Abstract
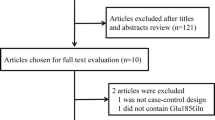
Several previous studies have investigated the association between the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism and the risk of bladder cancer in various populations. However, these results remain inconsistent. Therefore, we performed this meta-analysis to evaluate the relationship between the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism and the risk of bladder cancer. An extensive literature search was performed to identify all eligible studies regarding this association. The odds ratios (ORs) with 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were used to estimate the strength of risk under fixed and random effects models. We identified and included eight case-control studies including 2,036 cases and 2,273 controls. No significant association was found between the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism and the risk of bladder cancer under the dominant model; however, those with the SULT1A1 Arg/Arg genotype had a significantly increased risk (OR = 1.218, 95 % CI = 1.067–1.392, P = 0.0044) under the recessive model. In the subgroup analysis of ethnicity, a significant association was observed in Caucasians under the recessive model (OR = 1.269, 95 % CI = 1.069–1.506, P = 0.007). Furthermore, an increased risk of bladder cancer was observed between the Arg213His polymorphism and never smokers in the recessive model (OR = 1.428, 95 % CI = 1.079–1.890, P = 0.013). The results of this meta-analysis indicate that the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism is associated with the risk bladder cancer under a recessive model; however, a possibly higher risk for Caucasians with the Arg/Arg genotype and never smokers needs further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volanis D, Kadiyska T, Galanis A, Delakas D, Logotheti S, Zoumpourlis V. Environmental factors and genetic susceptibility promote urinary bladder cancer. Toxicol Lett. 2010;193:131–7.
Autrup H. Genetic polymorphisms in human xenobiotica metabolizing enzymes as susceptibility factors in toxic response. Mutat Res. 2000;464:65–76.
Glatt H. Sulfotransferases in the bioactivation of xenobiotics. Chem Biol Interact. 2000;129:141–70.
Chou HC, Lang NP, Kadlubar FF. Metabolic activation of the N-hydroxy derivative of the carcinogen 4-aminobiphenyl by human tissue sulfotransferases. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:413–7.
Dooley TP, Haldeman-Cahill R, Joiner J, Wilborn TW. Expression profiling of human sulfotransferase and sulfatase gene superfamilies in epithelial tissues and cultured cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;277:236–45.
Raftogianis RB, Wood TC, Otterness DM, Van Loon JA, Weinshilboum RM. Phenol sulfotransferase pharmacogenetics in humans: association of common SULT1A1 alleles with TS PST phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;239:298–304.
Ozawa S, Tang YM, Yamazoe Y, Kato R, Lang NP, Kadlubar FF. Genetic polymorphisms in human liver phenol sulfotransferases involved in the bioactivation of N-hydroxy derivatives of carcinogenic arylamines and heterocyclic amines. Chem Biol Interact. 1998;109:237–48.
Coughtrie MW, Gilissen RA, Shek B, Strange RC, Fryer AA, Jones PW, et al. Phenol sulphotransferase SULT1A1 polymorphism: molecular diagnosis and allele frequencies in Caucasian and African populations. Biochem J. 1999;337:45–9.
Carlini EJ, Raftogianis RB, Wood TC, Jin F, Zheng W, Rebbeck TR, et al. Sulfation pharmacogenetics: SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 allele frequencies in Caucasian. Chinese and African-American subjects. Pharmacogenetics. 2001;11:57–68.
Ozawa S, Shimizu M, Katoh T, Miyajima A, Ohno Y, Matsumoto Y, et al. Sulfating-activity and stability of cDNA-expressed allozymes of human phenol sulfotransferase, ST1A3*1 (213Arg) and ST1A3*2 (213His), both of which exist in Japanese as well as Caucasians. J Biochem. 1999;126:271–7.
Ozawa S, Katoh T, Inatomi H, Imai H, Kuroda Y, Ichiba M, et al. Association of genotypes of carcinogen-activating enzymes, phenol sulfotransferase SULT1A1 (ST1A3) and arylamine N-acetyltransferase NAT2, with urothelial cancer in a Japanese population. Int J Cancer. 2002;102:418–21.
Tang D, Rundle A, Mooney L, Cho S, Schnabel F, Estabrook A, et al. Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) polymorphism, PAH-DNA adduct levels in breast tissue and breast cancer risk in a case-control study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;78:217–22.
Liang G, Miao X, Zhou Y, Tan W, Lin D. A functional polymorphism in the SULT1A1 gene (G638A) is associated with risk of lung cancer in relation to tobacco smoking. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:773–8.
Tsukino H, Kuroda Y, Nakao H, Imai H, Inatomi H, Osada Y, et al. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A1, and N-acetyltransferase (NAT) 2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to urothelial cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:99–106.
Nowell S, Ratnasinghe DL, Ambrosone CB, Williams S, Teague-Ross T, Trimble L, et al. Association of SULT1A1 phenotype and genotype with prostate cancer risk in African-Americans and Caucasians. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:270–6.
Kellen E, Zeegers M, Paulussen A, Van Dongen M, Buntinx F. Fruit consumption reduces the effect of smoking on bladder cancer risk. The Belgian case control study on bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:2572–8.
Jerevall PL, Ahmadi A, Bergman M, Stal O, Wingren S. Sulfotransferase1A1 and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:2515–7.
Hung RJ, Boffetta P, Brennan P, Malaveille C, Hautefeuille A, Donato F, et al. GST, NAT, SULT1A1, CYP1B1 genetic polymorphisms, interactions with environmental exposures and bladder cancer risk in a high-risk population. Int J Cancer. 2004;110(4):598–604.
Covolo L, Placidi D, Gelatti U, Carta A, Scotto Di Carlo A, et al. Bladder cancer, GSTs, NAT1, NAT2, SULT1A1, XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD genetic polymorphisms and coffee consumption: a case-control study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2008;23(5):355–62.
Wang YH, Lee YH, Tseng PT, Shen CH, Chiou HY. Human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) and Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) polymorphisms and urothelial cancer risk in Taiwan. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134(2):203–9.
Cui X, Lu X, Hiura M, Omori H, Miyazaki W, Katoh T. Association of genotypes of carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes and smoking status with bladder cancer in a Japanese population. Environ Health Prev Med. 2013;18(2):136–42.
Pereira WO, Paiva AS, Queiroz JW, Toma L, Dietrich CP, Nader HB, et al. Genetic polymorphism in the sulfotransferase SULT1A1 gene in cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005;160:55–60.
Zheng L, Wang Y, Schabath MB, Grossman HB, Wu X. Sulfotransferase 1A1 (SULT1A1) polymorphism and bladder cancer risk: a case-control study. Cancer Lett. 2003;202:61–9.
Wu MT, Wang YT, Ho CK, Wu DC, Lee YC, Hsu HK, et al. SULT1A1 polymorphism and esophageal cancer in males. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:101–4.
Tiemersma EW, Bunschoten A, Kok FJ, Glatt H, de Boer SY, Kampman E. Effect of SULT1A1 and NAT2 genetic polymorphism on the association between cigarette smoking and colorectal adenomas. Int J Cancer. 2004;108:97–103.
Dalhoff K, Buus Jensen K, Enghusen Poulsen H. Cancer and molecular biomarkers of phase 2. Methods Enzymol. 2005;400:618–27.
Hengstler JG, Arand M, Herrero ME, Oesch F. Polymorphisms of N-acetyltransferases, glutathione S-transferases, microsomal epoxide hydrolase and sulfotransferases: influence on cancer susceptibility. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1998;154:47–85.
Li K, Ren YW, Wan Y, Yin ZH, Wu W, Zhou BS. SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism and susceptibility of environment-related cancers: a meta-analysis of 5,915 cases and 7,900 controls. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(3):2597–605.
Kotnis A, Kannan S, Sarin R, Mulherkar R. Case-control study and meta-analysis of SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism for gene, ethnicity and environment interaction for cancer risk. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(8):1340–7.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Science Council, Taiwan (grant no.: NSC 101-2314-B-038-058) and Taipei Medical University, Taiwan (grant no.: TMU101-AE1-B40).
Conflicts of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chih-Ming Su and Mei-Chieh Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, CM., Chen, MC., Lin, IC. et al. Association between the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism and the risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 35, 7147–7153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1954-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1954-5