Abstract
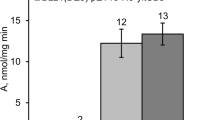
Expression of modified xynA gene fragments in Escherichia coli BL21 was studied, using the complete xynA gene from Bacillus subtilis BE-91 as the positive control. The technical workflow consisted of the following steps: (1) predicting protein structures relative to the xynA gene; (2) designing primers for modifiers; (3) amplifying the modifiers; (4) integrating the modifiers with the pET-28a(+) vector; (5) transferring the recombinant plasmids into E. coli BL21; (6) evaluating and analyzing the expression of modified cells. The results were: (1) the xynA gene from BE-91 with the untranslated region deleted on both ends was able to promote XynA activity by 28.9 %; (2) deletion of the 1- to 16-amino acid (AA) coding sequence in the open reading frame on the 5′-end, deletion of the 209- to 213-AA fragment on the 3′-end and deletion of the 20 AA on both ends could promote XynA activity by 27.2, 27.7 and 24.0 %,respectively; (3) deletion of the 1- to 29-AA fragment on the 5′-end and deletion of the 197- to 213-AA fragment on the 3′-end could reduce XynA activity dramatically by 95.6 and 74.8 %, respectively; (4) inactivation factors of XynA would be either the first β-fold and the hydrophilic structure domain or the last two α-screws and the seventeenth turn region. The results mean that any deletion in the catalytic domain would lead to a decline or inactivation in XynA activity while the deletion of any sequence outside the catalytic domain could effectively promote XynA activity, as such sequences are unnecessary for XynA function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MK, Fukumura M, Sakano K, Karita S, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (1999) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene encoding the Clostridium stercorarium xylanase C in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:1596–1604
Bao YH, Liu WF, Dong ZY (2008) Studies on the over-expression of alkali-tolerant xylanase in Bacillus Pumilus. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol 8:37–43
Bernier R, Driguez H, Desrochers M (1983) Molecular cloning of a Bacillus subtilis xylanase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene 26:59–65
Chen CC, Westpheling J (1998) Partial characterization of the Streptomyces lividans xlnB promoter and its use for expression of a thermostable xylanase from Thermotoga maritima. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4217–4225
Deuerling E, Paeslack B, Schumann W (1995) The ftsH gene of Bacillus subtilis is transiently induced after osmotic and temperature upshift. J Bacteriol 177:4105–4112
Dwivedi PP, Gibbs MD, Saul DJ, Bergquist PL (1996) Cloning, sequencing and over expressionin Escherichia coli of a xylanase gene, xynA from the thermophilic bacterium Rt8B.4 genus Caldicellulosiruptor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:86–93
Ferreira LM, Durrant AJ, Hall J, Hazlewoodt GP, Gilbert HJ (1990) Spatial separation of protein domains is not necessary for catalytic activity or substrate binding in a xylanase. Biochem J 269:261–264
Grange DC, Pretorius IS, Zyl WH (1996) Expression of a Trichoderma reesei beta-xylanase gene (XYN2) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1036–1044
Grepinet O, Chebrou MC, Beguin P (1988) Nucleotide sequence and deletion analysis of the xylanase gene (xynZ) of Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol 170:4582–4588
Guo G, Liu ZC, Xu JF, Liu JP, Dai XY, Xie DP, Peng KQ, Feng XY, Duan SW, Zheng K, Cheng LF, Fu YG (2011) Purification and characterization of a xylanase from Bacillus subtilis isolated from the degumming line. J Basic Microb 51:1–10
Jialin S, Tetsu K, Tetsuya K, Shuichi K, Kazuo S, Kunio O (1997) High expression of the xylanase B gene from Clostridium stercorarium in tobacco cell. J Ferment Bioeng 84:219–223
Kakar S, Burgart LJ, Thibodeau SN, Rabe KG, Petersen GM, Goldberg RM, Lindor NM (2003) Frequency of loss of hMLH1 expression in colorectal carcinoma increases with advancing age. Cancer 97:1421–1427
Lee Y, Lowe SE, Henrissat B, Zeikusl JG (1993) Characterization of the active site and thermostability regions of endoxylanase from Thermoanaerobacterium. J Bacteriol 175:5890–5898
Liu ZC (2007) Review and prospect of researches of microorganism engineering for bast fibers extracting. Sci Agric Sin 40(supplement):363–367
Liu ZC, Dai XY, Zhang JZ, Xu JF, Duan SW, Zheng K, Feng XY, Cheng LF, Shi J (2011) Screening of a xylanase high-producing strain and its rapid separation and purification. Ann Microbiol 61:901–906
Mach-Aigner AR, Pucher ME, Mach RL (2010) D-Xylose as a repressor or inducer of xylanase expression in Hypocreajecorina (Trichodermareesei). Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1770–1776
Matsumoto K, Satoh T, Irie A, Ishii J, Kuwao S, Iwamura M, Baba S (2008) Loss expression of uroplakin III is associated with clinicopathologic features of aggressive bladder cancer. Urology 72:444–449
Ogasawara W, Shida Y, Furukawa T, Shimada R, Nakagawa S, Kawamura M, Yagyu T, Kosuge A, Xu J, Nogawa M, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2006) Cloning, functional expression and promoter analysis of xylanase III gene from Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:995–1003
Rodríguez S, Santamaría RI, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Díaz M (2005) Identification of the sequences involved in the glucose-repressed transcription of the Streptomyces halstedii JM8 xysA promoter. Gene 351:1–9
Shin HD, McClendon S, Vo T, Chen RR (2010) Escherichia coli binary culture engineered for direct fermentation of hemicellulose to a biofuel. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:8150–8159
Stec-Michalska K, Antoszczyk S, Klupinska G, Nawrot B (2005) Loss of FHIT expression in gastric mucosa of patients with family histories of gastric cancer and Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 11:17–21
Tanjore H, Kalluri R, Ikeda K, Ishikawa N, Egami H, Nakao M, Sado Y, Ninomiya Y, Baba H (2006) Loss of expression of type IV collagen α5 and α6 chains in colorectal cancer associated with the hypermethylation of their promoter region. Am J Pathol 168(715–717):856–865
Waldeck J, Meyer-Rammes H, Wieland S, Feesche J, Maurer KH, Meinhardt F (2007) Targeted deletion of genes encoding extracellular enzymes in Bacillus licheniformis and the impact on the secretion capability. J Biotechnol 130:124–132
Wang H, Wang TH (2002) Cloning and sequence analysis of xylanase I gene from Trichoderma reesei and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Shandong Inst Light Ind (Nat Sci Ed) 3:13–16
Wang XS, Liu ZC, Li B, Feng XY, Duan SW, Zheng K, Cheng LF (2009) Study on the construction of special compound enzyme engineering strain for bio-extracting herbaceous fiber. J Anhui Agric Sci 37:3928–3930
Yang RCA, Mackenzie CR, Bilous D, Narang SA (1989) Hyperexpression of a Bacillus circulans xylanase gene in Escherichia coli and characterization of the gene product. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1192–1195
Zhang YX, Liu ZC, Chen XB (2007) Cloning and expression of a mannanase gene from Erwinia carotovora CXJZ95-198. Ann Microbiol 57:623–628
Zheng RJ (2006) Homologous expression and characterization of the xylanase from Aspergillus niger. M.Sc thesis. Tongji University, Shanghai
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by a grant from the National Project for High-technology Research (2006AA02Z249) and also funded by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-19-E24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z. Liu and J. Xu contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Xu, J., Duan, S. et al. Expression of modified xynA gene fragments from Bacillus subtilis BE-91. Ann Microbiol 64, 139–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0642-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0642-9