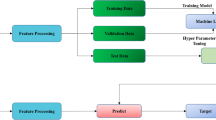
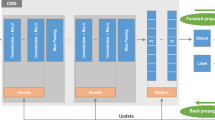
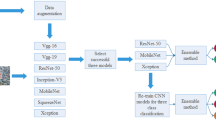
Abstract
Pneumonia is a disease caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi that settle in the alveolar sacs of the lungs and can lead to serious health complications in humans. Early detection of pneumonia is necessary for early treatment to manage and cure the disease. Recently, machine learning-based pneumonia detection methods have focused on pneumonia in adults. Machine learning relies on manual feature engineering, whereas deep learning can automatically detect and extract features from data. This study proposes a deep learning feature extraction-based hybrid approach that combines deep learning and machine learning to detect pediatric pneumonia, which is difficult to standardize. The proposed hybrid approach enhances the accuracy of detecting pediatric pneumonia and simplifies the approach by eliminating the requirement for advanced feature extraction. The experiments indicate that the hybrid approach using a Medium Neural Network based on AlexNet feature extraction achieved a 97.9% accuracy rate and 98.0% sensitivity rate. The results show that the proposed approach achieved higher accuracy rates than state-of-the-art approaches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yılmaz G, Uzel N, Işık N, Uğur S, Aslan S, Badur S (2000) Akut alt solunum yolu infeksiyonu olan çocuklarda viral etkenler ve respiratory syncytial virus alt grupları. İnfeksiyon Dergisi 14(2):157–164
WHO: Child mortality (under 5 years). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/levels-and-trends-in-child-under-5-mortality-in-2020
Almaslukh, B.: A lightweight deep learning-based pneumonia detection approach for energy-efficient medical systems. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2021 (2021)
Kocabaş E, Ersöz D, Karakoç F et al (2009) Türk toraks derneği çocukluklarda toplumda gelişen pnömoni tanı ve tedavi uzlaşı raporu. Toraks Dergisi 10:1–24
WHO: Pneumonia in children. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia
Ayan, E., Karabulut, B., Ünver, H.M.: Diagnosis of pediatric pneumonia with ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks in chest x-ray images. Arab J Sci Eng pp. 1–17 (2021)
Sharif, M., Saeed, T., Saheel, K., Khan, K., Hussain, M., Sharif, A.H.M., Saeed, T., Saheel, K., Khan, K., Hussain, M., et al.: Comparison of chest x-ray with lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia in children aged 02 months to 12 years. J Rawalpindi Med Coll 25(1) (2021)
Ahmad HK, Milne MR, Buchlak QD, Ektas N, Sanderson G, Chamtie H, Karunasena S, Chiang J, Holt X, Tang CH et al (2023) Machine learning augmented interpretation of chest x-rays: a systematic review. Diagnostics 13(4):743
Zhang, X.D.: Machine learning. In: A Matrix Algebra Approach to Artificial Intelligence, pp. 223–440. Springer (2020)
Choose classifier options. https://uk.mathworks.com/help/stats/choose-a-classifier.html
Zhang L, Wang S, Liu B (2018) Deep learning for sentiment analysis: a survey. Wiley Interdiscip Rev: Data Min Knowl Discov 8(4):e1253
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Chouhan V, Singh SK, Khamparia A, Gupta D, Tiwari P, Moreira C, Damaševičius R, De Albuquerque VHC (2020) A novel transfer learning based approach for pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images. Appl Sci 10(2):559
Erdem E, Aydın T (2021) Detection of pneumonia with a novel cnn-based approach. Sakarya Univ J Comput Inform Sci 4(1):26–34
Zhang D, Ren F, Li Y, Na L, Ma Y (2021) Pneumonia detection from chest x-ray images based on convolutional neural network. Electronics 10(13):1512
Jain R, Nagrath P, Kataria G, Kaushik VS, Hemanth DJ (2020) Pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Measurement 165:108046
Mittal A, Kumar D, Mittal M, Saba T, Abunadi I, Rehman A, Roy S (2020) Detecting pneumonia using convolutions and dynamic capsule routing for chest x-ray images. Sensors 20(4):1068
El Asnaoui, K., Chawki, Y., Idri, A.: Automated methods for detection and classification pneumonia based on x-ray images using deep learning. In: Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain for Future Cybersecurity Applications, pp. 257–284. Springer (2021)
Liang G, Zheng L (2020) A transfer learning method with deep residual network for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis. Comput Methods Programs in Biomed 187:104964
Chakraborty, S., Aich, S., Sim, J.S., Kim, H.C.: Detection of pneumonia from chest x-rays using a convolutional neural network architecture. In: International Conference on Future Information & Communication Engineering, vol. 11, pp. 98–102 (2019)
Kundu R, Das R, Geem ZW, Han GT, Sarkar R (2021) Pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images using an ensemble of deep learning models. PLoS ONE 16(9):e0256630
Hashmi MF, Katiyar S, Keskar AG, Bokde ND, Geem ZW (2020) Efficient pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images using deep transfer learning. Diagnostics 10(6):417
Sun MG, Saha S, Shah SA, Luz S, Nair H, Saha S (2021) Study protocol and design for the assessment of paediatric pneumonia from x-ray images using deep learning. BMJ Open 11(4):e044461
Chagas JVSD, de Rodrigues D, Ivo RF, Hassan MM, de Albuquerque VHC et al (2021) A new approach for the detection of pneumonia in children using cxr images based on an real-time iot system. J Real-Time Image Process 18(4):1099–1114
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2818–2826 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., Alemi, A.A.: Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Thirty-first AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2017)
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: An introduction to statistical learning, vol. 112. Springer (2013)
Garstka, J., Strzelecki, M.: Pneumonia detection in x-ray chest images based on convolutional neural networks and data augmentation methods. In: 2020 Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications, pp. 18–23. IEEE (2020)
Funding
The authors have declared that no funds, grants, or other support has been received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Manisa Celal Bayar University Clinical Research Ethics Committee approved this study on September 21, 2020.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publication
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figs. 1, 2, and 3.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, U., Bal, A., Moral, Ö.T. et al. A deep learning feature extraction-based hybrid approach for detecting pediatric pneumonia in chest X-ray images. Phys Eng Sci Med 47, 109–117 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-023-01347-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-023-01347-z