Abstract
Background
Pulmonary infections by rapidly growing mycobacteria are rare in immunocompetent children.
Case characteristics
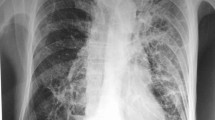
A 2-year-old boy with persistent right upper lobe pneumonia.
Observation
Bronchoalveolar lavage culture demonstrated growth of Mycobacterium atocessus.
Outcome
Complete resolution of disease with multidrug chemotherapy with imipenam, clarithromycin and amikacin.
Message
Persistent upper lobe cavitory lesions can rarely be caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han XY, Dé I, Jacobson KL. Rapidly growing mycobacteria: Clinical and microbiologic studies of 115 cases. Am J ClinPathol. 2007;128:612–621.
Jönsson BE, Gilljam M, Lindblad A, Ridell M, Woldand AE, Welinder-Olsson C. Molecular Epidemiology of Mycobacterium abscessus, with Focus on Cystic Fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:1497–1504.
H Medjahed, J L Gaillard, J M Reyrat. Mycobacterium abscessus: a new player in the mycobacterial field. Trends in Microbiology. 2010;18:117–123.
Sexton P, Harrison AC. Susceptibility to nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. ERJ. 2008;31:1322–1333.
Han XY, IndraDé, Jacobson KL. Rapidly Growing Mycobacteria. Clinical and Microbiologic Studies of 115 Cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128:612–621.
Griffith DE, Girard WM, Wallace RJ. Clinical features of pulmonary disease caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria. An analysis of 154 patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:1271–1278.
Freeman AF, Olivier KN, Rubio TT, Bartlett G, Ochi JW, Claypool RJ, et al. Intrathoracic nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in otherwise healthy children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009;44:1051–1056.
Nolt D, Michaels MG, Wald ER. Intrathoracic disease from nontuberculous mycobacteria in children: two cases and a review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2003; 112:e434.
Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, et al. An Official ATS/IDSA Statement: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Diseases. Respir Crit Care. 2007;175:367–416
De Groote MA, Huitt G. Infections due to rapidly growing mycobacteria. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:1756–1763.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalpana, S., Sarath Balaji, B. Pulmonary infection by rapidly growing mycobacterium in an immunocompetent child. Indian Pediatr 51, 223–224 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0355-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0355-6