Abstract
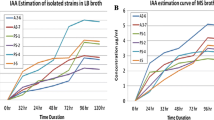
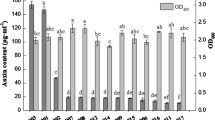
Auxin production and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase of rhizobacteria are very important plant growth promoting attributes. In the present study, Pseudomonas strains exhibiting these traits were evaluated for their growth promoting effects on Vigna mungo (L.). Colorimetric analysis revealed that Pseudomonas alcaliphila AvR-2, Pseudomonas sp. AvH-4 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa As-17, respectively, produced 40.30, 32.90 and 36.50 μg auxin ml−1 in the presence of 6% of glucose, sucrose and fructose. Similarly, Pseudomonas sp. AvH-4 expressed highest ACC-deaminase activity (355 nmol h−1) as compared to P. alcaliphila AvR-2 (115 nmol h−1) and P. aeruginosa As-17 (197 nmol h−1). Antibiotic sensitivity pattern of rhizobacteria also showed resistance against oxytetracyclin, erythromycin and penicillin. Inoculation of V. mungo with rhizobacteria positive for auxin production and ACC-deaminase activity enhanced plant growth in pot trials. In laboratory experiments (under axenic conditions), P. aeruginosa As-17 was the most effective at enhancing shoot length (70.90%), seedling fresh weight (185.70%) and root length (84.20%). Pot trials conducted under natural environmental conditions showed up to 45.60, 54.10 and 72.50% increases in shoot length, root length and number of pods, respectively, over control.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali B, Sabri AN, Ljung K, Hasnain S (2009a) Quantification of indole-3-acetic acid from plant associated Bacillus spp. and their phytostimulatory effect on Vigna radiata (L.). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:519–526
Ali B, Sabri AN, Ljung K, Hasnain S (2009b) Auxin production by plant associated bacteria: impact on endogenous IAA content and growth of Triticum aestivum L. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:542–547
Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Bleecker AB, Kende H (2000) Ethylene: a gaseous signal molecule in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:1–18
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2002) Microbiology: a laboratory manual. Pearson, Signapore
Dworkin M, Foster JW (1958) Experiments with some microorganisms which utilize ethane and hydrogen. J Bacteriol 75:592–603
Egamberdieva D, Kamilova F, Validov S, Gafurova L, Kucharova Z, Lugtenberg B (2008) High incidence of plant growth-stimulating bacteria associated with the rhizosphere of wheat grown on salinated soil in Uzbekistan. Environ Microbiol 10:1–9
Glick BR (2005) Modulation of plant ethylene levels by bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 251:1–7
Grichko VP, Glick BR (2001) Amelioration of flooding stress by ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:11–17
Holden N, Pritchard L, Toth I (2009) Colonization outwith the colon: plants as an alternate environment reservoir for human pathogenic enterobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:689–703
Ji P, Wilson M (2002) Assessment of the importance of similarity in carbon source utilization profiles between the biological control agent and the pathogen in biological control of bacterial speck of tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4383–4389
Kamilova F, Kravchenko LV, Shaposhnikov AI, Azarova T, Makarova N, Lugtenberg B (2006) Organic acids, sugars, and L-tryptophan in exudates of vegetables growing on stonewool and their effects on activities of rhizosphere bacteria. Mol Plant Microb Int 19:250–256
Kravchenko LV, Azarova TS, Makarova NM, Tikhonovich IA (2004) The effect of tryptophan present in plant root exudates on the phytostimulating activity of rhizobacteria. Microbiology 73:156–158
Leveau JHJ, Lindow SE (2005) Utilization of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid for growth by Pseudomonas putida strain 1290. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2365–2371
Ma W, Guinel FC, Glick BR (2003) Rhizobium leguminosarum Biovar viciae 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase promotes nodulation of pea plants. Appl Environ Micrbiol 69:4396–4402
Malhotra M, Srivastava S (2009) Stress-responsive indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis by Azospirillum brasilense SM and its ability to modulate plant growth. Eur J Soil Biol 45:73–80
Nagatsu T, Yagi K (1966) A simple assay of monoamine oxidase and D-amino acid oxidase by measuring ammonia. J Biochem 60:219–221
Ona O, Impe JV, Prinsen E, Vnaderleyden J (2005) Growth and indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis of Azospirillum brasilense Sp 245 is environmentally controlled. FEMS Microbiol Lett 246:125–132
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Physiol 118:10–15
Raddadi N, Cherif A, Boudabous A, Daffonchio D (2008) Screening of plant growth promoting traits of Bacillus thuringiensis. Ann Microbiol 58:47–52
Saravanakumar D, Samiyappan R (2007) ACC deaminase from Pseudomonas fluorescens mediated saline resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogea) plants. J Appl Microbiol 102:1283–1292
Shahroona B, Arshad M, Zahir ZA (2006) Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria containing ACC-deaminase on maize (Zea mays L.) growth under axenic conditions and on nodulation in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Lett Appl Microbiol 42:155–159
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448
Tang WY, Borner J (1979) Enzymes involved in synthesis and breakdown of indoleacetic acid. In: Paech K, Tracey MV (eds) Modern methods of plant analysis, vol. 7. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 238–241
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005) Auxin: regulation, action and interaction. Ann Bot 95:707–735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noreen, S., Ali, B. & Hasnain, S. Growth promotion of Vigna mungo (L.) by Pseudomonas spp. exhibiting auxin production and ACC-deaminase activity. Ann Microbiol 62, 411–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0277-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0277-7