Abstract
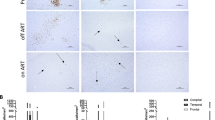
Persistence of HIV-1 reservoirs in the central nervous system (CNS) is an obstacle to cure strategies. However, little is known about residual viral distribution, viral replication levels, and genetic diversity in different brain regions of HIV-infected individuals on combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). Because myeloid cells particularly microglia are likely major reservoirs in the brain, and more microglia exist in white matter than gray matter in a human brain, we hypothesized the major viral reservoirs in the brain are the white matter reflected by higher levels of viral DNA. To address the issue, we used the Chinese rhesus macaque (ChRM) model of SIV infection, and treated 11 SIVmac251-infected animals including long-term nonprogressors with cART for up to 24 weeks. SIV reservoirs were assessed by SIV DNA levels in 16 specific regions of the brain and 4 regions of spinal cord. We found relatively high frequencies of SIV in basal ganglia and brain stem compared to other regions. cART-receiving animals had significantly lower SIV DNA levels in the gray matter than white matter. Moreover, a shortened envelope gp120 with 21 nucleotide deletions and guanine-to-adenine hypermutations were observed. These results demonstrate that SIV enters the CNS in SIV-infected ChRM with a major reservoir in the white matter after cART; the SIV/ChRM/cART is an appropriate model for studying HIV CNS reservoirs and testing new eradication strategies. Further, examining multiple regions of the CNS may be needed when assessing whether an agent is successful in reducing the size of SIV reservoirs in the CNS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) Anatomic analysis of blood vessels in germinal matrix, cerebral cortex, and white matter in developing infants. Pediatr Res 56:117–124
Becker JT, Maruca V, Kingsley LA, Sanders JM, Alger JR, Barker PB, Goodkin K, Martin E, Miller EN, Ragin A, Sacktor N, Selnes O, Multicenter ACS (2012) Factors affecting brain structure in men with HIV disease in the post-HAART era. Neuroradiology 54:113–121
Brew BJ, Robertson K, Wright EJ, Churchill M, Crowe SM, Cysique LA, Deeks S, Garcia JV, Gelman B, Gray LR, Johnson T, Joseph J, Margolis DM, Mankowski JL, Spencer B (2015) HIV eradication symposium: will the brain be left behind? J Neuro-Oncol 21:322–334
Churchill M, Nath A (2013) Where does HIV hide? A focus on the central nervous system. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 8:165–169
Churchill MJ, Deeks SG, Margolis DM, Siliciano RF, Swanstrom R (2016) HIV reservoirs: what, where and how to target them. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:55–60
Churchill MJ, Wesselingh SL, Cowley D, Pardo CA, McArthur JC, Brew BJ, Gorry PR (2009) Extensive astrocyte infection is prominent in human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. Ann Neurol 66:253–258
Clements JE, Gama L, Graham DR, Mankowski JL, Zink MC (2011) A simian immunodeficiency virus macaque model of highly active antiretroviral treatment: viral latency in the periphery and the central nervous system. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 6:37–42
Cory TJ, Schacker TW, Stevenson M, Fletcher CV (2013) Overcoming pharmacologic sanctuaries. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 8:190–195
Dahl V, Gisslen M, Hagberg L, Peterson J, Shao W, Spudich S, Price RW, Palmer S (2014) An example of genetically distinct HIV type 1 variants in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma during suppressive therapy. J Infect Dis 209:1618–1622
Del Prete GQ, Scarlotta M, Newman L, Reid C, Parodi LM, Roser JD, Oswald K, Marx PA, Miller CJ, Desrosiers RC, Barouch DH, Pal R, Piatak M Jr, Chertova E, Giavedoni LD, O'Connor DH, Lifson JD, Keele BF (2013) Comparative characterization of transfection- and infection-derived simian immunodeficiency virus challenge stocks for in vivo nonhuman primate studies. J Virol 87:4584–4595
Depboylu C, Eiden LE, Weihe E (2007) Increased APOBEC3G expression is associated with extensive G-to-A hypermutation in viral DNA in rhesus macaque brain during lentiviral infection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:901–912
Eden A, Fuchs D, Hagberg L, Nilsson S, Spudich S, Svennerholm B, Price RW, Gisslen M (2010) HIV-1 viral escape in cerebrospinal fluid of subjects on suppressive antiretroviral treatment. J Infect Dis 202:1819–1825
Fennema-Notestine C, Ellis RJ, Archibald SL, Jernigan TL, Letendre SL, Notestine RJ, Taylor MJ, Theilmann RJ, Julaton MD, Croteau DJ, Wolfson T, Heaton RK, Gamst AC, Franklin DR Jr, Clifford DB, Collier AC, Gelman BB, Marra C, McArthur JC, McCutchan JA, Morgello S, Simpson DM, Grant I, Group C (2013) Increases in brain white matter abnormalities and subcortical gray matter are linked to CD4 recovery in HIV infection. J Neuro-Oncol 19:393–401
Fourati S, Lambert-Niclot S, Soulie C, Malet I, Valantin MA, Descours B, Ait-Arkoub Z, Mory B, Carcelain G, Katlama C, Calvez V, Marcelin AG (2012) HIV-1 genome is often defective in PBMCs and rectal tissues after long-term HAART as a result of APOBEC3 editing and correlates with the size of reservoirs. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:2323–2326
Garrido C, Margolis DM (2015) Translational challenges in targeting latent HIV infection and the CNS reservoir problem. J Neuro-Oncol 21:222–226
Hansen SG, Ford JC, Lewis MS, Ventura AB, Hughes CM, Coyne-Johnson L, Whizin N, Oswald K, Shoemaker R, Swanson T, Legasse AW, Chiuchiolo MJ, Parks CL, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Jarvis MA, Piatak M Jr, Lifson JD, Picker LJ (2011) Profound early control of highly pathogenic SIV by an effector memory T-cell vaccine. Nature 473:523–527
Heaton RK, Clifford DB, Franklin DR Jr, Woods SP, Ake C, Vaida F, Ellis RJ, Letendre SL, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Rivera-Mindt M, Vigil OR, Taylor MJ, Collier AC, Marra CM, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Morgello S, Simpson DM, McCutchan JA, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I (2010) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders persist in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy: CHARTER Study. Neurology 75:2087–2096
Keele BF, Giorgi EE, Salazar-Gonzalez JF, Decker JM, Pham KT, Salazar MG, Sun C, Grayson T, Wang S, Li H, Wei X, Jiang C, Kirchherr JL, Gao F, Anderson JA, Ping LH, Swanstrom R, Tomaras GD, Blattner WA, Goepfert PA, Kilby JM, Saag MS, Delwart EL, Busch MP, Cohen MS, Montefiori DC, Haynes BF, Gaschen B, Athreya GS, Lee HY, Wood N, Seoighe C, Perelson AS, Bhattacharya T, Korber BT, Hahn BH, Shaw GM (2008) Identification and characterization of transmitted and early founder virus envelopes in primary HIV-1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7552–7557
Knoepfel SA, Di Giallonardo F, Daumer M, Thielen A, Metzner KJ (2011) In-depth analysis of G-to-A hypermutation rate in HIV-1 env DNA induced by endogenous APOBEC3 proteins using massively parallel sequencing. J Virol Methods 171:329–338
Letendre S, Marquie-Beck J, Capparelli E, Best B, Clifford D, Collier AC, Gelman BB, JC MA, McCutchan JA, Morgello S, Simpson D, Grant I, Ellis RJ, Group C (2008) Validation of the CNS penetration-effectiveness rank for quantifying antiretroviral penetration into the central nervous system. Arch Neurol 65:65–70
Ling B, Mohan M, Lackner AA, Green LC, Marx PA, Doyle LA, Veazey RS (2010) The large intestine as a major reservoir for simian immunodeficiency virus in macaques with long-term, nonprogressing infection. J Infect Dis 202:1846–1854
Ling B, Piatak M Jr, Rogers L, Johnson A-M, Russell-Lodrigue K, Hazuda DJ, Lifson JD, Veazey RS (2014) Effects of treatment with suppressive combination antiretroviral drug therapy and the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; (SAHA) on SIV-infected Chinese rhesus macaques. PLoS One 9:e102795
Ling B, Rogers L, Johnson AM, Piatak M, Lifson J, Veazey RS (2013) Effect of combination antiretroviral therapy on Chinese rhesus macaques of simian immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 29:1465–1474
Ling B, Veazey RS, Hart M, Lackner AA, Kuroda M, Pahar B, Marx PA (2007) Early restoration of mucosal CD4 memory CCR5 T cells in the gut of SIV-infected rhesus predicts long term non-progression. AIDS 21:2377–2385
Ling B, Veazey RS, Luckay A, Penedo C, Xu K, Lifson JD, Marx PA (2002a) SIV(mac) pathogenesis in rhesus macaques of Chinese and Indian origin compared with primary HIV infections in humans. AIDS 16:1489–1496
Ling B, Veazey RS, Penedo C, Xu K, Lifson JD, Marx PA (2002b) Longitudinal follow up of SIVmac pathogenesis in rhesus macaques of Chinese origin: emergence of B cell lymphoma. J Med Primatol 31:154–163
Liu H, Xiao QH, Liu JB, Li JL, Zhou L, Xian QY, Wang Y, Zhang J, Wang X, Ho WZ, Zhuang K (2016) SIV infection impairs the central nervous system in Chinese rhesus macaques. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 11:592–600
Marthas ML, Lu D, Penedo MC, Hendrickx AG, Miller CJ (2001) Titration of an SIVmac251 stock by vaginal inoculation of Indian and Chinese origin rhesus macaques: transmission efficiency, viral loads, and antibody responses. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 17:1455–1466
Matsuda K, Brown CR, Foley B, Goeken R, Whitted S, Dang Q, Wu F, Plishka R, Buckler-White A, Hirsch VM (2013) Laser capture microdissection assessment of virus compartmentalization in the central nervous systems of macaques infected with neurovirulent simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 87:8896–8908
Mittelbronn M, Dietz K, Schluesener HJ, Meyermann R (2001) Local distribution of microglia in the normal adult human central nervous system differs by up to one order of magnitude. Acta Neuropathol 101:249–255
Monceaux V, Viollet L, Petit F, Cumont MC, Kaufmann GR, Aubertin AM, Hurtrel B, Silvestri G, Estaquier J (2007) CD4+ CCR5+ T-cell dynamics during simian immunodeficiency virus infection of Chinese rhesus macaques. J Virol 81:13865–13875
Monjure CJ, Tatum CD, Panganiban AT, Arainga M, Traina-Dorge V, Marx PA Jr, Didier ES (2014) Optimization of PCR for quantification of simian immunodeficiency virus genomic RNA in plasma of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) using armored RNA. J Med Primatol 43:31–43
Mullins JI, Heath L, Hughes JP, Kicha J, Styrchak S, Wong KG, Rao U, Hansen A, Harris KS, Laurent JP, Li D, Simpson JH, Essigmann JM, Loeb LA, Parkins J (2011) Mutation of HIV-1 genomes in a clinical population treated with the mutagenic nucleoside KP1461. PLoS One 6:e15135
Nath A (2015) Eradication of human immunodeficiency virus from brain reservoirs. J Neuro-Oncol 21:227–234
Rengachary SS, Ellenbogen RG (2005) Principles of neurosurgery, 2nd edn. Elsevier Mosby, Edinburgh; New York
Sarma MK, Nagarajan R, Keller MA, Kumar R, Nielsen-Saines K, Michalik DE, Deville J, Church JA, Thomas MA (2014) Regional brain gray and white matter changes in perinatally HIV-infected adolescents. Neuroimage Clin 4:29–34
Schnell G, Joseph S, Spudich S, Price RW, Swanstrom R (2011) HIV-1 replication in the central nervous system occurs in two distinct cell types. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002286
Schnell G, Price RW, Swanstrom R, Spudich S (2010) Compartmentalization and clonal amplification of HIV-1 variants in the cerebrospinal fluid during primary infection. J Virol 84:2395–2407
Schnell G, Spudich S, Harrington P, Price RW, Swanstrom R (2009) Compartmentalized human immunodeficiency virus type 1 originates from long-lived cells in some subjects with HIV-1-associated dementia. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000395
Steinbrink F, Evers S, Buerke B, Young P, Arendt G, Koutsilieri E, Reichelt D, Lohmann H, Husstedt IW, German Competence Network HA (2013) Cognitive impairment in HIV infection is associated with MRI and CSF pattern of neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurol 20:420–428
Sturdevant CB, Dow A, Jabara CB, Joseph SB, Schnell G, Takamune N, Mallewa M, Heyderman RS, Van Rie A, Swanstrom R (2012) Central nervous system compartmentalization of HIV-1 subtype C variants early and late in infection in young children. PLoS Pathog 8:e1003094
Sturdevant CB, Joseph SB, Schnell G, Price RW, Swanstrom R, Spudich S (2015) Compartmentalized replication of R5 T cell-tropic HIV-1 in the central nervous system early in the course of infection. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004720
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Valcour V, Chalermchai T, Sailasuta N, Marovich M, Lerdlum S, Suttichom D, Suwanwela NC, Jagodzinski L, Michael N, Spudich S, van Griensven F, de Souza M, Kim J, Ananworanich J, Group RSS (2012) Central nervous system viral invasion and inflammation during acute HIV infection. J Infect Dis 206:275–282
Venneti S, Bonneh-Barkay D, Lopresti BJ, Bissel SJ, Wang G, Mathis CA, Piatak M Jr, Lifson JD, Nyaundi JO, Murphey-Corb M, Wiley CA (2008) Longitudinal in vivo positron emission tomography imaging of infected and activated brain macrophages in a macaque model of human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis correlates with central and peripheral markers of encephalitis and areas of synaptic degeneration. Am J Pathol 172:1603–1616
Wang B, Liu Z, Liu J, Tang Z, Li H, Tian J (2016) Gray and white matter alterations in early HIV-infected patients: combined voxel-based morphometry and tract-based spatial statistics. J Magn Reson Imaging 43:1474–1483
Whitney JB, Hraber PT, Luedemann C, Giorgi EE, Daniels MG, Bhattacharya T, Rao SS, Mascola JR, Nabel GJ, Korber BT, Letvin NL (2011) Genital tract sequestration of SIV following acute infection. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001293
Williams KC, Corey S, Westmoreland SV, Pauley D, Knight H, deBakker C, Alvarez X, Lackner AA (2001) Perivascular macrophages are the primary cell type productively infected by simian immunodeficiency virus in the brains of macaques: implications for the neuropathogenesis of AIDS. J Exp Med 193:905–915
Yeh WW, Rahman I, Hraber P, Coffey RT, Nevidomskyte D, Giri A, Asmal M, Miljkovic S, Daniels M, Whitney JB, Keele BF, Hahn BH, Korber BT, Shaw GM, Seaman MS, Letvin NL (2010) Autologous neutralizing antibodies to the transmitted/founder viruses emerge late after simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 infection of rhesus monkeys. J Virol 84:6018–6032
Zhao L, Galligan DC, Lamers SL, Yu S, Shagrun L, Salemi M, McGrath MS (2009) High level HIV-1 DNA concentrations in brain tissues differentiate patients with post-HAART AIDS dementia complex or cardiovascular disease from those with AIDS. Sci China C Life Sci 52:651–656
Zhou Y, Bao R, Haigwood NL, Persidsky Y, Ho WZ (2013) SIV infection of rhesus macaques of Chinese origin: a suitable model for HIV infection in humans. Retrovirology 10:89
Zhu GW, Liu ZQ, Joag SV, Pinson DM, Adany I, Narayan O, McClure HM, Stephens EB (1995) Pathogenesis of lymphocyte-tropic and macrophage-tropic SIVmac infection in the brain. J Neuro-Oncol 1:78–91
Zink MC, Brice AK, Kelly KM, Queen SE, Gama L, Li M, Adams RJ, Bartizal C, Varrone J, Rabi SA, Graham DR, Tarwater PM, Mankowski JL, Clements JE (2010) Simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy have reduced central nervous system viral replication and inflammation but persistence of viral DNA. J Infect Dis 202:161–170
Acknowledgements
We thank M Duplantis, L Nieburg, Dr. P Didier, and Dr. M Bouljihad of the Division of Comparative Pathology for tissue collection, and the animal care staff of the Division of Veterinary Medicine for their technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by NIAID R01 AI093307 (BL), NIMH R01 MH102144 (YW), and the TNPRC base grant OD011104. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, preparation of the manuscript, or decision for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experimental procedures performed on rhesus macaques used in this study were approved by the Tulane Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). All animals were housed indoors throughout the study period at the Tulane National Primate Research Center (TNPRC). TNPRC facilities are fully accredited by the Association of Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International (AAALAC) in accordance with standard husbandry practices following the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH).
Disclaimer
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, S., Johnson, AM., Xiang, Sh. et al. Persistence of SIV in the brain of SIV-infected Chinese rhesus macaques with or without antiretroviral therapy. J. Neurovirol. 24, 62–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-017-0594-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-017-0594-0