Abstract
A 2,175-bp modified gene (cry11Ba-S1) encoding Cry11Ba from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan was designed and the recombinant protein was expressed as a fusion protein with glutathione S-transferase in Escherichia coli. The recombinant Cry11Ba was highly toxic against Culex pipiens mosquito larvae, being nine and 17 times more toxic than mosquitocidal Cry4Aa and Cry11Aa from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis, respectively. Interestingly, a further increase in the toxicity of the recombinant Cry11Ba was achieved by mixing with Cry4Aa, but not with Cry11Aa. These findings suggested that Cry11Ba worked synergistically with Cry4Aa, but not with Cry11Aa, in exhibiting toxicity against C. pipiens larvae. On the other hand, the amount of Cry toxin bound to brush border membrane vesicles (BBMVs) did not significantly change between individual toxins and the toxin mixtures, suggesting that the increase in toxins binding to BBMVs was not a reason for the observed synergistic effect. It is generally accepted that synergism of toxins is a potentially powerful tool for enhancing insecticidal activity and managing Cry toxin resistance in mosquitoes. The mixture of Cry4Aa and Cry11Ba in order to increase toxicity would be very valuable in terms of mosquito control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah MA, Alzate O, Mohammad M, McNall RJ, Adang MJ, Dean DH (2003) Introduction of Culex toxicity into Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba by protein engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5343–5353. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.9.5343-5353.2003
Abdullah MA, Valaitis AP, Dean DH (2006) Identification of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxin-binding aminopeptidase from the mosquito, Anopheles quadrimaculatus. BMC Biochem 7:16. doi:10.1186/1471-2091-7-16
Ben-Dov E (2014) Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and its dipteran-specific toxins. Toxins 6:1222–1243. doi:10.3390/toxins6041222
Boonserm P, Min M, Angsuthanasombat C, Lescar J (2006) Structure of the functional form of the mosquito-larvicidal Cry4Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at a 2.80-angstorm resolution. J Bacteriol 188:3391–3401. doi:10.1128/JB.188.9.3391-3401.2006
Breman JG, Alilio MS, Mills A (2004) Conquering the intolerable burden of malaria: what’s new, what’s needed: a summary. Am J Trop Med Hyg 71:1–15
Chen J, Aimanova KG, Pan S, Gill SS (2009) Identification and characterization of Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N as a putative receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxin. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 9:688–696. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.08.003
Cheong H, Gill SS (1997) Cloning and characterization of a cytolytic and mosquitocidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3254–3260
Crickmore N, Bone EJ, Williams JA, Ellar DJ (1995) Contribution of the individual components of the δ-endotoxin crystal to the mosquitocidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 131:249–254
Delécluse A, Poncet S, Klier A, Rapoport G (1993) Expression of cryIVA and cryIVB genes, independently or in combination, in a crystal-negative strain of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3922–3927
Delécluse A, Rosso ML, Ragni A (1995) Cloning and expression of a novel toxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan encoding a highly mosquitocidal protein. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4230–4235
Fernandez LE, Aimanova KG, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberón M (2006) A GPI-anchored alkaline phosphatase is a functional midgut receptor of Cry11Aa toxin in Aedes aegypti larvae. Biochem J 394:77–84
Fernandez-Luna MT, Lanz-Mendoza H, Gill SS, Bravo A, Soberon M, Miranda-Rios J (2010) An alpha-amylase is a novel receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa toxins in the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles albimanus (Diptera: Culicidae). Environ Microbiol 12:746–757. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02117.x
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, London
Georghiou GP, Wirth MC (1997) Influence of exposure to single versus multiple toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis on development of resistance in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1095–1101
Hayakawa T, Howlader MT, Yamagiwa M, Sakai H (2008) Design and construction of a synthetic Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Aa gene-Hyperexpression in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:1033–1037. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1560-9
Howlader MT, Kagawa Y, Sakai H, Hayakawa T (2009) Biological properties of loop-replaced mutants of Bacillus thuringiensis mosquitocidal Cry4Aa. J Biosci Bioeng 108:179–183. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.03.016
Howlader MT, Kagawa Y, Miyakawa A, Yamamoto A, Taniguchi T, Hayakawa T, Sakai H (2010) Alanine scanning analyses of the three major loops in domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis mosquitocidal toxin Cry4Aa. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:860–865. doi:10.1128/AEM.02175-09
Kawalek MD (1998) Cloning and characterization of mosquitocidal genes from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Riverside
Otieno-Ayayo ZN, Zaritsky A, Wirth MC, Manasherob R, Khasdan V, Cahan R, Ben-Dov E (2008) Variations in the mosquito larvicidal activities of toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis. Environ Microbiol 10:2191–2199. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01696.x
Pérez C, Fernandez LE, Sun J, Folch JL, Gill SS, Soberón M, Bravo A (2005) Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cyt1Aa synergizes Cry11Aa toxin by functioning as a membrane-bound receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18303–18308. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505494102
Pérez C, Muñoz-Garay C, Portugal LC, Sánchez J, Gill SS, Soberón M, Bravo A (2007) Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. israelensis Cyt1Aa enhances activity of Cry11Aa toxin by facilitating the formation of a pre-pore oligomeric structure. Cell Microbiol 9:2931–2937. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01007.x
Poncet S, Delécluse A, Klier A, Rapoport G (1995) Evaluation of synergistic interactions among the CryIVA, CryIVB, and CryIVD toxic components of B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystals. J Invertebr Pathol 66:131–135
Rosso ML, Delécluse A (1997) Contribution of the 65-kilodalton protein encoded by the cloned gene cry19A to the mosquitocidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4449–4455
Servant P, Rosso ML, Hamon S, Poncet S, Delécluse A, Rapoport G (1999) Production of Cry11A and Cry11Ba toxins in Bacillus sphaericus confers toxicity towards Aedes aegypti and resistant Culex populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3021–3026
Sun Y, Zhao Q, Xia L, Ding X, Hu Q, Federici BA, Park HW (2013) Identification and characterization of three previously undescribed crystal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3364–3370. doi:10.1128/AEM.00078-13
Tabashnik BE (1992) Evaluation of synergism among Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3343–3346
Wirth MC, Georghiou GP, Federici BA (1997) CytA enables CryIV endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis to overcome high levels of CryIV resistance in the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10536–10540. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.20.10536
Wirth MC, Yang Y, Walton WE, Federici BA, Berry C (2007) Mtx toxins synergize Bacillus sphaericus and Cry11Aa against susceptible and insecticide-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6066–6071. doi:10.1128/AEM.00654-07
Wirth MC, Walton WE, Federici BA (2012) Inheritance, stability, and dominance of cry resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) selected with the three cry toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Med Entomol 49:886–894. doi:10.1603/ME11192
Wu D, Johnson JJ, Federici BA (1994) Synergism of mosquitocidal toxicity between CytA and CryIVD proteins using inclusions produced from cloned genes of Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol Microbiol 13:965–972. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00488.x
Yamagiwa M, Sakagawa K, Sakai H (2004) Functional analysis of two processed fragments of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:523–528. doi:10.1271/bbb.68.523
Zhang R, Hua G, Andacht TM, Adang MJ (2008) A 106-kDa aminopeptidase is a putative receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxin in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Biochemistry 47:11263–11272. doi:10.1021/bi801181g
Zhang Q, Hua G, Bayyareddy K, Adang MJ (2013) Analyses of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, as receptors of Cry11Ba toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43:907–915. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.07.003
Acknowledgments
C. pipiens eggs were kindly supplied by the Research and Development Laboratory at Dainihon Jochugiku, Osaka. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (Grant Nos. JP24380034 and JP26660268).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13355_2016_454_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
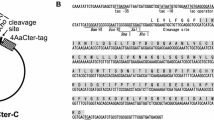
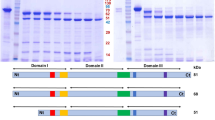
Supplemental Fig. 1 Alignment of the native and the synthetic cry11Ba gene. The amino acid sequence is shown above the nucleotide sequence. The nucleotide residues modified in accordance with the codon preference of E. coli gene are indicated. Nucleotide and amino acid numbers are shown on the right. Supplemental Fig. 2 Schematic structure of Cry protoxins and the recombinant Cry toxins used in this study. Insecticidal toxin regions are shaded. Arrow heads Internal cleavage site located in the insecticidal toxin region. After ingestion by susceptible mosquito larvae, Cry toxins are processed by residential proteases in the midgut, and the protease-resistant segments which form a heterodimer as an insecticidal toxin are generated (PPTX 182 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayakawa, T., Yoneda, N., Okada, K. et al. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba works synergistically with Cry4Aa but not with Cry11Aa for toxicity against mosquito Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Appl Entomol Zool 52, 61–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-016-0454-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-016-0454-z