Abstract
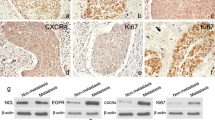
NF45 (also known as ILF2), as one subunit of NF-AT (nuclear factor of activated T cells), repairs DNA breaks, inhibits viral replication, and also functions as a negative regulator in the microRNA processing pathway in combination with NF90. Recently, it was found that implicated in the mitotic control of HeLa cells and deletion of endogenous NF45 decreases growth of HeLa cells. While the role of NF45 in cancer biology remains under debate. In this study, we analyzed the expression and clinical significance of NF45 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC. The expression of NF45 was evaluated by Western blot in 8 paired fresh ESCC tissues and immunohistochemistry on 105 paraffin-embedded slices. NF45 was highly expressed in ESCC and significantly associated with ESCC cells tumor stage and Ki-67. Besides, high NF45 expression was an independent prognostic factor for ESCC patients’ poor survival. To determine whether NF45 could regulate the proliferation of ESCC cells, we increased endogenous NF45 and analyzed the proliferation of TE1 ESCC cells using Western blot, CCK8, flow cytometry assays and colony formation analyses, which together indicated that overexpression of NF45 favors cell cycle progress of TE1 ESCC cells. While knockdown of NF45 resulted in cell cycle arrest at G0/G1-phase and thus abolished the cell growth. These findings suggested that NF45 might play an important role in promoting the tumorigenesis of ESCC, and thus be a promising therapeutic target to prevent ESCC progression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. The NewEngland journal of medicine. 2003;349(23):2241–52. doi:10.1056/NEJMra035010.
Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(4):220–41. doi:10.3322/caac.21149.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29. doi:10.3322/caac.20138.
Hiyama T, Yoshihara M, Tanaka S, Chayama K. Genetic polymorphisms and esophageal cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(8):1643–58. doi:10.1002/ijc.23044.
Kao PN, Chen L, Brock G, Ng J, Kenny J, Smith AJ, et al. Cloning and expression of cyclosporin A- and FK506-sensitive nuclear factor of activated T-cells: NF45 and NF90. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(32):20691–9.
Corthesy B, Kao PN. Purification by DNA affinity chromatography of two polypeptides that contact the NF-AT DNA binding site in the interleukin 2 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(32):20682–90.
Lin HF, Shao JZ, Xiang LX, Wang HJ. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) NF45 (ILF2) cDNA, a subunit of the nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NF-AT). Fish & shellfish immunology. 2006;21(4):385–92. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2006.01.003.
Zhao G, Shi L, Qiu D, Hu H, Kao PN. NF45/ILF2 tissue expression, promoter analysis, and interleukin-2 transactivating function. Exp Cell Res. 2005;305(2):312–23. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.12.030.
Kiesler P, Haynes PA, Shi L, Kao PN, Wysocki VH, Vercelli D. NF45 and NF90 regulate HS4-dependent interleukin-13 transcription in T cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(11):8256–67. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.041004.
Reichman TW, Muniz LC, Mathews MB. The RNA binding protein nuclear factor 90 functions as both a positive and negative regulator of gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(1):343–56.
Stricker RL, Behrens SE, Mundt E. Nuclear factor NF45 interacts with viral proteins of infectious bursal disease virus and inhibits viral replication. J Virol. 2010;84(20):10592–605. doi:10.1128/JVI.02506-09.
Isken O, Baroth M, Grassmann CW, Weinlich S, Ostareck DH, Ostareck-Lederer A, et al. Nuclear factors are involved in hepatitis C virus RNA replication. RNA. 2007;13(10):1675–92. doi:10.1261/rna.594207.
Isken O, Grassmann CW, Sarisky RT, Kann M, Zhang S, Grosse F, et al. Members of the NF90/NFAR protein group are involved in the life cycle of a positive-strand RNA virus. EMBO J. 2003;22(21):5655–65. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg562.
Isken O, Grassmann CW, Yu H, Behrens SE. Complex signals in the genomic 3' nontranslated region of bovine viral diarrhea virus coordinate translation and replication of the viral RNA. RNA. 2004;10(10):1637–52. doi:10.1261/rna.7290904.
Huang Q, He X, Qiu X, Liu X, Sun G, Guo J et al. Expression of NF45 correlates with malignant grade in gliomas and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2014. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2310-5.
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Lewis-Antes A, Azzam EI, Lagunoff D, Pe'ery T, et al. The NF90/NF45 complex participates in DNA break repair via nonhomologous end joining. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(23):4832–43. doi:10.1128/MCB.05849-11.
Guan D, Altan-Bonnet N, Parrott AM, Arrigo CJ, Li Q, Khaleduzzaman M, et al. Nuclear factor 45 (NF45) is a regulatory subunit of complexes with NF90/110 involved in mitotic control. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(14):4629–41. doi:10.1128/MCB.00120-08.
Sakamoto S, Aoki K, Higuchi T, Todaka H, Morisawa K, Tamaki N, et al. The NF90-NF45 complex functions as a negative regulator in the microRNA processing pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(13):3754–69. doi:10.1128/MCB.01836-08.
Sobin LH, Fleming ID. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, fifth edition (1997). Union Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer. 1997;80(9):1803–4.
Yang X, Cheng L, Li M, Shi H, Ren H, Ding Z, et al. High expression of SGTA in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with proliferation and poor prognosis. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(1):141–50. doi:10.1002/jcb.24641.
Liu Y, Lv L, Xue Q, Wan C, Ni T, Chen B, et al. Vacuolar protein sorting 4B, an ATPase protein positively regulates the progression of NSCLC via promoting cell division. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;381(1–2):163–71. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1699-2.
Morris GF, Mathews MB. Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(23):13856–64.
Yu C, Chen K, Zheng H, Guo X, Jia W, Li M, et al. Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and pathogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(5):894–901. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp064.
Lahmann PH, Pandeya N, Webb PM, Green AC, Whiteman DC, Australian CS. Body mass index, long-term weight change, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: is the inverse association modified by smoking status? Cancer. 2012;118(7):1901–9. doi:10.1002/cncr.26455.
Radojicic J, Zaravinos A, Spandidos DA. HPV, KRAS mutations, alcohol consumption and tobacco smoking effects on esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma carcinogenesis. Int J Biol Markers. 2012;27(1):1–12. doi:10.5301/JBM.2011.8737.
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Pe'ery T, Mathews MB. Induction of p53, p21 and apoptosis by silencing the NF90/NF45 complex in human papilloma virus-transformed cervical carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2013;32(43):5176–85. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.533.
Uchida F, Uzawa K, Kasamatsu A, Takatori H, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, et al. Overexpression of cell cycle regulator CDCA3 promotes oral cancer progression by enhancing cell proliferation with prevention of G1 phase arrest. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:321. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-321.
Miyai K, Yamamoto S, Iwaya K, Asano T, Tamai S, Tsuda H, et al. Altered expression of p27(Kip1)-interacting cell-cycle regulators in the adult testicular germ cell tumors: potential role in tumor development and histological progression. APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica. 2012;120(11):890–900. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2012.02919.x.
Hur W, Rhim H, Jung CK, Kim JD, Bae SH, Jang JW, et al. SOX4 overexpression regulates the p53-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical implication and functional analysis in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31(7):1298–307. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq072.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Martin Holcik (Department of Pediatrics, University of Ottawa) for his kindly donation of pcDNA3-Flag-NF45 plasmid. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272708).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sujie Ni and Junya Zhu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, S., Zhu, J., Zhang, J. et al. Expression and clinical role of NF45 as a novel cell cycle protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Tumor Biol. 36, 747–756 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2683-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2683-5