Abstract
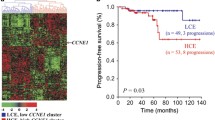
Previous research revealed that CMTM8 acts as a tumor suppressor gene in variety cancers. However, the role of CMTM8 in bladder cancer has never been reported. In this study, the expression profile of CMTM8 was examined in bladder cancer tissues and bladder cancer cell lines. The effects of CMTM8 on bladder cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were examined. Bladder tumor tissues from 84 cases were examined for CMTM8 expression by immunohistochemistry. Disease-specific survival was investigated using a Kaplan-Meier analysis, and Cox proportional hazards analysis was assessed. Our results showed that upregulation of CMTM8 in the T24 cell line could suppress T24 cells proliferation, migration and invasion and enhance the sensitivity to Epirubicin. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the expression of CMTM8 was correlated with the survival time of bladder cancer patients. Altogether, our data suggested that CMTM8 is an important tumor suppressor gene in human bladder cancer and qualified as a useful prognostic indicator for patients with bladder cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Bachir BG, Aprikian AG, Fradet Y, Chin JL, Izawa J, Rendon R, et al. Regional differences in practice patterns and outcomes in patients treated with radical cystectomy in a universal healthcare system. Canadian Urological Association journal = Journal de l’Association des urologues du Canada. 2013;7(11–12):E667–72. doi:10.5489/cuaj.201.
Tilki D, Reich O, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI, Kassouf W, Novara G, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with clinical carcinoma in situ only treated with radical cystectomy: an international study of 243 patients. J Urol. 2010;183(5):1757–63. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2010.01.025.
Sangar VK, Ragavan N, Matanhelia SS, Watson MW, Blades RA. The economic consequences of prostate and bladder cancer in the UK. BJU Int. 2005;95(1):59–63. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05249.x.
Han W, Ding P, Xu M, Wang L, Rui M, Shi S, et al. Identification of eight genes encoding chemokine-like factor superfamily members 1–8 (CKLFSF1-8) by in silico cloning and experimental validation. Genomics. 2003;81(6):609–17.
Jin C, Ding P, Wang Y, Ma D. Regulation of EGF receptor signaling by the MARVEL domain-containing protein CKLFSF8. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(28):6375–82. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.10.021.
Li D, Jin C, Yin C, Zhang Y, Pang B, Tian L, et al. An alternative splice form of CMTM8 induces apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(11):2107–19. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2007.06.002.
Jin C, Wang Y, Han W, Zhang Y, He Q, Li D, et al. CMTM8 induces caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis through a mitochondria-mediated pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2007;211(1):112–20. doi:10.1002/jcp.20914.
Zhang W, Mendoza MC, Pei X, Ilter D, Mahoney SJ, Zhang Y, et al. Down-regulation of CMTM8 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like changes via c-MET/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(15):11850–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.258236.
Neal DE, Marsh C, Bennett MK, Abel PD, Hall RR, Sainsbury JR, et al. Epidermal-growth-factor receptors in human bladder cancer: comparison of invasive and superficial tumours. Lancet. 1985;1(8425):366–8.
Black PC, Dinney CP. Growth factors and receptors as prognostic markers in urothelial carcinoma. Curr Urol Rep. 2008;9(1):55–61.
Schafer B, Gschwind A, Ullrich A. Multiple G-protein-coupled receptor signals converge on the epidermal growth factor receptor to promote migration and invasion. Oncogene. 2004;23(4):991–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207278.
Batsi O, Giannopoulou I, Nesseris I, Valavanis C, Gakiopoulou H, Patsouris ES, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of CXCL12-CXCR4 axis and VEGFR3 expression in primary urothelial cancer and its recurrence. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(7):3537–42.
Eisenhardt A, Frey U, Tack M, Rosskopf D, Lummen G, Rubben H, et al. Expression analysis and potential functional role of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor in bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2005;47(1):111–7. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2004.10.001.
Epstein JI, Amin MB, Reuter VR, Mostofi FK. The World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology consensus classification of urothelial (transitional cell) neoplasms of the urinary bladder. Bladder Consensus Conference Committee. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22(12):1435–48.
Hour TC, Chung SD, Kang WY, Lin YC, Chuang SJ, Huang AM, et al. EGFR mediates docetaxel resistance in human castration-resistant prostate cancer through the Akt-dependent expression of ABCB1 (MDR1). Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(4):591–605. doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1275-x.
Germano S, O’Driscoll L. Breast cancer: understanding sensitivity and resistance to chemotherapy and targeted therapies to aid in personalised medicine. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009;9(3):398–418.
Burger JA, Peled A. CXCR4 antagonists: targeting the microenvironment in leukemia and other cancers. Leukemia. 2009;23(1):43–52. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.299.
Sanchez-Pulido L, Martin-Belmonte F, Valencia A, Alonso MA. MARVEL: a conserved domain involved in membrane apposition events. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27(12):599–601.
Pearse BM, Smith CJ, Owen DJ. Clathrin coat construction in endocytosis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2000;10(2):220–8.
Le Roy C, Wrana JL. Clathrin- and non-clathrin-mediated endocytic regulation of cell signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(2):112–26. doi:10.1038/nrm1571.
Lajoie P, Goetz JG, Dennis JW, Nabi IR. Lattices, rafts, and scaffolds: domain regulation of receptor signaling at the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 2009;185(3):381–5. doi:10.1083/jcb.200811059.
Vieira AV, Lamaze C, Schmid SL. Control of EGF receptor signaling by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Science. 1996;274(5295):2086–9.
Hammond DE, Carter S, McCullough J, Urbe S, Vande Woude G, Clague MJ. Endosomal dynamics of Met determine signaling output. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14(4):1346–54. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-09-0578.
Marchese A, Benovic JL. Agonist-promoted ubiquitination of the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4 mediates lysosomal sorting. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(49):45509–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100527200.
Gacche RN, Meshram RJ. Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013;113(2):333–54. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 81272830 and 31200673) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20120001110001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study of tissue was performed under a protocol approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University People’s Hospital and all procedures were performed after obtaining written informed consents.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Shiying Zhang and Xiaolei Pei contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Pei, X., Hu, H. et al. Functional characterization of the tumor suppressor CMTM8 and its association with prognosis in bladder cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 6217–6225 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4508-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4508-6