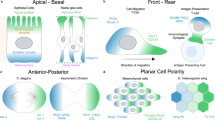
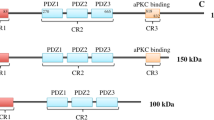
Abstract
Cancerous tumors are the result of uncontrolled growth of cells. A growing body of evidence points to cancer stem cells as being the genesis of this uncontrolled growth. Cancer stem cells appear to show dramatic alterations in cellular function when compared to their benign counterparts. Among these alterations are aberrant cell polarity and deviation in asymmetric and symmetric cellular division. Aberrations in cell polarity and orientation of mitotic spindle can compromise the fidelity of asymmetric cellular division and lead to improper cellular differentiation and an overgrowth of immature cancerous cells stem cells. Over the last several decades there has been a rapid acquisition of knowledge of the wide array of mutations in cancer. While the myriad of genetic mutations seemingly have little in common with each other, a thorough review of the literature uncovers that the most widely studied mutations have a mutual effect on altering cell polarity. This article summarizes how mutations of elements of some of the most important signalling pathways can lead to altered polarity and promote oncogenesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudureheman A, Ainiwaer J, Hou Z, Niyaz M, Turghun A, Hasim A, et al. High MLL2 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression by inducing EMT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144:1025–35.
Adler CE, Fetter RD, Bargmann CI. UNC-6/Netrin induces neuronal asymmetry and defines the site of axon formation. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:511–8.
Álvarez-Quilón A, Serrano-Benítez A, Lieberman JA, Quintero C, Sánchez-Gutiérrez D, Escudero LM, et al. ATM specifically mediates repair of double-strand breaks with blocked DNA ends. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3347.
Amin N, Khan A, St Johnston D, Tomlinson I, Martin S, Brenman J, et al. LKB1 regulates polarity remodeling and adherens junction formation in the Drosophila eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:8941–6.
Aranda V, Haire T, Nolan ME, Calarco JP, Rosenberg AZ, Fawcett JP, et al. Par6-aPKC uncouples ErbB2 induced disruption of polarized epithelial organization from proliferation control. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1235–45.
Arima Y, Hayashi H, Kamata K, Goto TM, Sasaki M, Kuramochi A, et al. Decreased expression of neurofibromin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in neurofibromatosis type 1. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:e136–e141141.
Atay O, Skotheim JM. Spatial and temporal signal processing and decision making by MAPK pathways. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:317–30.
Baek ST, Tallquist MD. Nf1 limits epicardial derivative expansion by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition and proliferation. Development. 2012;139:2040–9.
Bahm I, Barriga EH, Frolov A, Theveneau E, Frankel P, Mayor R. PDGF controls contact inhibition of locomotion by regulating N-cadherin during neural crest migration. Development. 2017;144:2456–68.
Bhagwat AS, Vakoc CR. Targeting transcription factors in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2015;1:53–655.
Bilder D. Epithelial polarity and proliferation control: links from the Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressors. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1909–25.
Bonelli MA, Cavazzoni A, Saccani F, Alfieri RR, Quaini F, La Monica S, et al. Inhibition of PI3K pathway reduces invasiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in squamous lung cancer cell lines harboring PIK3CA gene alterations. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:1916–27.
Borovski T, Vellinga TT, Laoukili J, Santo EE, Fatrai S, van Schelven S, et al. Inhibition of RAF1 kinase activity restores apicobasal polarity and impairs tumour growth in human colorectal cancer. Gut. 2017;66:1106–15.
Boudeau J, Sapkota G, Alessi D. LKB1, a protein kinase regulating cell proliferation and polarity. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:159–65.
Boyer A, Hermo L, Paquet M, Robaire B, Boerboom D. Seminiferous tubule degeneration and infertility in mice with sustained activation of WNT/CTNNB1 signaling in sertoli cells. Biol Reprod. 2008;79:475–85.
Brumby AM, Richardson HE. Scribble mutants cooperate with oncogenic Ras or Notch to cause neoplastic overgrowth in Drosophila. EMBO J. 2003;22:5769–79.
Burotto M, Chiou VL, Lee JM, Kohn EC. The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: a new perspective. Cancer. 2014;120:3446–56.
Cai Y, Zhang M, Qiu X, Wang B, Fu Y, Zeng J, et al. Upregulation of FBXW7 suppresses renal cancer metastasis and epithelial mesenchymal transition. Dis Markers. 2017;2017:8276939.
Calzada MJ, Esteban MA, Feijoo-Cuaresma M, Castellanos MC, Naranjo-Suárez S, Temes E, et al. von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein regulates the assembly of intercellular junctions in renal cancer cells through hypoxia-inducible factor-independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1553–600.
Casimiro MC, Crosariol M, Loro E, Li Z, Pestell RG. Cyclins and cell cycle control in cancer and disease. Genes Cancer. 2012;3:649–57.
Caussinus E, Hirth F. Asymmetric stem cell division in development and cancer. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2007;45:205–25.
Chaudhury A, Howe PH. The tale of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signaling: a soigné enigma. IUBMB Life. 2009;61(10):929–39.
Chavali M, Klingener M, Kokkosis AG, Garkun Y, Felong S, Maffei A, et al. Non-canonical Wnt signaling regulates neural stem cell quiescence during homeostasis and after demyelination. Nat Commun. 2018;9:36.
Chilov D, Sinjushina N, Rita H, Taketo MM, Mäkelä TP, Partanen J. Phosphorylated β-catenin localizes to centrosomes of neuronal progenitors and is required for cell polarity and neurogenesis in developing midbrain. J Dev Biol. 2011;357:259–68.
Cho SJ, Yoon C, Lee JH, Chang KK, Lin JX, Kim YH, et al. KMT2C mutations in diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinoma promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:6556–699.
Choi HJ, Park JH, Park M, Won HY, Joo HS, Lee CH, et al. UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and HDAC1. EMBO Rep. 2015;16:1288–98.
Chou J, Provot S, Werb Z. GATA3 in development and cancer differentiation: cells GATA have it! Cell Physiol. 2010;222:42–9.
Chung CY, Potikyan G, Firtel RA. Control of cell polarity and chemotaxis by Akt/PKB and PI3 kinase through the regulation of PAKa. Mol Cell. 2001;7:937–47.
Cicalese A, Bonizzi G, Pasi C, Faretta M, Ronzoni S, Giulini B, et al. The tumor suppressor p53 regulates polarity of self-renewing divisions in mammary stem cells. Cell. 2009;138:1083–95.
Cicchini C, de Nonno V, Battistelli C, Cozzolino AM, De Santis PM, Ciafrè SA, et al. Epigenetic control of EMT/MET dynamics: HNF4α impacts DNMT3s through miRs-29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849:919–29.
Cohen-Dvashi H, Ben-Chetrit N, Russell R, Carvalho S, Lauriola M, Nisani S, et al. Navigator-3, a modulator of cell migration, may act as a suppressor of breast cancer progression. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:299–314.
Collin L, Schlessinger K, Hall A. APC nuclear membrane association and microtubule polarity. Biol Cell. 2008;100:243–52.
Coradini D, Fornili M, Ambrogi F, Boracchi P, Biganzoli E. TP53 mutation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemlike features in breast cancer subtypes. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:254085.
Cowan CR, Hyman AA. Cyclin E-Cdk2 temporally regulates centrosome assembly and establishment of polarity in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:1441–7.
Darido C, Buchert M, Pannequin J, Bastide P, Zalzali H, Mantamadiotis T, et al. Defective claudin-7 regulation by Tcf-4 and Sox-9 disrupts the polarity and increases the tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4258–68.
Daulat AM, Borg JP. When mTORC2-AKT signaling meets cell polarity. Cell Cycle. 2016;15:3003–4.
Desgrange A, Heliot C, Skovorodkin I, Akram SU, Heikkilä J, Ronkainen VP, et al. HNF1B controls epithelial organization and cell polarity during ureteric bud branching and collecting duct morphogenesis. Development. 2017;144:4704–19.
Deshpande A, Sicinski P, Hinds PW. Cyclins and cdks in development and cancer: a perspective. Oncogene. 2005;24:2909–15.
Devarajan E, Song YH, Krishnappa S, Alt E. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer lines is mediated through PDGF-D released by tissue-resident stem cells. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:1023–31.
Dong L, Pietsch S, Englert C. Towards an understanding of kidney diseases associated with WT1 mutations. Kidney Int. 2015;88:684–90.
Dorighi KM, Swigut T, Henriques T, Bhanu NV, Scruggs BS, Nady N, et al. Mll3 and Mll4 facilitate enhancer RNA synthesis and transcription from promoters independently of H3K4 monomethylation. J Mol Cell. 2017;66:568–76.
Drubin DG, Nelson WJ. Origins of cell polarity. Cell. 1996;84:335–44.
Duchi S, Fagnocchi L, Cavaliere V, Hsouna A, Gargiulo G, Hsu T. Drosophila VHL tumor-suppressor gene regulates epithelial morphogenesis by promoting microtubule and aPKC stability. Development. 2010;137:1493–503.
Duronio RJ, Xiong Y. Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a008904.
Eder AM, Sui X, Rosen DG, Nolden LK, Cheng KW, Lahad JP, et al. Atypical PKCι contributes to poor prognosis through loss of apical-basal polarity and Cyclin E overexpression in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:12519–24.
Ekpe-Adewuyi E, Lopez-Campistrous A, Tang X, Brindley DN, McMullen TP. Platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha mediates nodal metastases in papillary thyroid cancer by driving the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 2016;7:83684–700.
El-Hashash AH, Warburton D. Cell polarity and spindle orientation in the distal epithelium of embryonic lung. Dev Dyn. 2011;240:441–5.
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Cdc42 regulates GSK-3beta and adenomatous polyposis coli to control cell polarity. Nature. 2003;421:753–6.
Etienne-Manneville S, Manneville JB, Nicholls S, Ferenczi MA, Hall A. Cdc42 and Par6–PKCζ regulate the spatially localized association of Dlg1 and APC to control cell polarization. J Cell Biol. 2005;170:895–901.
Fábián Á, Vereb G, Szöllősi J. The hitchhikers guide to cancer stem cell theory: markers, pathways and therapy. Cytometry A. 2013;83:62–71.
Fatehullah A, Appleton PL, Näthke IS. Cell and tissue polarity in the intestinal tract during tumourigenesis: cells still know the right way up, but tissue organization is lost. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013;368:20130014.
Feng W, Wu H, Chan LN, Zhang M. Par-3-mediated junctional localization of the lipid phosphatase PTEN is required for cell polarity establishment. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:23440–9.
Gao F, Zhang J, Wang X, Yang J, Chen D, Huff V, et al. WT1 functions in ovarian follicle development by regulating granulosa cell differentiation. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:333–41.
Gasch C, Ffrench B, O'Leary JJ, Gallagher MF. Catching moving targets: cancer stem cell hierarchies, therapy-resistance & considerations for clinical intervention. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:43.
Gómez-López S, Lerner R, Petritsch C. Asymmetric cell division of stem and progenitor cells during homeostasis and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71:575–97.
Gong F, Guo Y, Niu Y, Jin J, Zhang X, Shi X, et al. Epigenetic silencing of TET2 and TET3 induces an EMT-like process in melanoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:315–28.
Grände M, Franzen A, Karlsson JO, Ericson LE, Heldin NE, Nilsson M. Transforming growth factor-beta and epidermal growth factor synergistically stimulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) through a MEK-dependent mechanism in primary cultured pig thyrocytes. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:4227–366.
Grassian AR, Lin F, Barrett R, Liu Y, Jiang W, Korpal M, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations promote a reversible ZEB1/microRNA (miR)-200-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:42180–94.
Grifoni D, Garoia F, Bellosta P, Parisi F, De Biase D, Collina G, et al. aPKCζ cortical loading is associated with Lgl cytoplasmic release and tumor growth in Drosophila and human epithelia. Oncogene. 2007;26:5960–5.
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, Klein-Szanto AJ, van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W, et al. The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2172–8.
He H, Dai J, Xu Z, He W, Wang X, Zhu Y, et al. Fbxw7 regulates renal cell carcinoma migration and invasion via suppression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:3694–702.
He Z, Kannan N, Nemirovsky O, Chen H, Connell M, Taylor B, et al. BRCA1 controls the cell division axis and governs ploidy and phenotype in human mammary cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:32461–75.
Hernandez P, Tirnauer JS. Tumor suppressor interactions with microtubules: keeping cell polarity and cell division on track. Dis Model Mech. 2010;3:304–15.
Hoot KE, Lighthall J, Han G, Lu SL, Li A, Ju W. Keratinocyte-specific Smad2 ablation results in increased epithelial-mesenchymal transition during skin cancer formation and progression. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2722–32.
Huang L, Muthuswamy SK. Polarity protein alterations in carcinoma: a focus on emerging roles for polarity regulators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2010;20:41–50.
Humar B, Guilford P. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: a manifestation of lost cell polarity. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1151–7.
Iijima M, Devreotes P. Tumor suppressor PTEN mediates sensing of chemoattractant gradients. Cell. 2002;109:599–610.
Itoh N, Nakayama M, Nishimura T, Fujisue S, Nishioka T, Watanabe T, et al. Identification of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) as Par3 partners by proteomic analysis. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2010;67:297–308.
Ivaniutsin U, Chen Y, Mason JO, Price DJ, Pratt T. Adenomatous polyposis coli is required for early events in the normal growth and differentiation of the developing cerebral cortex. Neural Dev. 2009;4:3.
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R, Seither P, Kraut N, Capodiecci P, et al. Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1561–70.
Jędroszka D, Orzechowska M, Hamouz R, Górniak K, Bednarek AK. Markers of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reflect tumor biology according to patient age and Gleason score in prostate cancer. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0188842.
Ji X, Jin S, Qu X, Li K, Wang H, He H, et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 5C promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion through inhibition BMP7 expression. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:801.
Jiang H, Guo W, Liang X, Rao Y. Both the establishment and the maintenance of neuronal polarity require active mechanisms: critical roles of GSK-3beta and its upstream regulators. Cell. 2005;120:123–35.
Jiang YG, Luo Y, He DL, Li X, Zhang LL, Peng T, et al. Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Int J Urol. 2007;14(11):1034–9.
Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K, Niu B, Lu C, et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature. 2013;502:333–9.
Kim S, Ishidate T, Sharma R, Soto MC, Conte D Jr, Mello CC, et al. Wnt and CDK-1 regulate cortical release of WRM-1/β-catenin to control cell division orientation in early Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E918–E927927.
Kleyman M, Kabeche L, Compton DA. STAG2 promotes error correction in mitosis by regulating kinetochore–microtubule attachments. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:4225–333.
Klezovitch O, Fernandez TE, Tapscott SJ, Vasioukhin V. Loss of cell polarity causes severe brain dysplasia in Lgl1 knockout mice. Genes Dev. 2004;18:559–71.
Knauf JA, Sartor MA, Medvedovic M, Lundsmith E, Ryder M, Salzano M, et al. Progression of BRAF-induced thyroid cancer is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition requiring concomitant MAP kinase and TGFβ signaling. Oncogene. 2011;30:3153–62.
Knoblich JA. Mechanisms of asymmetric stem cell division. Cell. 2008;132:583–97.
Komiya Y, Habas R. Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis. 2008;4:68–75.
Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Li Y, Wang Z, Sethi S, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12445.
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Kim HR, et al. miR-200 regulates PDGF-D-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion, and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27:1712–21.
Lan M, Kojima T, Osanai M, Chiba H, Sawada N. Oncogenic Raf-1 regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition via distinct signal transduction pathways in an immortalized mouse hepatic cell line. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:2385–95.
Langhammer TS, Roolf C, Krohn S, Kretzschmar C, Huebner R, Rolfs A, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling interacts with Wnt/β-Catenin signaling but does not induce an accumulation of β-Catenin in the nucleus of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Blood. 2013;122:4886.
Langlois MJ, Bergeron S, Bernatchez G, Boudreau F, Saucier C, Perreault N, et al. The PTEN phosphatase controls intestinal epithelial cell polarity and barrier function: role in colorectal cancer progression. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e15742.
Laprise P, Chailler P, Houde M, Beaulieu JF, Boucher MJ, Rivard N. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase controls human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation by promoting adherens junction assembly and p38 MAPK activation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:8226–344.
Lee M, Vasioukhin V. Cell polarity and cancer-cell and tissue polarity as a non-canonical tumor suppressor. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:1141–50.
Lee MG, Villa R, Trojer P, Norman J, Yan KP, Reinberg D, et al. Demethylation of H3K27 regulates polycomb recruitment and H2A ubiquitination. Science. 2007;318:447–50.
Lehmann K, Janda E, Pierreux CE, Rytömaa M, Schulze A, McMahon M, et al. Raf induces TGFβ production while blocking its apoptotic but not invasive responses: a mechanism leading to increased malignancy in epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2610–22.
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2010;141:1117–34.
Lesko AC, Goss KH, Yang FF, Schwertner A, Hulur I, Onel K, et al. The APC tumor suppressor is required for epithelial cell polarization and three-dimensional morphogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1853:711–23.
Li X, Young NM, Tropp S, Hu D, Xu Y, Hallgrímsson B, et al. Quantification of shape and cell polarity reveals a novel mechanism underlying malformations resulting from related FGF mutations during facial morphogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:5160–72.
Löf-Öhlin ZM, Nyeng P, Bechard ME, Hess K, Bankaitis E, Greiner TU, et al. EGFR signalling controls cellular fate and pancreatic organogenesis by regulating apicobasal polarity. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:1313–25.
Lucs AV, Muller WJ, Muthuswamy SK. Shc is required for ErbB2-induced inhibition of apoptosis but is dispensable for cell proliferation and disruption of cell polarity. Oncogene. 2010;29:174–87.
Madero-Pérez J, Fdez E, Fernández B, Lara Ordóñez AJ, Blanca Ramírez M, Gómez-Suaga P, et al. Parkinson disease-associated mutations in LRRK2 cause centrosomal defects via Rab8a phosphorylation. Mol Neurodegener. 2018;13:3.
Magudia K, Lahoz A, Hall A. K-Ras and B-Raf oncogenes inhibit colon epithelial polarity establishment through up-regulation of c-myc. Cell Biol. 2012;198:185–94.
Main H, Radenkovic J, Jin SB, Lendahl U, Andersson ER. Notch signaling maintains neural rosette polarity. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e62959.
Malminen M, Peltonen S, Koivunen J, Peltonen J. Functional expression of NF1 tumor suppressor protein: association with keratin intermediate filaments during the early development of human epidermis. BMC Dermatol. 2002;2:10.
Markus SM, Lee WL. Microtubule-dependent path to the cell cortex for cytoplasmic dynein in mitotic spindle orientation. Bioarchitecture. 2011;1:209–15.
Maslova K, Kyriakakis E, Pfaff D, Frachet A, Frismantiene A, Bubendorf L, et al. EGFR and IGF-1R in regulation of prostate cancer cell phenotype and polarity: opposing functions and modulation by T-cadherin. FASEB J. 2015;29:494–507.
Maxwell CA, Benítez J, Gómez-Baldó L, Osorio A, Bonifaci N, Fernández-Ramires R, et al. Interplay between BRCA1 and RHAMM regulates epithelial apicobasal polarization and may influence risk of breast cancer. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1001199.
Mayor R, Theveneau E. The role of the non-canonical Wnt-planar cell polarity pathway in neural crest migration. Biochem J. 2014;457:19–26.
McCaffrey LM, Macara IG. Epithelial organization, cell polarity and tumorigenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2011;21:727–35.
McCain J. The MAPK (ERK) pathway: investigational combinations for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. P T. 2013;38:96–108.
Mendoza MC, Er EE, Blenis J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:320–8.
Meng Y, Cai KQ, Moore R, Tao W, Tse JD, Smith ER, et al. Pten facilitates epiblast epithelial polarization and proamniotic lumen formation in early mouse embryos. Dev Dyn. 2017;246:517–30.
Meyer AE, Gatza CE, How T, Starr M, Nixon AB, Blobe GC. Role of TGF-β receptor III localization in polarity and breast cancer progression. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25:2291–304.
Mirouse V, Swick LL, Kazgan N, St Johnston D, Brenman JE. LKB1 and AMPK maintain epithelial cell polarity under energetic stress. J Cell Biol. 2007;177:387–92.
Mizumoto A, Yamamoto K, Nakayama Y, Takara K, Nakagawa T, Hirano T, et al. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of epidermal growth factor receptor contributes to sunitinib resistance in human renal cell carcinoma cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;355:152–8.
Montesano R, Carrozzino F, Soulié P. Low concentrations of transforming growth factor-beta-1 induce tubulogenesis in cultured mammary epithelial cells. BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:7.
Moore JK, Cooper JA. Coordinating mitosis with cell polarity: Molecular motors at the cell cortex. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21:283–9.
Morikawa M, Derynck R, Miyazono K. TGF-β and the TGF-β family: context-dependent roles in cell and tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a021873.
Mu Y, Zang G, Engström U, Busch C, Landström M. TGFβ-induced phosphorylation of Par6 promotes migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2015;112:1223–311.
Mukherjee S, Kong J, Brat DJ. Cancer stem cell division: when the rules of asymmetry are broken. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24:405–16.
Murawala P, Tripathi MM, Vyas P, Salunke A, Joseph J. Nup358 interacts with APC and plays a role in cell polarization. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3113–222.
Muthuswamy SK. Regulation of epithelial cell polarity during carcinogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:S19.
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ, Brugge JS. ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:785–92.
Naishiro Y, Yamada T, Takaoka AS, Hayashi R, Hasegawa F, Imai K, et al. Restoration of epithelial cell polarity in a colorectal cancer cell line by suppression of beta-catenin/T-cell factor 4-mediated gene transactivation. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2751–8.
Nakano A, Takashima S. LKB1 and AMP-activated protein kinase: regulators of cell polarity. Genes Cells. 2012;17:737–47.
Narayan N, Massimi P, Banks L. CDK phosphorylation of the discs large tumour suppressor controls its localisation and stability. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:65–74.
Neumüller RA, Knoblich JA. Dividing cellular asymmetry: asymmetric cell division and its implications for stem cells and cancer. Genes Dev. 2009;23:2675–99.
Ngok SP, Lin WH, Anastasiadis PZ. Establishment of epithelial polarity-GEF who's minding the GAP? J Cell Sci. 2014;127:3205–15.
Nguyen AH, Tremblay M, Haigh K, Koumakpayi IH, Paquet M, Pandolfi PP, et al. Gata3 antagonizes cancer progression in Pten-deficient prostates. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:2400–10.
Oh SJ, Shin JH, Kim TH, Lee HS, Yoo JY, Ahn JY, et al. β-Catenin activation contributes to the pathogenesis of adenomyosis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Pathol. 2013;231:210–22.
O'Kane D, Jackson MV, Kissenpfennig A, Spence S, Damkat-Thomas L, et al. SMAD inhibition attenuates epithelial to mesenchymal transition by primary keratinocytes in vitro. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:497–503.
Okuda H, Saitoh K, Hirai S, Iwai K, Takaki Y, Baba M, et al. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein mediates ubiquitination of activated atypical protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:43611–7.
Olivier M, Hollstein M, Hainaut P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a001008.
Onishi K, Higuchi M, Asakura T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y. The PI3K-Akt pathway promotes microtubule stabilization in migrating fibroblasts. Genes Cells. 2007;12:535–46.
Ordinario E, Han HJ, Furuta S, Heiser LM, Jakkula LR, Rodier F, et al. ATM suppresses SATB1-induced malignant progression in breast epithelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e51786.
Orlando K, Guo W. Membrane organization and dynamics in cell polarity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1:a001321.
Ortega-Cava CF, Raja SM, Laiq Z, Bailey TA, Luan H, Mohapatra B, et al. Continuous requirement of ErbB2 kinase activity for loss of cell polarity and lumen formation in a novel ErbB2/Neu-driven murine cell line model of metastatic breast cancer. J Carcinog. 2011;10:29.
Ozawa Y, Nakamura Y, Fujishima F, Felizola SJ, Takeda K, Okamoto H, et al. Decreased expression of ARID1A contributes to infiltrative growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Med. 2015;235:185–91.
Ozdamar B, Bose R, Barrios-Rodiles M, Wang HR, Zhang Y, Wrana JL. Regulation of the polarity protein Par6 by TGFbeta receptors controls epithelial cell plasticity. Science. 2005;307:1603–9.
Pao GM, Zhu Q, Perez-Garcia CG, Chou SJ, Suh H, Gage FH, et al. Role of BRCA1 in brain development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E1240–E12481248.
Parisi T, Balsamo M, Gertler F, Lees JA. The Rb tumor suppressor regulates epithelial cell migration and polarity. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57:1640–50.
Park GB, Kim D. Insulin-like growth factor-1 activates different catalytic subunits p110 of PI3K in a cell-type-dependent manner to induce lipogenesis-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the regulation of ADAM10 and ADAM17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;439:199–21111.
Payankaulam S, Yeung K, McNeill H, Henry RW, Arnosti DN. Regulation of cell polarity determinants by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22879.
Perez-Mockus G, Schweisguth F. Cell polarity and notch signaling: linked by the E3 ubiquitin ligase neuralized? Bioessays. 2017;39(11):1700128.
Piek E, Moustakas A, Kurisaki A, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P. TGF-(beta) type I receptor/ALK-5 and Smad proteins mediate epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation in NMuMG breast epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1999;112:4557–688.
Pistore C, Giannoni E, Colangelo T, Rizzo F, Magnani E, Muccillo L, et al. DNA methylation variations are required for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by cancer-associated fibroblasts in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 2017;36:5551–66.
Pohl M, Radacz Y, Pawlik N, Schoeneck A, Baldus SE, Munding J, et al. SMAD4 mediates mesenchymal-epithelial reversion in SW480 colon carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:2603–13.
Ramadoss S, Chen X, Wang CY. Histone demethylase KDM6B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:44508–17.
Rancati G, Li R. Polarized cell growth: double grip by CDK1. Curr Biol. 2007;17:R600–R603603.
Regad T. Targeting RTK signaling pathways in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2015;7:1758–84.
Rich JN. Cancer stem cells: understanding tumor hierarchy and heterogeneity. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:S2–7.
Richardson RB. p53 mutations associated with aging-related rise in cancer incidence rates. Cell Cycle. 2013;12:2468–78.
Royer C, Lu X. Epithelial cell polarity: a major gatekeeper against cancer? Cell Death Differ. 2011;18:1470–7.
Russell R, Perkhofer L, Liebau S, Lin Q, Lechel A, Feld FM, et al. Loss of ATM accelerates pancreatic cancer formation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7677.
Sasaki AT, Chun C, Takeda K, Firtel RA. Localized Ras signaling at the leading edge regulates PI3K, cell polarity, and directional cell movement. J Cell Biol. 2004;167:505–18.
Schermer B, Ghenoiu C, Bartram M, Müller RU, Kotsis F, Höhne M, et al. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein controls ciliogenesis by orienting microtubule growth. J Cell Biol. 2006;175:547–54.
Schoenenberger CA, Zuk A, Kendall D, Matlin KS. Multilayering and loss of apical polarity in MDCK cells transformed with viral K-ras. J Cell Biol. 1991;112:873–89.
Schramm K, Krause K, Bittroff-Leben A, Goldin-Lang P, Thiel E, Kreuser ED. Activated K-ras is involved in regulation of integrin expression in human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2000;87:155–64.
Sciacovelli M, Frezza C. Metabolic reprogramming and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. FEBS J. 2017;284:3132–44.
Sell S. On the stem cell origin of cancer. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:2584–494.
Sever R, Brugge JS. Signal transduction in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5:a006098.
Shafer MER, Nguyen AHT, Tremblay M, Viala S, Béland M, Bertos NR, et al. Lineage specification from prostate progenitor cells requires gata3-dependent mitotic spindle orientation. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8:1018–31.
Shen L, Chen L, Wang Y, Jiang X, Xia H, Zhuang Z. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes brain metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. J Neurooncol. 2015;121:101–8.
Shukla S, Sinha S, Khan S, Kumar S, Singh K, Mitra K, et al. Cucurbitacin B inhibits the stemness and metastatic abilities of NSCLC via downregulation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling axis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21860.
Siller KH, Doe CQ. Spindle orientation during asymmetric cell division. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:365–74.
Smith CL, Baek ST, Sung CY, Tallquist MD. Epicardial-derived cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and fate specification require PDGF receptor signaling. Circ Res. 2011;108:e15–26.
Song G, Zhang H, Chen C, Gong L, Chen B, Zhao S, et al. miR-551b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer by inhibiting ERBB4 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8:45725–35.
Stehbens SJ, Ju RJ, Adams MN, Perry SR, Haass NK, Bryant DM, et al. FGFR2-activating mutations disrupt cell polarity to potentiate migration and invasion in endometrial cancer cell models. J Cell Sci. 2018;131:jcs213678.
Strippoli R, Loureiro J, Moreno V, Benedicto I, Pérez Lozano ML, Barreiro O, et al. Caveolin-1 deficiency induces a MEK-ERK1/2-Snail-1-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis during peritoneal dialysis. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:102–23.
Sun M, Guo X, Qian X, Wang H, Yang C, Brinkman KL, et al. Activation of the ATM-Snail pathway promotes breast cancer metastasis. J Mol Cell Biol. 2012;4:304–15.
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35:600–4.
Takao C, Morikawa A, Ohkubo H, Kito Y, Saigo C, Sakuratani T, et al. Downregulation of ARID1A, a component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, in breast cancer. J Cancer. 2017;8:1–8.
Tan M, Yu D. Molecular mechanisms of erbB2-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:119–29.
Tanabe S, Aoyagi K, Yokozaki H, Sasaki H. Molecular network pathway of ERBB in diffuse-type gastric cancer: mesenchymal stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Epigenet. 2018;4:13.
Tang M, Miyamoto Y, Huang EJ. Multiple roles of beta-catenin in controlling the neurogenic niche for midbrain dopamine neurons. Development. 2009;136:2027–38.
Tang Y, Katuri V, Srinivasan R, Fogt F, Redman R, Anand G, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta suppresses nonmetastatic colon cancer through Smad4 and adaptor protein ELF at an early stage of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4228–377.
Tanwar PS, Kaneko-Tarui T, Zhang L, Teixeira JM. Altered LKB1/AMPK/TSC1/TSC2/mTOR signaling causes disruption of Sertoli cell polarity and spermatogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:4394–405.
Terashima M, Ishimura A, Wanna-Udom S, Suzuki T. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by KDM6A histone demethylase in lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490:1407–13.
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH, Moustakas A. TGF-β and the Smad signaling pathway support transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell transition. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:1987–2002.
Valkenburg KC, Graveel CR, Zylstra-Diegel CR, Zhong Z, Williams BO. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in normal and cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 2011;3:2050–79.
Veikkolainen V, Naillat F, Railo A, Chi L, Manninen A, Hohenstein P, et al. ErbB4 modulates tubular cell polarity and lumen diameter during kidney development. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:112–22.
Viloria-Petit AM, David L, Jia JY, Erdemir T, Bane AL, Pinnaduwage D, et al. A role for the TGFbeta-Par6 polarity pathway in breast cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:14028–33.
von Stein W, Ramrath A, Grimm A, Müller-Borg M, Wodarz A. Direct association of Bazooka/PAR-3 with the lipid phosphatase PTEN reveals a link between the PAR/aPKC complex and phosphoinositide signaling. Development. 2005;132:1675–86.
Voon DC, Wang H, Koo JK, Chai JH, Hor YT, Tan TZ, et al. EMT-induced stemness and tumorigenicity are fueled by the EGFR/Ras pathway. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e70427.
Voorneveld PW, Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Liv N, Zonnevylle AC, Hoogenboom JP, et al. Loss of SMAD4 alters BMP signaling to promote colorectal cancer cell metastasis via activation of Rho and ROCK. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:196–208.
Waghmare I, Page-McCaw A. Wnt signaling in stem cell maintenance and differentiation in the Drosophila germarium. Genes (Basel). 2018;9(3):127.
Wang H, Meyer CA, Fei T, Wang G, Zhang F, Liu XS. A systematic approach identifies FOXA1 as a key factor in the loss of epithelial traits during the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:680.
Wang H, Zhong J, Wu C, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zou X, et al. Stromal antigen 2 functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:917–25.
Wang W, Friedland SC, Guo B, O'Dell MR, Alexander WB, Whitney-Miller CL, et al. ARID1A, a SWI/SNF subunit, is critical to acinar cell homeostasis and regeneration and is a barrier to transformation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the pancreas. Gut. 2019;68(7):1245–58.
Wang X, Dong B, Zhang K, Ji Z, Cheng C, Zhao H, et al. E-cadherin bridges cell polarity and spindle orientation to ensure prostate epithelial integrity and prevent carcinogenesis in vivo. PLoS Genet. 2018;14:e1007609.
Wang X, Nie J, Zhou Q, Liu W, Zhu F, Chen W, et al. Downregulation of Par-3 expression and disruption of Par complex integrity by TGF-beta during the process of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in rat proximal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1782:51–9.
Wang X, Wang S, Li X, Jin S, Xiong F, Wang X. The critical role of EGF-β-catenin signaling in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human glioblastoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:2781–9.
Wang XN, Li ZS, Ren Y, Jiang T, Wang YQ, Chen M, et al. The Wilms tumor gene, Wt1, is critical for mouse spermatogenesis via regulation of sertoli cell polarity and is associated with non-obstructive azoospermia in humans. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003645.
Warner DR, Pisano MM, Roberts EA, Greene RM. Identification of three novel Smad binding proteins involved in cell polarity. FEBS Lett. 2003;539:167–73.
Waters R. Maintaining genome integrity. EMBO Rep. 2006;7:377–81.
Whitaker AT, Berthet E, Cantu A, Laird DJ, Alliston T. Smad4 regulates growth plate matrix production and chondrocyte polarity. Biol Open. 2017;6:358–64.
Williams E, Villar-Prados A, Bowser J, Broaddus R, Gladden AB. Loss of polarity alters proliferation and differentiation in low-grade endometrial cancers by disrupting Notch signaling. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(12):e0189081.
Williams T, Brenman JE. LKB1 and AMPK in cell polarity and division. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:193–8.
Witte D, Otterbein H, Förster M, Giehl K, Zeiser R, Lehnert H, et al. Negative regulation of TGF-β1-induced MKK6-p38 and MEK-ERK signalling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Rac1b. Sci Rep. 2017;7:17313.
Wodarz A, Näthke I. Cell polarity in development and cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:1016–24.
Wu N, Wei J, Wang Y, Yan J, Qin Y, Tong D, et al. Ribosomal L22-like1 (RPL22L1) promotes ovarian cancer metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0143659.
Wu ZQ, Brabletz T, Fearon E, Willis AL, Hu CY, Li XY, et al. Canonical Wnt suppressor, Axin2, promotes colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:11312–7.
Xian W, Pappas L, Pandya D, Selfors LM, Derksen PW, de Bruin M, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-transformed mammary epithelial cells are dependent on RSK activity for growth and survival. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2244–51.
Xian W, Schwertfeger KL, Rosen JM. Distinct roles of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 and 2 in regulating cell survival and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:987–1000.
Xiong Y, Wang J, Zhu H, Liu L, Jiang Y. Chronic oxymatrine treatment induces resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:967–76.
Xue G, Hemmings BA. PKB/Akt–dependent regulation of cell motility. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:393–404.
Yamashita Y, Yuan H, Cheng J, Hunt AJ. Polarity in stem cell division: asymmetric stem cell division in tissue homeostasis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a001313.
Yan HB, Wang XF, Zhang Q, Tang ZQ, Jiang YH, Fan HZ, et al. Reduced expression of the chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A enhances gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via downregulation of E-cadherin transcription. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:867–76.
Yan W, Cao QJ, Arenas RB, Bentley B, Shao R. GATA3 inhibits breast cancer metastasis through the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:14042–511.
Yan Z, Chen M, Perucho M, Friedman E. Oncogenic Ki-ras but not oncogenic Ha-ras blocks integrin beta1-chain maturation in colon epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30928–36.
Yang H, Lu X, Liu Z, Chen L, Xu Y, Wang Y, et al. FBXW7 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastatic potential of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:6310–25.
Yap YS, McPherson JR, Ong CK, Rozen SG, Teh BT, Lee AS, et al. The NF1 gene revisited: from bench to bedside. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5873–92.
Yeom E, Hong ST, Choi KW. Crumbs and XPD in mitosis. Oncoscience. 2015;2:821–2.
Yokota Y, Kim WY, Chen Y, Wang X, Stanco A, Komuro Y, et al. The adenomatous polyposis coli protein is an essential regulator of radial glial polarity and construction of the cerebral cortex. Neuron. 2009;61:42–56.
Yu JS, Cui W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143:3050–60.
Zhang L, Zhang W, Li Y, Alvarez A, Li Z, Wang Y, et al. SHP-2-upregulated ZEB1 is important for PDGFRα-driven glioma epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in mice and humans. Oncogene. 2016;35:5641–52.
Zhang Y, Yan W, Chen X. Mutant p53 disrupts MCF-10A cell polarity in three-dimensional culture via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16218–28.
Zhang Y, Zhou R, Qu Y, Shu M, Guo S, Bai Z. Lipoamide inhibits NF1 deficiency-induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition in murine schwann cells. Arch Med Res. 2017;48:498–505.
Zhang Z, Qu J, Zheng C, Zhang P, Zhou W, Cui W, et al. Nrf2 antioxidant pathway suppresses Numb-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition during pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:83.
Zhou W, Mo X, Cui W, Zhang Z, Li D, Li L, et al. Nrf2 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing snail expression during pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38646.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Editor: Manoj Prasad.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grifone, T.J. Cell polarity and oncogenesis: common mutations contribute to altered cellular polarity and promote malignancy. Nucleus 63, 91–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-020-00313-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-020-00313-4