Abstract
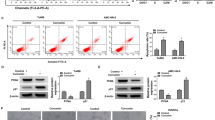
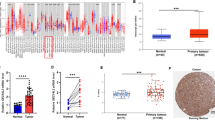
This study aimed to analyze the expression, clinical significance of epithelial membrane protein-1 (EMP1) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and the biological effect in its cell line by EMP1 overexpression. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot were used to analyze the EMP1 protein expression in 75 cases of nasopharyngeal cancer and 31 cases of normal tissues to study the relationship between EMP1 expression and clinical factors. Recombinant lentiviral vector was constructed to overexpress EMP1 and then infect nasopharyngeal cancer CNE2 cell line. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR and Western blot were used to detect the mRNA level and protein of EMP1. MTT assay, cell apoptosis, migration, and invasion assays were also conducted to determine the influence of the upregulated expression of EMP1 that might be found on CNE2 cells’ biological effect. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot: The level of EMP1 protein expression was found to be significantly lower in nasopharyngeal cancer tissue than in the normal tissues (P < 0.05). Decreased expression of EMP1 was significantly correlated with T stages, lymph node metastasis, clinic stage, and histological grade of patients with nasopharyngeal cancer (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, the loss of EMP1 expression correlated significantly with poor overall survival time by Kaplan–Meier analysis (P < 0.05). The result of biological function has shown that CNE2 cell-transfected EMP1 had a lower survival fraction, higher cell apoptosis, significant decrease in migration and invasion, higher caspase-9, and lower vascular endothelial growth factor C protein expression compared with CNE2 cell-untransfected EMP1 (P < 0.05). EMP1 expression decreased in nasopharyngeal cancer and correlated significantly T stages, lymph node metastasis, clinic stage, histological grade, and poor overall survival, suggesting that EMP1 may play important roles as a negative regulator to nasopharyngeal cancer cell.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:423–8.
Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2005;365:2041–54.
Lai S, Wang G, Cao X, Li Z, Hu J, Wang J. EMP-1 promotes tumorigenesis of NSCLC through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2012;32:834–8.
Sobin LH, Fleming ID. TNM classification of malignant tumors, 5th ed. Union Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer. 1997;80:1803–4.
Taylor V, Welcher AA, Program AE, Suter U. Epithelial membrane protein-1, peripheral myelin protein 22, and lens membrane protein 20 define a novel gene family. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28824–33.
Lobsiger CS, Magyar JP, Taylor V, Wulf P, Welcher AA, Program AE, et al. Identification and characterization of a cDNA and the structural gene encoding the mouse epithelial membrane protein-1. Genomics. 1996;36:379–87.
Wulf P, Suter U. Embryonic expression of epithelial membrane protein 1 in early neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999;116:169–80.
Zoidl G, Blass-Kampmann S, D’Urso D, Schmalenbach C, Müller HW. Retroviral-mediated gene transfer of the peripheral myelin protein PMP22 in Schwann cells: modulation of cell growth. EMBO J. 1995;14:1122–8.
Jetten AM, Suter U. The peripheral myelin protein 22 and epithelial membrane protein family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2000;64:97–129.
Lee HS, Sherley JL, Chen JJ, Chiu CC, Chiou LL, Liang JD, et al. EMP1 is a junctional protein in a liver stem cell line and in the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334:996–1003.
Gnirke AU, Weidle UH. Investigation of prevalence and regulation of expression of progression associated protein (PAP). Anticancer Res. 1998;18:4363–9.
Wang HT, Kong JP, Ding F, et al. Analysis of gene expression profile induced by EMP-1 in esophageal cancer cells using cDNA microarray. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:392–8.
Zhang J, Cao W, Xu Q, Chen WT. The expression of EMP1 is downregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma and possibly associated with tumour metastasis. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:25–9.
Liao Q, Guo X, Li X, Xiong W, Li X, Yang J, et al. Prohibitin is an important biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and prognosis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2013;22:68–76.
Zhou JY, Chong VF, Khoo JB, Chan KL, Huang J. The relationship between nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor volume and TNM T-classification: a quantitative analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007;264:169–74.
Wu Z, Zeng RF, Su Y, Gu MF, Huang SM. Prognostic significance of tumor volume in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Head Neck. 2013;35:689–94.
Fu L, Chen W, Guo W, Wang J, Tian Y, Shi D, et al. Berberine targets AP-2/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2, HIF-1α/VEGF and cytochrome-c/caspase signaling to suppress human cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 2013;8:e69240.
Sen S, Kawahara B, Chaudhuri G. Mitochondrial-associated nitric oxide synthase activity inhibits cytochrome c oxidase: implications for breast cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;57:210–20.
Zhang JM, Wang HC, Wang HX, Ruan LH, Zhang YM, Li JT, et al. Oxidative stress and activities of caspase-8, -9, and -3 are involved in cryopreservation-induced apoptosis in granulosa cells. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;166:52–5.
Peng J, Shao N, Peng H, Chen LQ. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Buon. 2013;18:398–406.
Xie LX, Zhai TT, Yang LP, Yang E, Zhang XH, Chen JY, et al. Lymphangiogenesis and prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor C in gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Int J Exp Pathol. 2013;94:39–46.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G.G., Lu, Y.F., Fu, Z.Z. et al. EMP1 inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer cell growth and metastasis through induction apoptosis and angiogenesis. Tumor Biol. 35, 3185–3193 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1416-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1416-5