Abstract
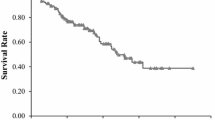
Recent studies have shown the combination of C-reactive protein (CRP) and albumin (The modified Glasgow Prognostic Score, mGPS) had prognostic value in some solid tumors. However, no studies have examined its prognostic role in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients. In this retrospective study, 460 consecutive SCLC patients were screened. Eligible patient was assigned a mGPS of 0, 1, or 2 based on pre-treatment plasma CRP and albumin (0: CRP ≤ 10 mg/L; 1: CRP >10 mg/L and albumin ≥ 35 g/L; 2: CRP > 10 mg/L and albumin < 35 g/L). Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to assess the prognostic value of relevant factors for SCLC. A total of 359 patients were analyzed. The mGPS of 0, 1, and 2 was assigned to 66.3, 30.6, and 3.1 % of total patients. For patients with mGPS of 0, 1, and 2, median overall survival (OS) was 30.4, 28.2, and 14.3 months, respectively (P < 0.001). Performance status (P < 0.001), disease stage (P < 0.001) and pre-treatment LDH (P < 0.001) also significantly predicted OS. Multivariate analyses showed mGPS was an independent prognostic factor (P < 0.001). This study demonstrated that higher mGPS independently predicts worse OS for SCLC patients. The assessment of mGPS could assist the identification of patients with poor prognosis and be a hierarchical factor in the future SCLC clinical trials.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Lally BE, Urbanic JJ, Blackstock AW, Miller AA, Perry MC. Small cell lung cancer: have we made any progress over the last 25 years? Oncologist. 2007;12(9):1096–104. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-9-1096.
Simos D, Sajjady G, Sergi M, Liew MS, Califano R, Ho C, et al. Third-line chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: an international analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014;15(2):110–8. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2013.11.003.
Mountain CF. Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest. 1997;111(6):1710–7.
Stinchcombe TE, Gore EM. Limited-stage small cell lung cancer: current chemoradiotherapy treatment paradigms. Oncologist. 2010;15(2):187–95. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0298.
Ma M, Wang M, Xu Y, Hu K, Liu H, Li L, et al. First-line chemotherapy and its survival analysis of 394 patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in a single institute. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014;17(1):8–14. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.01.02.
Li J, Dai CH, Chen P, Wu JN, Bao QL, Qiu H, et al. Survival and prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2010;27(1):73–81. doi:10.1007/s12032-009-9174-3.
Paesmans M, Sculier JP, Lecomte J, Thiriaux J, Libert P, Sergysels R, et al. Prognostic factors for patients with small cell lung carcinoma: analysis of a series of 763 patients included in 4 consecutive prospective trials with a minimum follow-up of 5 years. Cancer. 2000;89(3):523–33.
Fizazi K, Cojean I, Pignon JP, Rixe O, Gatineau M, Hadef S, et al. Normal serum neuron specific enolase (NSE) value after the first cycle of chemotherapy: an early predictor of complete response and survival in patients with small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;82(6):1049–55.
Mantovani A. Cancer: inflaming metastasis. Nature. 2009;457(7225):36–7. doi:10.1038/457036b.
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Seruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocana A, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(6):dju124. doi:10.1093/jnci/dju124.
Templeton AJ, Ace O, McNamara MG, Al-Mubarak M, Vera-Badillo FE, Hermanns T, et al. Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23(7):1204–12. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0146.
Laird BJ, Kaasa S, McMillan DC, Fallon MT, Hjermstad MJ, Fayers P, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced cancer: a comparison of clinicopathological factors and the development of an inflammation-based prognostic system. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(19):5456–64. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1066.
Crumley AB, McMillan DC, McKernan M, McDonald AC, Stuart RC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score in patients with inoperable gastro-oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(5):637–41. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602998.
Al Murri AM, Bartlett JM, Canney PA, Doughty JC, Wilson C, McMillan DC. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(2):227–30. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602922.
McMillan DC. An inflammation-based prognostic score and its role in the nutrition-based management of patients with cancer. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008;67(3):257–62. doi:10.1017/s0029665108007131.
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dunlop DJ. Evaluation of cumulative prognostic scores based on the systemic inflammatory response in patients with inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89(6):1028–30. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601242.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357(9255):539–45. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04046-0.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420(6917):860–7. doi:10.1038/nature01322.
Hwang EC, Hwang IS, Yu HS, Kim SO, Jung SI, Hwang JE, et al. Utility of inflammation-based prognostic scoring in patients given systemic chemotherapy first-line for advanced inoperable bladder cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012;42(10):955–60. doi:10.1093/jjco/hys124.
Oremek GM, Sauer-Eppel H, Bruzdziak TH. Value of tumour and inflammatory markers in lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(4A):1911–5.
Hong S, Kang YA, Cho BC, Kim DJ. Elevated serum C-reactive protein as a prognostic marker in small cell lung cancer. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(1):111–7. doi:10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.111.
Suh SY, Ahn HY. Lactate dehydrogenase as a prognostic factor for survival time of terminally ill cancer patients: a preliminary study. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43(6):1051–9. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.01.031.
Petrovic M, Bukumiric Z, Zdravkovic V, Mitrovic S, Atkinson HD, Jurisic V. The prognostic significance of the circulating neuroendocrine markers chromogranin A, pro-gastrin-releasing peptide, and neuron-specific enolase in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(2):823. doi:10.1007/s12032-013-0823-1.
Zhao WX, Luo JF. Serum neuron-specific enolase levels were associated with the prognosis of small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(5):3245–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0896-7.
Emin Erbaycu A, Gunduz A, Batum O, Zeren Ucar Z, Tuksavul F, Zeki Guclu S. Pre-treatment and treatment-induced neuron-specific enolase in patients with small-cell lung cancer: an open prospective study. Arch Bronconeumol. 2010;46(7):364–9. doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2010.04.005.
Leifsson BG, Ahren B. Serum calcium and survival in a large health screening program. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(6):2149–53. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.6.8964843.
Temme EH, Zhang J, Schouten EG, Kesteloot H. Serum bilirubin and 10-year mortality risk in a Belgian population. Cancer Causes Control. 2001;12(10):887–94.
Du Clos TW, Mold C. C-reactive protein: an activator of innate immunity and a modulator of adaptive immunity. Immunol Res. 2004;30(3):261–77. doi:10.1385/ir:30:3:261.
Casamassima A, Picciariello M, Quaranta M, Berardino R, Ranieri C, Paradiso A, et al. C-reactive protein: a biomarker of survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with subcutaneous interleukin-2 based immunotherapy. J Urol. 2005;173(1):52–5. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000146713.50673.e5.
Hara M, Yonei A, Ayabe T, Tomita M, Nakamura K, Onitsuka T. Postoperative serum C-reactive protein levels in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;16(2):85–90.
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dunlop DJ. Comparison of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) with performance status (ECOG) in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(9):1704–6. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601789.
McMillan DC, Crozier JE, Canna K, Angerson WJ, McArdle CS. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) in patients undergoing resection for colon and rectal cancer. Int J Color Dis. 2007;22(8):881–6. doi:10.1007/s00384-006-0259-6.
Proctor MJ, Morrison DS, Talwar D, Balmer SM, Fletcher CD, O’Reilly DS, et al. A comparison of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with cancer. A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(17):2633–41. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.03.028.
Leung EY, Scott HR, McMillan DC. Clinical utility of the pretreatment Glasgow prognostic score in patients with advanced inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(4):655–62. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318244ffe1.
McMillan DC. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009;12(3):223–6. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832a7902.
Roxburgh CS, McMillan DC. Role of systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol. 2010;6(1):149–63. doi:10.2217/fon.09.136.
Roxburgh CS, Crozier JE, Maxwell F, Foulis AK, Brown J, McKee RF, et al. Comparison of tumour-based (Petersen Index) and inflammation-based (Glasgow Prognostic Score) scoring systems in patients undergoing curative resection for colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(5):701–6. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604926.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by: Wu Jieping Medical Foundation Project (Grant No. 08-JC-003), Innovative drug R & D center based on real-time high-throughput cell-based screening platform and large capacity compound library (Grant No. 2013ZX09401003-002), National Natural Science Funds of China (Grant No. 81372502) and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2012AA02A502). All the grant supporters have no roles in study design, data collection and analysis, and manuscript preparation.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ting Zhou and Shaodong Hong contributed equally to this work and share the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, T., Hong, S., Hu, Z. et al. A systemic inflammation-based prognostic scores (mGPS) predicts overall survival of patients with small-cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 337–343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2623-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2623-4