Abstract
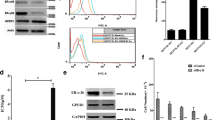
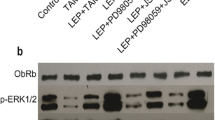
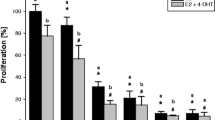
Development of new therapeutic strategies is becoming increasingly important to overcome tamoxifen resistance. Recently, much interest has been focused on anti-tumor effects of metformin commonly used to treat type II diabetes. Increased protein expression and signaling of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family is a possible mechanism involved in tamoxifen resistance. Since HER2/HER3 heterodimers are able to induce strong downstream signaling and activate various biological responses such as cellular proliferation and growth, we investigated the anti-cancer effect of metformin by inhibition of signaling pathway via downregulation of HER2 and HER3 using tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 (TR MCF-7) cells. Compared to MCF-7 cells, TR MCF-7 cells showed increased expression of EGFR, HER2, and HER3, and metformin inhibited the expression of these proteins in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Metformin inhibited activation of HER2 (Tyr1248)/HER3 (Tyr1289)/Akt (Ser473) as well as cell proliferation and colony formation by estrogenic promotion in MCF-7 and TR MCF-7 cells. Known as a HER3 ligand, heregulin (HRG)-β1-induced phosphorylation of HER2, HER3 and Akt, and protein interaction of HER2/HER3 and colony formation were inhibited by metformin in both cells. Consistent with the results in the two cell lines, we identified that metformin inhibited HER2/HER3/Akt signaling axis activated by HRG-β1 using the HER2 and HER3-overexpressing breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3. Lastly, lapatinib-induced HER3 upregulation was significantly inhibited by treatment of metformin in HER3 siRNA-transfected TR MCF-7 cells. These data suggest that metformin might overcome tamoxifen resistance through the inhibition of expression and signaling of receptor tyrosine kinase HER2 and HER3.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Group EBCTC. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):771–84.
Dowsett M, Cuzick J, Ingle J, Coates A, Forbes J, Bliss J, et al. Meta-analysis of breast cancer outcomes in adjuvant trials of aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(3):509–18.
Osborne CK, Elledge RM, Fuqua SA. Estrogen receptors in breast cancer therapy. Sci Med. 1996;3:32–41.
Horwitz K, Jackson T, Bain D, Richer J, Takimoto G, Tung L. Nuclear receptor coactivators and corepressors. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10(10):1167–77.
Ma J, Guo Y, Chen S, Zhong C, Xue Y, Zhang Y, et al. Metformin enhances tamoxifen-mediated tumor growth inhibition in ER-positive breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):172.
Wiebe VJ, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA, DeGregorio MW. Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1993;14(3):173–88.
Osipo C, Meeke K, Cheng D, Weichel A, Bertucci A, Liu H, et al. Role for HER2/neu and HER3 in fulvestrant-resistant breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2007;30(2):509–20.
Emde A, Mahlknecht G, Maslak K, Ribba B, Sela M, Possinger K, et al. Simultaneous inhibition of estrogen receptor and the HER2 pathway in breast cancer: effects of HER2 abundance. Transl Oncol. 2011;4(5):293–300.
Gullick WJ, Srinivasan R. The type 1 growth factor receptor family: new ligands and receptors and their role in breast cancer. Prognostic variables in node-negative and node-positive breast cancer. Springer; 1998. p. 133–43.
Holbro T, Civenni G, Hynes NE. The ErbB receptors and their role in cancer progression. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284(1):99–110.
Arteaga CL, Osborne CK. Growth factors as mediators of estrogen/antiestrogen action in human breast cancer cells. Regulatory Mechanisms in Breast Cancer. Springer; 1991. p. 289–304.
Keshamouni VG, Mattingly RR, Reddy KB. Mechanism of 17-β-estradiol-induced Erk1/2 activation in breast cancer cells. A role for HER2 and PKC-δ. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(25):22558–65.
Liu B, Ordonez-Ercan D, Fan Z, Huang X, Edgerton SM, Yang X, et al. Estrogenic promotion of ErbB2 tyrosine kinase activity in mammary tumor cells requires activation of ErbB3 signaling. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(11):1882–92.
Lee-Hoeflich ST, Crocker L, Yao E, Pham T, Munroe X, Hoeflich KP, et al. A central role for HER3 in HER2-amplified breast cancer: implications for targeted therapy. Cancer Res. 2008;68(14):5878–87.
Baselga J, Swain SM. Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(7):463–75.
Amin DN, Campbell MR, Moasser MM, editors. The role of HER3, the unpretentious member of the HER family, in cancer biology and cancer therapeutics. Seminars in cell & developmental biology; 2010: Elsevier.
Campbell MR, Amin D, Moasser MM. HER3 comes of age: new insights into its functions and role in signaling, tumor biology, and cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(5):1373–83.
Schoeberl B, Faber AC, Li D, Liang M-C, Crosby K, Onsum M, et al. An ErbB3 antibody, MM-121, is active in cancers with ligand-dependent activation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(6):2485–94.
Sheng Q, Liu X, Fleming E, Yuan K, Piao H, Chen J, et al. An activated ErbB3/NRG1 autocrine loop supports in vivo proliferation in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(3):298–310.
Wilson TR, Lee DY, Berry L, Shames DS, Settleman J. Neuregulin-1-mediated autocrine signaling underlies sensitivity to HER2 kinase inhibitors in a subset of human cancers. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(2):158–72.
Tzahar E, Waterman H, Chen X, Levkowitz G, Karunagaran D, Lavi S, et al. A hierarchical network of interreceptor interactions determines signal transduction by Neu differentiation factor/neuregulin and epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(10):5276–87.
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Soussan L, Waterman H, Levkowitz G, Alroy I, Klapper L, et al. Diversification of Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling by combinatorial receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1996;15(10):2452.
Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo S-H, Bardeesy N, DePinho RA, et al. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science. 2005;310(5754):1642–6.
Bailey CJ, Turner RC. Metformin. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(9):574.
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp M-C, Gu J, Lau S, Pollak MN, et al. In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(2):246–50.
Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE, et al. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(6):909–15.
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Deng X-S, Alimova IN, Lind SE, et al. Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(13):2031–40.
Marx J. Cancer-suppressing enzyme adds a link to type 2 diabetes. Science. 2005;310(5752):1259.
Goodwin PJ, Pritchard KI, Ennis M, Clemons M, Graham M, Fantus IG. Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2008;8(6):501–5.
Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Willett WC. The lifelong interplay of genes, lifestyle, and hormones. Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6(5):213.
DiAugustine RP, Petrusz P, Bell GI, Brown CF, Korach KS, McLachlan JA, et al. Influence of estrogens on mouse uterine epidermal growth factor precursor protein and messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1988;122(6):2355–63.
Dickson RB, Lippman ME. Estrogenic regulation of growth and polypeptide growth factor secretion in human breast carcinoma. Endocr Rev. 1987;8(1):29–43.
Reddy KB, Mangold GL, Tandon AK, Yoneda T, Mundy GR, Zilberstein A, et al. Inhibition of breast cancer cell growth in vitro by a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 1992;52(13):3636–41.
Garratt AN. “To erb-B or not to erb-B…” Neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling in heart development and function. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 2006;41(2):215.
Kim J, Jeong H, Lee Y, Kim C, Kim H, Kim A. HRG-beta1-driven ErbB3 signaling induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(1):1–10.
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang M, Li Q, Qu Z, Shi V, et al. Downregulation of HER3 by a novel antisense oligonucleotide, EZN-3920, improves the antitumor activity of EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors in animal models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(4):427–37.
Saji S, Kimura-Tsuchiya R. Combination of molecular-targeted drugs with endocrine therapy for hormone-resistant breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015;1–5.
Zhao M, Ramaswamy B. Mechanisms and therapeutic advances in the management of endocrine-resistant breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2014;5(3):248.
Beck E, Scheen A. Metformin, an antidiabetic molecule with anti-cancer properties. Rev Med Liege. 2013;68(9):444–9.
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10269–73.
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(22):10804–12.
Zaczek A, Brandt B, Bielawski K. The diverse signaling network of EGFR, HER2, HER3 and HER4 tyrosine kinase receptors and the consequences for therapeutic approaches. 2005.
Liu B, Ordonez‐Ercan D, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Yang X, Thor AD. Downregulation of erbB3 abrogates erbB2‐mediated tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(9):1874–82.
Sweeney EE, McDaniel RE, Maximov PY, Fan P, Jordan VC. Models and mechanisms of acquired antihormone resistance in breast cancer: significant clinical progress despite limitations. Horm Mol Biol Clin Invest. 2012;9(2):143–63.
Lurje G, Lenz H-J. EGFR signaling and drug discovery. Oncology. 2009;77:400–10.
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, Blair J, Hann B, Shokat KM, et al. Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature. 2007;445(7126):437–41.
Amin DN, Sergina N, Ahuja D, McMahon M, Blair JA, Wang D, et al. Resiliency and vulnerability in the HER2-HER3 tumorigenic driver. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2(16):16ra7-ra7.
Grøvdal LM, Kim J, Holst MR, Knudsen SLJ, Grandal MV, van Deurs B. EGF receptor inhibitors increase ErbB3 mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2012;24(1):296–301.
Garrett JT, Olivares MG, Rinehart C, Granja-Ingram ND, Sánchez V, Chakrabarty A, et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational up-regulation of HER3 (ErbB3) compensates for inhibition of the HER2 tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108(12):5021–6.
Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E, Burton L, Chan E, et al. Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature. 2012;487(7408):505–9.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW), Republic of Korea (grant number: A120392).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Jinkyoung Kim, Jiyun Lee and Chungyeul Kim contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Lee, J., Kim, C. et al. Anti-cancer effect of metformin by suppressing signaling pathway of HER2 and HER3 in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 5811–5819 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4440-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4440-9