Abstract
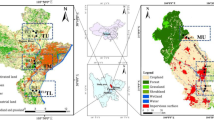
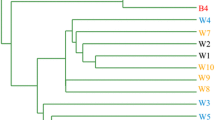
Perchlorate is a refractory and mobile contaminant that is wildly distributed in surface water, and due to its tremendous inhibitory effect on mammalian thyroid function, it has gained much attention in recent years. Numerous studies have focused on environmental detection of perchlorate, especially in water. However, less attention has been paid to the effects of perchlorate on the composition of the microbial community in rivers. Upstream of the Qingyi River, an important source of drinking water for local residents, there are two perchlorate manufacturers. In this study, we selected eight study sites from upstream to downstream of the Qingyi River, including sites located upstream and downstream of the perchlorate manufacturers. Our results indicated that perchlorate was detected in all sites except for QYR2, QYR3, and QYR10. The concentration of perchlorate in the five study sites was much higher than the reference dose proposed by the National Academy of Science, and ranged from 187 to 9647.00 μg/L. We utilized 16S rDNA high throughput sequencing to analyze changes in the composition of the microbial community, based on the Illumina 2 × 250 MiSeq platform. The results showed that, when microbial communities were exposed to high concentration of perchlorate, there was an increase in the ratio of Betaproteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, and Saccharibacteria in the microbial community along with a decrease in the ratio of Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobia, and Gammaproteobacteria. Our study has provided a theoretical basis for the alteration of the microbial community caused by the perchlorate pollution, which maybe have a truly important impact on the quality of groundwater.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Achenbach LA, Michaelidou U, Bruce RA, Fryman J, Coates JD (2001) Dechloromonas agitata gen. nov., sp. nov. and Dechlorosoma suillum gen. nov., sp. nov., two novel environmentally dominant (per)chlorate-reducing bacteria and their phylogenetic position. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:527–533
Archilla LI, Marin I, Amils R (2001) Microbial community composition and ecology of an acidic aquatic environment: the Tinto River, Spain. Microb Ecol 41:20–35
Balaji RT, Greta JO, Ken AR, Srinath R, Renee MS, Bridget RS, David AS, Michelle AW, Walvoord AWJ (2007) Widespread natural perchlorate in unsaturated zones of the southwest United States. Environ Sci Tech 41(13):4522–4528
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10(1):57–59
Bulaeva E, Lanctot C, Reynolds L, Trudeau VL, Navarro-Martin L (2015) Sodium perchlorate disrupts development and affects metamorphosis- and growth-related gene expression in tadpoles of the wood frog (Lithobates sylvaticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 222:33–43
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D et al (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Coates JD, Achenbach LA (2004) Microbial perchlorate reduction: rocket-fuelled metabolism. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:569–580
Coates JD, Michaelidou U, Bruce RA, O'Connor SM, Crespi JN, Achenbach LA (1999) Ubiquity and diversity of dissimilatory (per)chlorate-reducing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5234–5241
Cotner JB, Biddanda BA (2002) Small players, large role: microbial influence on biogeochemical processes in pelagic aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 5:105–121
Edgar R (2004) Muscle: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10(10):996–998
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Fisher J, McLanahan E (2008) Toxicol Lett 180:S182
Flood DE, Langlois VS (2014) Crosstalk between the thyroid hormone and androgen axes during reproductive development in Silurana tropicalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 203:232–240
Gessner MO, Swan CM, Dang CK, Mckie BG, Bardget RD et al (2010) Diversity meets decomposition. Trends Ecol Evol 25:372–380
Goleman WL, Carr JA (2006) Contribution of ammonium ions to the lethality and antimetamorphic effects of ammonium perchlorate. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1060–1067
Gunajit G, Priyadarshini D, Pompi SSB, Ramkrishna S, Robin CB, Madhumita B (2017) Diversity and functional properties of acid-tolerant bacteria isolated from tea plantation soil of Assam. 3 Biotech 7:229
Huang XF (2000) Survey, observation and analysis of lake ecology. China Standard Press, Beijing
Kang N, Anderson TA, Jackson WA (2006) Photochemical formation of perchlorate from aqueous oxychlorine anions. Anal Chim Acta 567(1):48–56
Leung AM, Pearce EN, Braverman LE (2010) Perchlorate, iodine and the thyroid. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 24(1):133–141
Liu TH, Yang ZS, Zhang XM, Han NP, Yuan JL, Cheng Y (2017) 16S rDNA analysis of the effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on pulmonary and intestinal flora. 3 Biotech 7:370
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27(21):2957–2963
Massimo Tonacchera AP, Antonio D, Eleonora F, Patrizia A, Vi P, Ferruccio S, Kenny C, John G (2004) Relative potencies and additivity of perchlorate, thiocyanate, nitrate, and iodide on the inhibition of radioactive iodide uptake by the human sodium iodide symporter. Thyroid 14(12):1012–1019
NAS (National Academy of Sciences) (2005) Health implications of perchlorate ingestion. National Academies Press, Washington
Nold S, Zwart G (1998) Patterns and governing forces in aquatic microbial communities. Aquat Ecol 32:17–35. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009991918036
Opitz R, Schmidt F, Braunbeck T, Wuertz S, Kloas W (2009) Perchlorate and ethylenethiourea induce different histological and molecular alterations in a non-mammalian vertebrate model of thyroid goitrogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 298(1–2):101–114
Poghosyan A, Sturchio NC, Morrison CG, Beloso AD Jr, Guan Y, Eiler JM, Jackson WA, Hatzinger PB (2014) Perchlorate in the great Lakes: isotopic composition and origin. Environ Sci Technol 48(19):11146–11153
Rajagopalan S, Anderson T, Cox S, Harvey G, Cheng Q, Jackson WA (2009) Perchlorate in wet deposition across north America. Environ Sci Tech 43(2):616–622
Srinivasan R, Sorial GA (2009) Treatment of perchlorate in drinking water: a critical review. Sep Purif Technol 69:7–21
Tomassini V (2010) Trends and sources of perchlorate in arctic snow. Environ Sci Tech 44(2):588–592
Xiao CC, Ran SJ, Huang ZW, Liang JP (2016) Bacterial diversity and community structure of supragingival plaques in adults with dental health or caries revealed by 16S pyrosequencing. Front Microbiol 7:1145
Ye L, You H, Yao J, Su HL (2012) Water treatment technologies for perchlorate: a review. Desalination 298:1–12
York RG, Barnett J, Girard MF et al (2005) Refining the effects observed in a developmental neuro behavioral study of ammonium perchlorate administered orally in drinking water to rats. II. Behavioral and neuro development effects. Int J Toxicol 24:451–467
Zeglin LH (2015) Stream microbial diversity in response to environmental changes: review and synthesis of existing research. Front Microbiol 6:454
Zeng B, Han SS, Wang P, Wen B, Jian WS et al (2015) The bacterial communities associated with fecal types and body weight of rex rabbits. Sci Rep 5:9342
Zhang HS, Bruns MA, Logan BE (2002) Perchlorate reduction by a novel chemolithoautotrophic, hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium. Environ Microbiol 4:570–576
Zhang LX, Yang ZQ, Li T, Zhou SQ, Wu ZY (2015) Perchlorate adsorption onto orange peel modified by cross-linking amine groups from aqueous solutions. Water Sci Technol 71(11):1629–1637
Zhang W, Jiao LF, Liu RX, Zhang Y et al (2018) The effect of exposure to high altitude and low oxygen on intestinal microbial communities in mice. PLoS ONE 13(9):e0203701
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Sichuan Environmental Protection Science and Technology Project (2018HB27) and the Ya'an Science and Technology Plan (2016yyjsykf005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sha, J., Wu, J., Bi, C. et al. Responses of microbial community to different concentration of perchlorate in the Qingyi River. 3 Biotech 10, 21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-2012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-2012-1