: correlation between nanostructure and synergistic effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 8617–8622 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp800805e
Bingwa, N.; Patala, R.; Noh, J.H.; Ndolomingo, M.J.; Tetyana, S.; Bewana, S.; Meijboom, R.: Synergistic effects of gold–palladium nanoalloys and reducible supports on the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Langmuir 33, 7086–7095 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00903
Singh, A.K.; Xu, Q.: Synergistic catalysis over bimetallic alloy nanoparticles. ChemCatChem 5, 652–676 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201200591
Jiang, F.; Li, R.; Cai, J.; Xu, W.; Cao, A.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Shu, C.: Ultrasmall Pd/Au bimetallic nanocrystals embedded in hydrogen-bonded supramolecular structures: facile synthesis and catalytic activities in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 19433–19438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA02260F
Ma, T.; Liang, F.; Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.: Synthesis of Au-Pd bimetallic nanoflowers for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanomaterials 7, 239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090239
Srisombat, L.; Nonkumwong, J.; Suwannarat, K.; Kuntalue, B.; Ananta, S.: Simple preparation Au/Pd core/shell nanoparticles for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 512, 17–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.10.026
Velpula, S.; Beedu, S.R.; Rupula, K.: Bimetallic nanocomposite (Ag–Au, Ag–Pd, Au–Pd) synthesis using gum kondagogu a natural biopolymer and their catalytic potentials in the degradation of 4-nitrophenol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 190, 159–169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.211
Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yan, H.; Yi, H.; Lu, J.: Precisely-controlled synthesis of Au@Pd core–shell bimetallic catalyst via atomic layer deposition for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J. Catal. 324, 59–68 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.01.019
Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, X.; Oh, R.; Shi, D.; Akdim, O.; Xia, M.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.: Au-Pd nanoparticles immobilized on TiO2 nanosheet as an active and durable catalyst for solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 588, 787–794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.11.112
Hosseinzadeh, R.; Aghili, N.; Tajbakhsh, M.: SBA-15 immobilized phenanthroline-copper (I) complex as a recyclable efficient catalyst for N-arylation of amides and N–H heterocycles with aryl halides. Catal. Lett. 146, 193–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-015-1622-4
Hosseinzadeh, R.; Aghili, N.; Mavvaji, M.: Synthesis and characterization of nano-cellulose immobilized phenanthroline-copper (I) complex as a recyclable and efficient catalyst for preparation of diaryl ethers N-aryl amides and N-aryl heterocycles. Polyhedron 213, 115631 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2021.115631
Abaszadeh, M.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Ghasemi, S.: The synthesis of functionalized magnetic graphene oxide with 5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline and investigation of its dual application in CN coupling reactions and adsorption of heavy metal ions. J. Mol. Struct. 1261, 132832 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132832
Rathore, P.S.; Patidar, R.; Thakore, S.: Nanoparticle-supported and magnetically recoverable organic–inorganic hybrid copper (II) nanocatalyst: a selective and sustainable oxidation protocol with a high turnover number. RSC Adv. 4, 41111–41121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06599A
Hosseinzadeh, R.; Mavvaji, M.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Lasemi, Z.: Synthesis and characterization of N-hydroxyphthalimide immobilized on SiO2-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetic catalyst for oxidation of benzyl alcohols and hydrocarbons. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 15, 893–904 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1288-5
Pazoki, F.; Mehraban, J.A.; Shamsayei, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Esfandiarpour, R.; Miraki, M.K.; Heydari, A.: Aza-Michael addition of 5-substituted tetrazole catalysed by a novel nanoparticle solid base catalyst involving a layered zinc hydroxide supported on a ferrite core. ChemistrySelect 4, 2568–2575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201804070
Mi, F.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Yin, S.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, H.: Facile synthesis of hierarchical core–shell Fe3O4@MgAl-LDH@Au as magnetically recyclable catalysts for catalytic oxidation of alcohols. Chem. Commun. 47, 12804–12806 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CC15858A
Sing, K.S.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T.: International union of pure and applied chemistry physical chemistry division reporting physisorption data for gas/soils systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 603–619 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W.; Huang, F.; Cao, W.: Synthetic strategies and application of gold-based nanocatalysts for nitroaromatics reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 652, 93–116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.215
Camacho-Espinoza, M.; Penieres-Carrillo, J.G.; Rios-Guerra, H.; Lagunas-Rivera, S.; Ortega-Jiménez, F.: An efficient and simple imidazole-hydrazone ligand for palladium-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions in water under infrared irradiation. J. Organomet. Chem. 880, 386–391 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2018.11.016
Dilauro, G.; Messa, F.; Bona, F.; Perrone, S.; Salomone, A.: Cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of aryl-and alkylaluminum derivatives with (hetero) aryl and alkyl bromides. Chem. Commun. 57, 10564–10567 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC04002B
Ren, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.: Copper/selectfluor-system catalyzed dehydration–oxidation of tertiary cycloalcohols: access to β-substituted cyclohex-2 enones, 4-arylcoumarins, and biaryls. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 5381–5388 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201500610
Hoffmann, I.; Blumenröder, B.; neé Thumann, S.O.; Dommer, S.; Schatz, J.: Suzuki cross-coupling in aqueous media. Green Chem. 17(7), 3844–3857 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC00794A
Han, Y.; Di, J.Q.; Zhao, A.D.; Zhang, Z.H.: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of palladium supported on pyridine-based covalent organic polymer for Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e5172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5172
Abe, T.; Mino, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yagishita, F.; Sakamoto, M.: Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of aryl sulfonates with arylboronic acids using a morpholine-Pd (OAc)2 catalyst system. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 3909–3916 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201402120
Chen, X.; Qian, D.; Xu, G.; Xu, H.; Dai, J.; Du, Y.: Magnetic Fe3O4 supported PdAu bimetallic nanoparticles with the enhanced catalytic activity for Heck and Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 573, 67–72 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.04.013
Dong, Z.; Gao, P.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.: Pd–Co nanoparticles supported on calcined Mg–Fe hydrotalcites for the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction in water with high turnover numbers. Catalysts 9, 1061 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9121061
Wang, Q.; Jing, X.; Han, J.; Yu, L.; Xu, Q.: Design and fabrication of low-loading palladium nano particles on polyaniline (nano Pd@ PANI): an effective catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling with high TON. Mater. Lett. 215, 65–67 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.12.064
Sahoo, M.; Mansingh, S.; Subudhi, S.; Mohapatra, P.; Parida, K.: A plasmonic AuPd bimetallic nanoalloy decorated over a GO/LDH hybrid nanocomposite via a green synthesis route for robust Suzuki coupling reactions: a paradigm shift towards a sustainable future. Catal. Sci. Technol. 9, 4678–4692 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CY01085H
Han, D.; Bao, Z.; Xing, H.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, Z.: Fabrication of plasmonic Au–Pd alloy nanoparticles for photocatalytic Suzuki–Miyaura reactions under ambient conditions. Nanoscale 9, 6026–6032 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR01950E
You, B.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhu, G.: Porous aromatic frameworks with high Pd nanoparticles loading as efficient catalysts for the Suzuki coupling reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 628, 1023–1032 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.026
Sahoo, M.; Parida, K.: Noble metal loaded ZnCr-LDH based hybrid material for Suzuki coupling reactions: a comparison study on heterogeneous catalysis with photo catalysis. Mater. Today Proc. 35, 229–232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.772
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (99012446) and the Research Council of the University of Mazandaran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinzadeh, R., Mavvaji, M. & Moradi, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@MgAl-LDH@Au.Pd as an Efficient and Magnetically Recyclable Catalyst for Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Suzuki Coupling Reactions. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 7525–7541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07543-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07543-5