Abstract
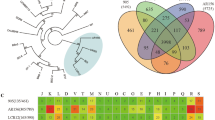
In the study, a previously isolated plant beneficial endophytic B. cereus CaB1 was selected for the detailed analysis by whole-genome sequencing. The WGS has generated a total of 1.9 GB high-quality data which was assembled into a 5,257,162 bp genome with G + C content of 35.2%. Interestingly, CaB1 genome was identified to have 40 genes with plant beneficial functions by bioinformatic analysis. At the same time, it also showed the presence of various virulence factors except the diarrhoeal toxin, cereulide. Upon comparative analysis of CaB1 with other B. cereus strains, it was found to have random distributions of virulence and plant growth promoting traits. The core genome phylogenetic analysis of the Bacillus cereus strains further showed the close relation of plant associated strains with isolates from spoiled food products. The observed genome flexibility of B. cereus thus indicates its ability to make use of diverse hosts, which can result either in beneficial or harmful effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akhtyamova N (2013) Human pathogens—the plant and useful endophytes. J Med Microbiol Diagn. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0703.1000e121
Akter N, Hussain Z, Trankler J, Parkpian P (2002) Hospital waste management and it’s probable health effect: a lesson learned from Bangladesh. Indian J Environ Health 44:124–137
Al-Kharousi ZS, Guizani N, Al-Sadi AM et al (2016) Hiding in fresh fruits and vegetables: opportunistic pathogens may cross geographical barriers. Int J Microbiol 2016:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4292417
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best A et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bai Y, D’Aoust F, Smith DL, Driscoll BT (2002) Isolation of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus strains from soybean root nodules. Can J Microbiol 48:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1139/w02-014
Bishnoi U (2015) PGPR interaction: an ecofriendly approach promoting the sustainable agriculture system. In: Advances in botanical research, vol 75. Academic Press, pp 81–113
Bottone EJ (2010) Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:382–398. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00073-09
Briggs L, Crush J, Ouyang L, Sprosen J (2013) Neotyphodium endophyte strain and superoxide dismutase activity in perennial ryegrass plants under water deficit. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1513–1520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1192-7
Chaudhry V, Patil PB (2016) Genomic investigation reveals evolution and lifestyle adaptation of endophytic Staphylococcus epidermidis. Sci Rep 6:19263. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19263
Floriştean V, Cretu C, Carp-Cărare M (2007) Bacteriological characteristics of Bacillus cereus isolates from poultry. Bull Univ Agric Sci Vet Med Cluj Napoca Vet Med 64:1–2
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Polyamines and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Signal Behav 5:26–33. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.1.10291
Granum PE, Lund T (2006) Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 157:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb12776.x
Hollants J, Leroux O, Leliaert F et al (2011) Who is in there? Exploration of endophytic bacteria within the siphonous green seaweed bryopsis (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). PLoS ONE 6(10):e26458. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026458
Jasim B, Geethu PR, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan EK (2015) Effect of endophytic Bacillus sp. from selected medicinal plants on growth promotion and diosgenin production in Trigonella foenum-graecum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 122:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0788-1
Mossel DAA, Koopman MJ, Jongerius E (1966) The enumeration of Bacillus cereus in foods. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 32:453. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02097503
Naranjo M, Denayer S, Botteldoorn N et al (2011) Sudden death of a young adult associated with Bacillus cereus food poisoning. J Clin Microbiol 49:4379–4381
Nassar AH, El-Tarabily KA, Sivasithamparam K (2003) Growth promotion of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by a polyamine-producing isolate of Streptomyces griseoluteus. Plant Growth Regul 40:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024233303526
Niu D-D, Liu H-X, Jiang C-H et al (2011) The plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus cereus AR156 induces systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana by simultaneously activating salicylate- and jasmonate/ethylene-dependent signaling pathways. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-09-10-0213
Okeke IN, Lamikanra A, Edelman R (1999) Socioeconomic and behavioral factors leading to acquired bacterial resistance to antibiotics in developing countries. Emerg Infect Dis 5:18–27. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0501.990103
Reinhold-Hurek B, Hurek T (2011) Living inside plants: bacterial endophytes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2011.04.004
Rosenblueth M, Martínez-Romero E (2006) Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19:827–837. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-19-0827
Santoyo G, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, del Carmen O-M, Glick BR (2016) Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol Res 183:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
Schikora A, Schenk ST, Hartmann A (2016) Beneficial effects of bacteria-plant communication based on quorum sensing molecules of the N-acyl homoserine lactone group. Plant Mol Biol 90:605–612
Takeno A, Okamoto A, Tori K et al (2012) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus cereus NC7401, which produces high levels of the emetic toxin cereulide. J Bacteriol 194:4767–4768
Treangen TJ, Ondov BD, Koren S et al (2014) The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol 15(11):1–15
Zhao Y, Wu J, Yang J et al (2012) PGAP: pan-genomes analysis pipeline. Bioinformatics 28:416–418. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr655
Acknowledgements
Acknowledging Miss. Jilna Babu and Miss. Celene Francis research assistants at Center for Bioinformatics, School of Biosciences, Mahatma Gandhi University.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: conceptualization, data analysis, writing; MP: data analysis, SBM: writing, CGI: writing, CSB: data analysis, AK: Software and whole genome analysis; RB: software and whole genome analysis; SNS: conceptualization, review and editing; EKR: conceptualization, supervision and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This is to declare that the authors have no conflict of interest on this research work.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sreejith, S., Paul, M., Mol, S.B. et al. Genomic insight into the environmental adaptations and toxigenic features of endophytic Bacillus cereus CaB1 isolated from Capsicum annuum L.. 3 Biotech 13, 68 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03463-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03463-9