Abstract
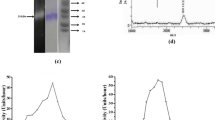
Upon examination of the fruit extract of Cucumis sativus L. for its pharmacological benefits, it was previously observed that it has potential proteolytic, fibrinogenolytic and procoagulant activities. These properties can be attributed to the presence of the protease. In this regard, the present study comprised of purification and characterization of protease. Purification of the enzyme involved ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography. The purified cucumis protease (CPro) exhibits homogeneity as attested by SDS-PAGE and RP-HPLC with a retention time of 14.246 min with molecular mass ~75.3 kDa. CPro was identified as a glycoprotein and serine protease. Azocasein is the preferred substrate for CPro as it showed low Km value of 0.3809 mg/ml. Purified CPro exhibits optimum activity at 37 °C and pH 8. CPro shows its involvement in hemostasis—the very first step in wound healing. CPro degrades the subunits of human fibrinogen in the order Aα > Bβ > γ. It also hydrolyzes the subunits of the partially cross-linked fibrin clot in the order α-polymer > γ–γ dimer > β-chain. CPro reduced the clotting time of citrated plasma, prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time of plasma. CPro is neither hemorrhagic nor edema-inducing, thus considered to be a non-toxic protease. This work provides evidence for the use of cucumber extract in wound healing and authenticates its use in cosmetics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPro:
-
Cucumis protease
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
- AqFEC:
-
Aqueous fruit extract of European cucumber
- RFC:
-
Relative clotting factor
- PMSF:
-
Phenyl methyl sulphonyl fluoride
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N, N, N′, N′-tetraacetic acid
- IAA:
-
Iodoacetic acid
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- APPT:
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- PAS:
-
Periodic acid-Schiff
References
Albalasmeh AA, Berhe AA, Ghezzehei TA (2013) A new method for rapid determination of carbohydrate and total carbon concentrations using UV spectrophotometry. Carbohydr Polym 97(2):253–261. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.072
Antao CM, Malcata FX (2005) Plant serine proteases: biochemical, physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol Biochem 43(7):637–650. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2005.05.001
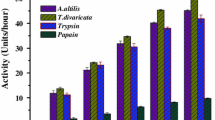
Asif-Ullah M, Kim KS, Yu YG (2006) Purification and characterization of a serine protease from Cucumis trigonus Roxburghi. Phytochemistry 67(9):870–875. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.02.020
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Casano LM, Desimone M, Trippi VS (1989) Proteolytic activity at alkaline pH in oat leaves isolation of an aminopeptidase. Plant Physiol 91(4):1414–1418
Condrea E, Yang CC, Rosenberg P (1983) Anticoagulant activity and plasma phosphatidylserine hydrolysis by snake venom phospholipases A2. Thromb Haemost 49(2):151
Deepak S, Shailasree S, Kini RK, Hause B, Shetty SH, Mithöfer A (2007) Role of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins in resistance of pearl millet against downy mildew pathogen Sclerospora graminicola. Planta 226(2):323–333. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0484-4
Devaraja S, Nagaraju S, Mahadeswaraswamy YH, Girish KS, Kemparaju K (2008) A low molecular weight serine protease: purification and characterization from Hippasa agelenoides (funnel web) spider venom gland extract. Toxicon 52(1):130–138. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.04.168
Kaneda M, Tominaga N (1975) Isolation and characterization of a proteinase from the sarcocarp of melon fruit. J Biochem 78(6):1287–1296
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
TK Lim (2012) Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants. Fruits, Vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht
Manjula B, Swamy YHM, Devaraja S, Girish KS, Kemparaju K (2015) Clot promoting and dissolving properties of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) sap, validating its use in traditional medicine. 2015:8
Nafeesa Z, Shivalingu BR, Vivek HK, Priya BS, Swamy SN (2015) Exploring a new serine protease from Cucumis sativus L. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(6):2787–2794. doi:10.1007/s12010-014-1462-5
Nema NK, Maity N, Sarkar B, Mukherjee PK (2011) Cucumis sativus fruit-potential antioxidant, anti-hyaluronidase, and anti-elastase agent. Arch Dermatol Res 303(4):247–252
Pande M, Dubey VK, Yadav SC, Jagannadham MV (2006) A novel serine protease cryptolepain from Cryptolepis buchanani: purification and biochemical characterization. J Agric Food Chem 54(26):10141–10150. doi:10.1021/jf062206a
Rahman AHMM (2013) Ethano-medico-botanical investigation on cucurbits of the Rajshahi Division. Bangladesh J Medicinal Plants Studies 1(3):118–125
Rajesh R, Raghavendra Gowda CD, Nataraju A, Dhananjaya BL, Kemparaju K, Vishwanath BS (2005) Procoagulant activity of Calotropis gigantea latex associated with fibrin(ogen)olytic activity. Toxicon 46(1):84–92. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.03.012
Rajesh R, Nataraju A, Gowda CD, Frey BM, Frey FJ, Vishwanath BS (2006) Purification and characterization of a 34-kDa, heat stable glycoprotein from Synadenium grantii latex: action on human fibrinogen and fibrin clot. Biochimie 88(10):1313–1322. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2006.06.007
Shivalingu BR, Vivek HK, Nafeesa Z, Priya BS, Swamy SN (2015) Comparative analysis of procoagulant and fibrinogenolytic activity of crude protease fractions of turmeric species. J Ethnopharmacol 172:261–264. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.018
Sotiroudis G, Melliou E, Sotiroudis TG, Chinou I (2010) chemical analysis, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of three Greek cucumber (Cucumis sativus) cultivars. J Food Biochem 3 (s1):61–78
Torres-Urrutia C, Guzman L, Schmeda-Hirschmann G, Moore-Carrasco R, Alarcon M, Astudillo L, Gutierrez M, Carrasco G, Yuri JA, Aranda E, Palomo I (2011) Antiplatelet, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic activity in vitro of extracts from selected fruits and vegetables. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 22(3):197–205. doi:10.1097/MBC.0b013e328343f7da
Uchikoba T, Horita H, Kaneda M (1990) Proteases from the sarcocarp of yellow snake-gourd. Phytochemistry 29(6):1879–1881
Uchikoba T, Yonezawa H, Kaneda M (1998) Cucumisin like protease from the sarcocarp of Benincasa hispida var. Ryukyu. Phytochemistry 49(8):2215–2219
Venkatesh BK, Achar RR, Sharanappa P, Priya BS, Swamy SN (2015) Synergistic caseinolytic activity and differential fibrinogenolytic action of multiple proteases of Maclura spinosa (Roxb. ex Willd.) latex. Pharmacogn Mag 11(Suppl 3):S457–S461. doi:10.4103/0973-1296.168987
Vishwanath BS, Kini RM, Gowda TV (1987) Characterization of three edema-inducing phospholipase A2 enzymes from habu (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) venom and their interaction with the alkaloid aristolochic acid. Toxicon 25(5):501–515
Wilimowska-Pelc A, Polanowski A, Kolaczkowska MK, Wieczorek M, Wilusz T (1982) Aspartyl proteinase from cucumber (Cucumis sativus) seeds. Prepration and characterstics. Acta Biochimica Polonica 30(1):23–31
Yamaguchi T, Yamashita Y, Takeda I, Kiso H (1982) Proteolytic enzymes in green asparagus, kiwi fruit and miut: occurrence and partial characterization. Agric Biol Chem 46(8):1983–1986. doi:10.1080/00021369.1982.10865376
Yariswamy M, Shivaprasad HV, Joshi V, Nanjaraj Urs AN, Nataraju A, Vishwanath BS (2013) Topical application of serine proteases from Wrightia tinctoria R. Br. (Apocyanaceae) latex augments healing of experimentally induced excision wound in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 149(1):377–383. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.056
Acknowledgements
ZN would like to express gratitude to the University Grant Commission, New Delhi for financial assistance under Maulana Azad National Fellowship (F1-17.1/2013-14/MANF-2013-14-MUS-KAR-20358).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nafeesa, Z., Shivalingu, B.R., Neema, K.N. et al. Procoagulant serine glycoprotease from Cucumis sativus L.: action on human fibrinogen and fibrin clot. 3 Biotech 7, 96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0686-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0686-9