Abstract
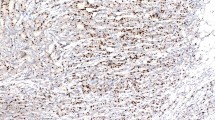
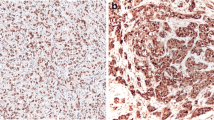
We aim to explore the associations of fascin-1 and cadherin-17 in gastric cancer (GC) to the clinicopathologic features and prognosis of GC. Case group included 204 GC tissues while control group comprised 204 paired adjacent cancer tissues. Expressions of fascin-1 and cadherin-17 were measured with immunohistochemistry and western blot and then analyzed statistically in relation to clinicopathologic features and survival time. Survival curve was drawn by Kaplan-Meier method, and independent prognostic factors were identified with Cox proportional hazards regression model. Fascin-1 was positively expressed in 45.1 % of GC tissues and in 27.5 % of adjacent cancer tissues, respectively (P < 0.05); cadherin-17 was positively expressed in 51.5 % of GC tissues and in 33.8 % of adjacent cancer tissues (P < 0.05). Fascin-1 expression in GC tissues was related to tumor size (P = 0.001) and Lauren classification (P = 0.001). Cadherin-17 expression in GC tissues was related to tumor size (P < 0.001), Lauren classification (P = 0.009), clinical staging (P = 0.001), and distant metastasis (P = 0.002). Fascin-1 expression was positively correlated with cadherin-17 expression in GC tissues (r = 0.828, P < 0.01). Patients with positive expression of both fascin-1 and cadherin-17 had lower survival rates than those with negative expression (all P < 0.01). Cox regression analysis showed that fascin-1 expression, cadherin-17 expression, tumor size, and differentiation were independent risk factors for GC (all P < 0.05). Fascin-1 and cadherin-17 are related to clinicopathologic features of GC and are independent adverse prognostic factors for GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Martel C, Forman D, Plummer M. Gastric cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013;42(2):219–40.
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86.
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23(5):700–13.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Qiu HB, Zhang LY, Ren C, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ, Luo HY, et al. Targeting CDH17 suppresses tumor progression in gastric cancer by downregulating wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e56959.
Hashimoto Y, Kim DJ, Adams JC. The roles of fascins in health and disease. J Pathol. 2011;224(3):289–300.
Chen L, Yang S, Jakoncic J, Zhang JJ, Huang XY. Migrastatin analogues target fascin to block tumour metastasis. Nature. 2010;464(7291):1062–6.
Hashimoto Y, Skacel M, Adams JC. Roles of fascin in human carcinoma motility and signaling: prospects for a novel biomarker? Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(9):1787–804.
Kulasingam V, Diamandis EP. Fascin-1 is a novel biomarker of aggressiveness in some carcinomas. BMC Med. 2013;11:53.
Tan VY, Lewis SJ, Adams JC, Martin RM. Association of fascin-1 with mortality, disease progression and metastasis in carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2013;11:52.
Kim SJ, Kim DC, Kim MC, Jung GJ, Kim KH, Jang JS, et al. Fascin expression is related to poor survival in gastric cancer. Pathol Int. 2012;62(12):777–84.
Ishiyama N, Lee SH, Liu S, Li GY, Smith MJ, Reichardt LF, et al. Dynamic and static interactions between p120 catenin and e-cadherin regulate the stability of cell-cell adhesion. Cell. 2010;141(1):117–28.
Takamura M, Yamagiwa S, Wakai T, Tamura Y, Kamimura H, Kato T, et al. Loss of liver-intestine cadherin in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma promotes angiogenesis by up-regulating metal-responsive transcription factor-1 and placental growth factor. Int J Oncol. 2010;36(1):245–54.
Bartolome RA, Barderas R, Torres S, Fernandez-Acenero MJ, Mendes M, Garcia-Foncillas J, et al. Cadherin-17 interacts with alpha2beta1 integrin to regulate cell proliferation and adhesion in colorectal cancer cells causing liver metastasis. Oncogene. 2014;33(13):1658–69.
Liu LX, Lee NP, Chan VW, Xue W, Zender L, Zhang C, et al. Targeting cadherin-17 inactivates Wnt signaling and inhibits tumor growth in liver carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009;50(5):1453–63.
Oh SY, Kim YB, Suh KW, Paek OJ, Moon HY. Prognostic impact of fascin-1 expression is more significant in advanced colorectal cancer. J Surg Res. 2012;172(1):102–8.
M PN. World Medical Association publishes the revised Declaration of Helsinki. Natl Med J India. 2014;27(1):56.
Koseki K, Takizawa T, Koike M, Ito M, Nihei Z, Sugihara K. Distinction of differentiated type early gastric carcinoma with gastric type mucin expression. Cancer. 2000;89(4):724–32.
Chen YC, Fang WL, Wang RF, Liu CA, Yang MH, Lo SS, et al. Clinicopathological variation of lauren classification in gastric cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 2015
Washington K. 7th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: stomach. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(12):3077–9.
Zheng H, Takahashi H, Murai Y, Cui Z, Nomoto K, Niwa H, et al. Expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF are closely linked to growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2006;26(5A):3579–83.
Maruyama K, Gunven P, Okabayashi K, Sasako M, Kinoshita T. Lymph node metastases of gastric cancer. General pattern in 1931 patients. Ann Surg. 1989;210(5):596–602.
Lehnert T, Rudek B, Buhl K, Golling M. Surgical therapy for loco-regional recurrence and distant metastasis of gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(4):455–61.
Maehara Y, Kabashima A, Koga T, Tokunaga E, Takeuchi H, Kakeji Y, et al. Vascular invasion and potential for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Surgery. 2000;128(3):408–16.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D, et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999;59(22):5830–5.
Yamamoto H, Kohashi K, Fujita A, Oda Y. Fascin-1 overexpression and miR-133b downregulation in the progression of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Mod Pathol. 2013;26(4):563–71.
Wang J, Kang WM, Yu JC, Liu YQ, Meng QB, Cao ZJ. Cadherin-17 induces tumorigenesis and lymphatic metastasis in gastric cancer through activation of NFkappaB signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14(3):262–70.
Lee NP, Poon RT, Shek FH, Ng IO, Luk JM. Role of cadherin-17 in oncogenesis and potential therapeutic implications in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1806(2):138–45.
Kim SJ, Choi IJ, Cheong TC, Lee SJ, Lotan R, Park SH, et al. Galectin-3 increases gastric cancer cell motility by up-regulating fascin-1 expression. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(3):1035–45. e1-2.
Huang LP, Yu YH, Sheng C, Wang SH. Up-regulation of cadherin 17 and down-regulation of homeodomain protein CDX2 correlate with tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22(7):1170–6.
Lee HJ, Nam KT, Park HS, Kim MA, Lafleur BJ, Aburatani H, et al. Gene expression profiling of metaplastic lineages identifies CDH17 as a prognostic marker in early stage gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(1):213–25. e3.
Lee SB, Kim JH, Kim DH, Jeon TY, Kim DH, Kim GH, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of remnant gastric cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2010;10(4):219–25.
Zieker D, Buhler S, Ustundag Z, Konigsrainer I, Manncke S, Bajaeifer K, et al. Induction of tumor stem cell differentiation—novel strategy to overcome therapy resistance in gastric cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398(4):603–8.
Vignjevic D, Schoumacher M, Gavert N, Janssen KP, Jih G, Lae M, et al. Fascin, a novel target of beta-catenin-TCF signaling, is expressed at the invasive front of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(14):6844–53.
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Cheong TC, Choi IJ, Lee YS, Park SH, et al. Galectin-3 germline variant at position 191 enhances nuclear accumulation and activation of beta-catenin in gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011;28(8):743–50.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272743) and Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (No. 13411950902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research was carried out in strict consistence with the protocols established by the Ethics Committee of Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. All the experimental procedures in this study were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The informed consents were obtained from all subjects who participated in this study, and this study was approved by the local institutional review board.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, L., Xu, J., Wang, M. et al. Correlations of fascin-1 and cadherin-17 protein expression with clinicopathologic features and prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 8775–8782 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4368-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4368-0