Abstract
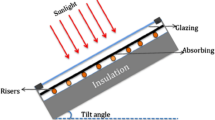
The present study experimentally investigated the thermal efficiency, collector area, weight, embodied energy, environmental CO2 emissions of Al2O3/water nanofluid flow in a flat-plate solar collector and with coiled wire turbulators. The experiments were performed at \(\phi \) that is equal to 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.3% and volume flow rate from 120 to 300 L/h. Results indicate that the collector thermal efficiency increased with the increase of particle volume loadings and volume flow rates. The thermal efficiency of the collector with water circulate is 53%, whereas it is enhanced to 65% at \(\phi \) = 0.3% nanofluid, and it is further enhanced to 77% for \(\phi \) = 0.3% nanofluid with 10-mm coiled wire insert in a collector tube at a volume flow rate of 300 L/h. The collector area is declined to 8.66% (\(\phi \) = 0.1%), 14% (\(\phi \) = 0.2%) and 18.66% (\(\phi \) = 0.3%) for nanofluids. The collector area is further reduced to 31.33% for \(\phi \) = 0.3% nanofluid and with a coiled wire pitch of 10 mm. The materials embodied energy is decreased to 1144.36 MJ for \(\phi \) = 0.3% nanofluid, and it is further reduced to 1022.6 MJ with the use of a wire coil pitch of 10 mm, but for water, it is 1451.4 MJ. The Nusselt number is increased to 23.22% with ϕ = 0.3% nanofluid, and it further enhanced to 53.56% at same particle loadings and coiled wire pitch of 10 mm over the water data.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(A_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Collector surface area (m2)
- c p :
-
Heat capacity (J/kg K)
- \(c_{{{\text{p}},{\text{bf}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of base fluid (J/kg K)
- \(c_{{{\text{p}},{\text{np}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of nanoparticles (J/kg K)
- \(c_{{{\text{p}},{\text{nf}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of nanofluid (J/kg K)
- d :
-
Tube diameter (m)
- \(d_{{\text{h}}}\) :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- \(d_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Coiled wire diameter (m)
- e :
-
Wire thickness (m)
- \(F_{{\text{R}}}\) :
-
Heat removal factor
- \(G_{{\text{T}}}\) :
-
Global solar radiation (W/m2)
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg/s)
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pitch (m)
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- \(\dot{Q}_{{\text{u}}}\) :
-
Useful energy gained rate (W)
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- \(T_{{\text{a}}}\) :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- \(T_{{\text{i}}}\) :
-
Fluid inlet temperature (K)
- \(T_{{\text{o}}}\) :
-
Fluid outlet temperature (K)
- \(U_{{\text{L}}}\) :
-
Overall heat loss coefficient (W/m2K)
- \(W\) :
-
Weight (g)
- \({\rm T}\alpha\) :
-
Absorptance–transmittance product
- P :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- \({\Delta }\) :
-
Particle size (nm)
- B(2θ):
-
Half-maximum intensity peak (radians)
- θ :
-
Maximum intensity peak angle
- T :
-
Solar collector time constant (min)
- \(\mu\) :
-
Viscosity (mPa s)
- \(\eta_{{\text{i}}}\) :
-
Instantaneous collector efficiency
- \({\Phi }\) :
-
Particle volume concentration (%)
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- EG:
-
Ethylene glycol
- MWCNT:
-
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes
- SDBS:
-
Sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate
References
Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A.: Enhanced heat transfer using nanofluids. US Patent 275 6221275 (2001)
Yousefi, T.; Shojaeizadeh, E.; Veysi, F.; Zinadini, S.: An experimental investigation on the effect of pH variation of MWCNT–H2O nanofluid on the efficiency of a flat-plate solar collector. Sol. Energy 86, 771–779 (2012)
Yousefi, T.; Veysi, F.; Shojaeizadeh, E.; Zinadini, S.: An experimental investigation on the effect of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid on the efficiency of flat-plate solar collectors. Renew. Energy 39, 293–298 (2012)
Said, Z.; Saidur, R.; Sabiha, M.A.; Hepbasli, A.; Rahim, N.A.: Energy and exergy efficiency of a flat plate solar collector using pH treated Al2O3 nanofluid. J. Clean. Prod. 112, 3915–3926 (2016)
Hussein, O.A.; Habib, K.; Muhsan, A.S.; Saidur, R.; Alawi, O.A.; Ibrahim, T.K.: Thermal performance enhancement of a flat plate solar collector using hybrid nanofluid. Sol. Energy 204, 208–222 (2020)
Choudhary, S.; Sachdeva, A.; Kumar, P.: Influence of stable zinc oxide nanofluid on thermal characteristics of flat plate solar collector. Renew. Energy 152, 1160–1170 (2020)
Tong, Y.; Lee, H.; Kang, W.; Cho, H.: Energy and exergy comparison of a flat-plate solar collector using water, Al2O3 nanofluid, and CuO nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 159, 113959 (2019)
Polvongsri, S.; Kiatsiriroat, T.: Performance analysis of flat-plate solar collector having silver nanofluid as a working fluid. Heat Transf. Eng. 35, 1183–1191 (2014)
Natarajan, E.; Sathish, R.: Role of nanofluids in solar water heater. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1876-8
Otanicar, T.; Phelan, P.E.; Prasher, R.S.; Rosengarten, G.; Taylor, R.A.: Nanofluid based direct absorption solar collector. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2, 033102 (2010)
Shojaeizadeh, E.; Veysi, F.; Yousefi, T.; Davodi, F.: An experimental investigation on the efficiency of a flat-plate solar collector with binary working fluid: a case study of propylene glycol (PG)–water. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 53, 218–226 (2014)
Karami, M.; Akhavan-Bahabadi, M.A.; Delfani, S.; Raisee, M.: Experimental investigation of CuO nanofluid-based direct absorption solar collector for residential applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 52, 793–801 (2015)
Kiliç, F.; Menlik, T.; Sözen, A.: Effect of titanium dioxide/water nanofluid use on thermal performance of the flat plate solar collector. Sol. Energy 164, 101–108 (2018)
Chaji, H.; Ajabshirchi, Y.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Heris, S.Z.; Hedayatizadeh, M.; Kahani, M.: Experimental study on thermal efficiency of flat plate solar collector using TiO2/water nanofluid. Mod. Appl. Sci. 7, 60–69 (2013)
Said, Z.; Saidur, R.; Rahim, N.A.: Energy and exergy analysis of a flat plate solar collector using different sizes of aluminium oxide based nanofluid. J. Clean. Prod. 133, 518–530 (2016)
Zamzamian, A.; Keyanpour Rad, M.; Kiani Neyestani, M.; Jamal-Abad, M.T.: An experimental study on the effect of Cu-synthesized/EG nanofluid on the efficiency of flat-plate solar collectors. Renew. Energy 71, 658–664 (2014)
Said, Z.; Sabiha, M.A.; Saidur, R.; Hepbasli, A.; Rahim, N.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Ward, T.A.: Performance enhancement of a flat plate solar collector using titanium dioxide nanofluid and polyethylene glycol dispersant. J. Clean. Prod. 92, 343 (2015)
Sabiha, M.A.; Saidur, R.; Hassani, S.; Said, Z.; Mekhilef, S.: Energy performance of an evacuated tube solar collector using single walled carbon nanotubes nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 105, 1377–1388 (2015)
Jouybari, H.J.; Saedodin, S.; Zamzamian, A.; Nimvari, M.E.; Wongwises, S.: Effects of porous material and nanoparticles on the thermal performance of a flat plate solar collector: An experimental study. Renew. Energy 114, 1407–1418 (2017)
Mahian, O.; Kianifar, A.; Kalogirou, S.A.; Pop, I.; Wongwises, S.: A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 582–594 (2013)
Javadi, F.S.; Saidur, R.; Kamalisarvestani, M.: Investigating performance improvement of solar collectors by using nanofluids. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 28, 232–245 (2013)
Garcia, A.; Vicente, P.G.; Viedma, A.: Experimental study of heat transfer enhancement with wire coil inserts in laminar-transition-turbulent regimes at different Prandtl numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 4640–4651 (2005)
Garcia, A.; Solano, J.P.; Vicente, P.G.; Viedma, A.: Enhancement of laminar and transitional flow heat transfer in tubes by means of wire coil inserts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 3176–3189 (2007)
Garcia, A.; Solano, J.P.; Vicente, P.G.; Viedma, A.: Flow pattern assessment in tubes with wire coil inserts in laminar and transition regimes. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 28, 516–525 (2007)
Sundar, L.S.; Bhramara, P.; Ravi Kumar, N.T.; Singh, M.K.; Sousa, A.C.M.: Experimental heat transfer, friction factor and effectiveness analysis of Fe3O4 nanofluid flow in a horizontal plain tube with return bend and wire coil inserts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 109, 440–453 (2017)
Abdul Hamid, K.; Azmi, W.H.; Mamat, R.; Sharma, K.V.: Heat transfer performance of TiO2–SiO2 nanofluids in a tube with wire coil inserts. Appl. Therm. Eng. 152, 275–286 (2019)
Goudarzi, K.; Jamali, H.: Heat transfer enhancement of Al2O3–EG nanofluid in a car radiator with wire coil inserts. Appl. Therm. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.03.016
Akyürek, E.F.; Gelis, K.; Sahin, B.; Manay, E.: Experimental analysis for heat transfer of nanofluid with wire coil turbulators in a concentric tube heat exchanger. Results Phys. 9, 376–389 (2018)
Sundar, L.S.; Singh, M.K.; Punnaiah, V.; Sousa, A.C.M.: Experimental investigation of Al2O3/water nanofluids on the effectiveness of solar flat-plate collectors with and without twisted tape inserts. Renew. Energy 119, 820–833 (2018)
Sundar, L.S.; Kirubeil, A.; Punnaiah, V.; Singh, M.K.; Sousa, A.C.M.: Effectiveness analysis of solar flat plate collector with Al2O3 water nanofluids and with longitudinal strip inserts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 127, 422–435 (2018)
Pak, B.C.; Cho, Y.I.: Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transf. 11, 151–170 (1998)
Einstein, A.: Investigation on Theory of Brownian Motion, 1st edn. Dover publications (1956)
Maxwell, J.C.: A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Cambridge (1904)
ASHRAE Standard 93–2003, Methods of testing to determine the thermal performance of solar collectors, Atlanta, GA, USA (2003)
Whillier, A.: Solar energy collection and its utilization for house heating. Sc. D. Thesis, MIT (1953)
Whillier, A.: Design factors influencing collector performance, low temperature engineering. In: Application of Solar Energy, ASHRAE, New York (1967)
Hottel, H.C.; Whillier, A.: Evaluation of fat plate collector performance. Trans. Config. Use Solar Energy 2(1), 74 (1958)
Bliss, R.W.: The derivation of several plate efficiency factors useful in the design of flat plate solar heat collectors. Sol. Energy 3, 55–64 (1959)
Ardante, F.; Beccali, G.; Cellura, M.; Brano, V.L.: Life cycle assessment of a solar thermal collector. Renew Energy 30, 1031–1054 (2005)
Faizal, M.; Saidur, R.; Mekhilef, S.; Hepbasli, A.; Mahbubul, I.M.: Energy, economic, and environmental analysis of a flat-plate solar collector operated with SiO2 nanofluid. Clean Technol Environ. Policy 17, 1457–1473 (2015)
Stalin, P.M.J.; Arjunan, T.V.; Matheswaran, M.M.; Dolli, H.; Sadanandam, N.: Energy, economic and environmental investigation of a flat plate solar collector with CeO2/water nanofluid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08670-2
Gnielinski, V.: New equations for heat and mass transfer in turbulent pipe and channel flow. Int. Chem. Eng. 16, 359–368 (1976)
Akhavan-Behabadi, M.A.; Shahidi, M.; Aligoodarz, M.R.: An experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of MWCNT–water nanofluid inside horizontal coiled wire inserted tube. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 63, 62–72 (2015)
Blasius, H.: Boundary layers in liquids with low friction. Z. Math. Phys. 56, 1–37 (1908)
Sharafeldin, M.A.; Gróf, G.; Abu-Nada, E.; Mahian, O.: Evacuated tube solar collector performance using copper nanofluid: energy and environmental analysis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 162, 114205 (2019)
Sharafeldin, M.A.; Gróf, G.: Experimental investigation of flat plate solar collector using CeO2–water nanofluid. Energy Convers. Manag. 155, 32–41 (2018)
Ghaderian, J.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Kasaeian, A.; Ghaderian, S.; Okhovat, A.; Pakzadeh, A.; Samion, S.; Yahy, W.J.: Performance of copper oxide/distilled water nanofluid in evacuated tube solar collector (ETSC) water heater with internal coil under thermo-syphon system circulations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 121, 520–536 (2017)
Saleh, B.; Sundar, L.S.: Thermosyphon flat plate collector with nanodiamond-water nanofluids: properties, friction factor, heat transfer, thermal efficiency, and cost analysis. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05371-7
Saleh, B.; Sundar, L.S.: Thermal efficiency, heat transfer, and friction factor analyses of MWCNT + Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluids in a solar flat plate collector under thermosyphon condition. Processes 9, 180 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010180
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project Number (TURSP-2020/49), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia. The authors would like to thank Taif University for financial support.
Funding
Taif University, TURSP-2020/49, B Saleh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, B., Sundar, L.S., Aly, A.A. et al. The Combined Effect of Al2O3 Nanofluid and Coiled Wire Inserts in a Flat-Plate Solar Collector on Heat Transfer, Thermal Efficiency and Environmental CO2 Characteristics. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 9187–9214 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06478-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06478-7