Abstract
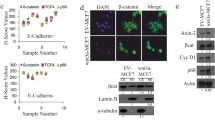
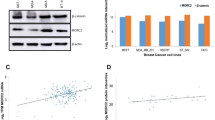
δ-Catenin is a member of the p120 catenin family. Similar to p120ctn, δ-catenin contains nine central Armadillo repeats and binds to the juxtamembrane domain (JMD) of E-cadherin. We used immunohistochemistry to detect δ-catenin expression in breast carcinoma (128 cases), and δ-catenin mRNA and protein expression was detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting (45 cases). The effects of δ-catenin on the activity of small GTPases and the biological behavior of breast cancer cells were explored by pulldown, flow cytometry, methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium, and Matrigel invasion assays. The results showed that δ-catenin expression increased in breast cancer tissues and was associated with a higher degree of malignancy (invasive lobular breast cancer, high tumor-node-metastasis stage, lymph node metastasis, and C-erbB-2+) and poor prognosis. Postoperative survival was shorter in patients with δ-catenin-positive expression than in patients with negative expression. δ-Catenin may regulate Cdc42/Rac1 activity, promote proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells, and alter cell cycle progression. We conclude that δ-catenin tends to overexpress in breast carcinoma and promotes the malignant phenotype.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matter C, Pribadi M, Liu X, Trachtenberg JT. Delta-catenin is required for the maintenance of neural structure and function in mature cortex in vivo. Neuron. 2009;64(3):320–7.
De Busk LM, Boelte K, Min Y, Lin PC. Heterozygous deficiency of delta-catenin impairs pathological angiogenesis. J Exp Med. 2010;207(1):77–84.
Gu D, Tonthat NK, Lee M, Ji H, Bhat KP, Hollingsworth F, et al. Caspase-3 cleavage links delta-catenin to the novel nuclear protein ZIFCAT. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(26):23178–88.
Zhang H, Dai SD, Zhang D, Liu D, Zhang FY, Zheng TY, et al. Delta-catenin promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by binding to E-cadherin in a competitive manner with p120 catenin. Target Oncol. 2014;9(1):53–61.
Brigidi GS, Sun Y, Beccano-Kelly D, Pitman K, Mobasser M, Borgland SL, et al. Palmitoylation of δ-catenin by DHHC5 mediates activity-induced synapse plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17(4):522–32.
Kim H, He Y, Yang I, Zeng Y, Kim Y, Seo YW, et al. δ-Catenin promotes E-cadherin processing and activates β-catenin-mediated signaling: implications on human prostate cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(4):509–21.
Zhang JY, Wang Y, Zhang D, Yang ZQ, Dong XJ, Jiang GY, et al. delta-catenin promotes malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer by non-competitive binding to E-cadherin with p120ctn in cytoplasm. J Pathol. 2010;222(1):76–88.
Lu Q, Lanford GW, Hong H, Chen YH. δ-Catenin as a potential cancer biomarker. Pathol Int. 2014;64(5):243–6.
Lu JP, Zhang J, Kim K, Case TC, Matusik RJ, Chen YH, et al. Human homolog of Drosophila Hairy and enhancer of split 1, Hes1, negatively regulates δ-catenin (CTNND2) expression in cooperation with E2F1 in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:304.
Wang M, Dong Q, Zhang D, Wang Y. Expression of delta-catenin is associated with progression of human astrocytoma. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:514.
Hatzfeld M. The p120 family of cell adhesion molecules. Eur J Cell Biol. 2005;84:205–14.
Burger MJ, Tebay MA, Keith PA, Samaratunga HM, Clements J, Lavin MF, et al. Expression analysis of delta-catenin and prostate-specific membrane antigen: their potential as diagnostic markers for prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;100(2):228–37.
Lu Q, Dobbs LJ, Gregory CW, Lanford GW, Revelo MP, Shappell S, et al. Increased expression of delta-catenin/neural plakophilin-related armadillo protein is associated with the down-regulation and redistribution of E-cadherin and p120ctn in human prostate cancer. Hum Pathol. 2005;36(10):1037–48.
Arikkath J, Peng IF, Ng YG, Israely I, Liu X, Ullian EM, et al. Delta-catenin regulates spine and synapse morphogenesis and function in hippocampal neurons during development. J Neurosci. 2009;29(17):5435–42.
Kawamura Y, Fan QW, Hayashi H, Michikawa M, Yanagisawa K, Komano H. Expression of the mRNA for two isoforms of neural plakophilin-related arm-repeat protein/delta-catenin in rodent neurons and glial cells. Neurosci Lett. 1999;277:185–8.
Lu Q, Paredes M, Medina M, et al. delta-catenin, an adhesive junction associated protein which promotes cell scattering. J Cell Biol. 1999;144:519–32.
Zhang JY, Zhang D, Wang EH. Overexpression of small GTPases directly correlates with expression of δ-catenin and their coexpression predicts a poor clinical outcome in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2013;52(5):338–47.
Lane J, Martin T, Weeks HP, Jiang WG. Structure and role of WASP and WAVE in Rho GTPase signalling in cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2014;11(3):155–65.
Zins K, Lucas T, Reichl P, Abraham D, Aharinejad S. A Rac1/Cdc42 GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor suppresses growth of primary human prostate cancer xenografts and prolongs survival in mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74924. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074924. eCollection 2013.
Dai SD, Wang Y, Zhang JY, Zhang D, Zhang PX, Jiang GY, et al. Upregulation of δ-catenin is associated with poor prognosis and enhances transcriptional activity through Kaiso in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102(1):95–103.
Nopparat J, Zhang J, Lu JP, Chen YH, Zheng D, Neufer PD, et al. δ-Catenin, a Wnt/β-catenin modulator, reveals inducible mutagenesis promoting cancer cell survival adaptation and metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene. 2014 Apr 14;0.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Dr. Shun-ichi Nakamura at Kobe University, Japan, for kindly providing pCMV5-FLAG/δ-catenin. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81101779 to Di Zhang, MD; no. 30870977 and 81071905 to En-Hua Wang, MD; no. 81201844 to Jun-Yi Zhang, MD; no. 81372338 to Shu-Li Liu).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhang, JY. & Wang, EH. δ-Catenin promotes the malignant phenotype in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 569–575 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2680-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2680-8