Abstract
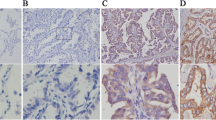
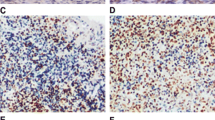
The CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) has been reported to be involved in the development and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). However, the role of CXCR4 in clinical outcome and prognosis of NPC patients remains controversial. In the present study, we investigated and reviewed the expression of CXCR4 in NPC tissues and then analyzed the definitive role of CXCR4 in clinical outcome and prognosis. Here, we found that the expression level of CXCR4 was significantly higher in NPC cancer specimens (61/98) than that in paired non-tumor tissues (p < 0.001). Together with our pathological analysis, statistic analysis revealed that CXCR4 expression was indeed closely correlated with UICC stage (p = 0.000), N stage (p = 0.019), and metastasis (p = 0.000). Most importantly, the systematic review combined with our survival and multivariate analysis that revealed high expression of CXCR4 was obviously associated with poor overall survival (OS) (p = 0.000) and progression-free survival (PFS) (p = 0.000) and can act as an independent prognostic factor in NPC patients. In conclusion, this study suggests that CXCR4 is highly activated and expressed in the development of NPC and may be recommended as an indicator in the diagnosis of NPC. Thus, targeting of CXCR4 gene or protein could be used as a potential therapy for NPC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT, et al. Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current practice and future perspective. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(29):3356–64.
Janvilisri T. Omics-based identification of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:762128.
Kamran SC, Riaz N, Lee N. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2015;24(3):547–61.
Hutajulu SH, Kurnianda J, Tan IB, et al. Therapeutic implications of Epstein-Barr virus infection for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:721–36.
Yao C, Li P, Song H, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis Upregulates Twist to Induce EMT in Human Glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015.
Shi P, Fang C, Pang X. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates CCL3/CCR5-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Erk1/2 and Akt signaling in cardiac myxoma. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(3):1319–26.
Lv S, Sun B, Zhong X, et al. The clinical implications of Chemokine receptor CXCR4 in grade and prognosis of glioma patients: a meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(1):555–61.
Dai C, Lv S, Shi R, et al. Nuclear protein C23 on the cell surface plays an important role in activation of CXCR4 signaling in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(3):1521–6.
Cheng S, Guo J, Yang Q, et al. Crk-like adapter protein regulates CCL19/CCR7-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via ERK signaling pathway in epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Med Oncol. 2015;32(3):47.
Yang P, Wang G, Huo H, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling up-regulates survivin to regulate human sacral chondrosarcoma cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway. Med Oncol. 2015;32(1):377.
Wang S, Lu J, Lv L, et al. Expression of Chemokine receptor CXCR4 in nasopharyngeal carcinomas and its clinical significance. Cancer Res Prev and Treat. 2008;35(1):8–10.
Luo H. The role of CXCR4 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Nanfang Med Univ. 2008;1(1):8.
Zheng D, Dong S, Chen J, et al. Expressions and clinical significance of CXCR4 and CCR7 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Hainan Med J. 2014;25(11):1567–9.
Wang N. Screening of CXCR4 and its expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlation with metastasis and survival. Zhongshan Univ. 2005;1(1):30–1.
Segawa Y, Oda Y, Yamamoto H, et al. Close correlation between CXCR4 and VEGF expression and their prognostic implications in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009;21(5):1197–202.
Li J, Li H, Liu J, et al. The clinical implications of human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in grade and prognosis of gliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2015.
Hu J, Deng X, Bian X, et al. The expression of functional chemokine receptor CXCR4 is associated with the metastatic potential of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(13):4658–65.
Ou DL, Chen CL, Lin SB, et al. Chemokine receptor expression profiles in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and their association with metastasis and radiotherapy. J Pathol. 2006;210(3):363–73.
Gao Y, Li J, Peng R. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in nasopharyngeaI carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 2008;15(8):594–6.
Luo HN, Li X, Liu X, et al. Association of CXCR4 and SDF-1 with organ-specific metastasis of nasopharyngeaI carcinoma. Chin J Oncol. 2009;31(4):260–4.
Luo DH, Chen QY, Liu H, et al. The independent, unfavorable prognostic factors endothelin A receptor and chemokine receptor 4 have a close relationship in promoting the motility of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the activation of AKT and MAPK pathways. J Transl Med. 2013;11:203.
Liao A, Shi R, Jiang Y, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis regulates cell cycle progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via up-regulation of survivin in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2014.
Richard CL, Blay J. CXCR4 in cancer and its regulation by PPARγ. PPAR Res. 2008;2008:19.
Li X, Huang Y, Xia J, et al. CXCR4 expression in patients with high-risk locally advanced renal cell carcinoma can independently predict increased risk of disease progression and poor overall survival. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12(12):3313–8.
Wang L, Wang L, Yang B, et al. Strong expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by renal cell carcinoma cells correlates with metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(8):1049–54.
Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, et al. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature. 1998;393(6685):591–4.
Furusato B, Mohamed A, Uhlén M, Rhim JS. CXCR4 and cancer. Pathol Int. 2010;60(7):497–505.
Lv B, Yang X, Lv S, et al. CXCR4 signaling induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by PI3K/AKT and ERK pathways in glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;52(3):1263–8.
Guo J, Tang B, Sheng XN, et al. Use of CXCR4 expression to predict the efficacy of sorafenib treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(7):359–64.
Ping YF, Yao XH, Chen JH, et al. The anti-cancer compound Nordy inhibits CXCR4-mediated production of IL-8 and VEGF by malignant human glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 2007;84:21–9.
Cavallaro S. CXCR4/CXCL12 in non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis to the brain. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:1713–27.
Gangadhar T, Nandi S, Salgia R. The role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;9:409–16.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province, China (ts20120505), and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2014YL034). We greatly thank other members of our lab for valuable suggestions and writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, H., Wei, Y., Wang, C. et al. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is closely correlated with clinical outcome in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 6099–6105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4464-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4464-1