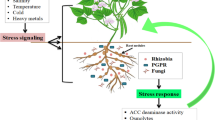
Abstract
Environmental stress conditions influence the growth and survival of rhizobia by affecting the signalling and infection process, nodule development and function. Stress factors such as osmotic stress, extremes of temperature and pH and accumulation of heavy metals result in reduced nodulation, leading to low levels of nitrogen fixation and crop yield. Some species of rhizobia are known to be tolerant to biotic and abiotic stresses and utilization of these stress-tolerant rhizobia strains as inoculants, can greatly improve biological nitrogen fixation. This review highlights the main environmental stresses known to cause cause rhizobial cell damage and death, including temperature, desiccation, drought, salinity, pH and heavy metal stresses. An understanding of the key physiological and molecular factors of how these stress responses affect the survival of rhizobia is crucial in the development of strains with high potential in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Key responses range from expression of stress-linked genes and proteins which aid in cell repair and protection, accumulation of compatible solutes such as sugars and polymers, carbon enrichment in drought stress, to extrusion of heavy metals. Biological nitrogen fixation can be improved by the selection of nitrogen-fixing endosymbionts that are well-adapted and tolerant to a broad range of environmental stresses is important in alleviating the effects of adverse conditions, potentially increasing the chances of success of legume inoculation with rhizobia thus improving the contribution of atmospheric nitrogen fixation in agroecosystems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla M, Vuong T, Harper J (1998) Genotypic differences in dinitrogen fixation response to NaCl stress in intact and grafted soybean. Crop Sci 38:72–77
Acebrón S, Martín I, del Castillo U, Moro F, Muga A (2009) DnaK-mediated association of ClpB to protein aggregates. A bichaperone network at the aggregate surface. FEBS Lett 583:2991–2996
Alexandre A, Oliveira S (2011) Most heat-tolerant rhizobia show high induction of major chaperone genes upon stress. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 75:28–36
Alexandre A, Laranjo M, Oliveira S (2013) Global transcriptional response to heat shock of the legume symbiont Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099 comprises extensive gene downregulation. DNA Res 21:195–206
Alloing G, Travers I, Sagot B, Le Rudulier D, Dupont L (2006) Proline betaine uptake in Sinorhizobium meliloti: characterization of Prb, an Opp-like ABC transporter regulated by both proline betaine and salinity stress. J Bacteriol 188:6308–6317
Alves BJR, Boddey RM, Urquiaga S (2003) The success of BNF in soybean in Brazil. Plant Soil 252:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1024191913296
Anyango B, Wilson KJ, Beynon JL, Giller KE (1995) Diversity of rhizobia nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. in two Kenyan soils with contrasting pHs. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4016–4021
Arora N, Khare E, Singh S, Maheshwari D (2010) Effect of Al and heavy metals on enzymes of nitrogen metabolism of fast and slow growing rhizobia under explanta conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:811–816
Atieno M, Herrmann L, Okalebo R, Lesueur D (2012) Efficiency of different formulations of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and effect of co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis with two different strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2541–2550
Atieno M, Wilson N, Casteriano A, Crossett B, Lesueur D, Deaker R (2018) Aqueous peat extract exposes rhizobia to sub-lethal stress which may prime cells for improved desiccation tolerance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:7521–7539
Bååth E, Díaz-Raviña M, Frostegård Å, Campbell CD (1998) Effect of metal-rich sludge amendments on the soil microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:238–245
Baldani JI, Weaver R, Hynes M, Eardly B (1992) Utilization of carbon substrates, electrophoretic enzyme patterns, and symbiotic performance of plasmid-cured clover rhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2308–2314
Barra L, Pica N, Gouffi K, Walker GC, Blanco C, Trautwetter A (2003) Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is required for sucrose and trehalose to be efficient osmoprotectants in Sinorhizobium meliloti. FEMS Microbiol Lett 229:183–188
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE, Prabhu S, Hernandez J-P (2014) Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: formulations and practical perspectives (1998–2013). Plant Soil 378:1–33
Beltra R, Del Solar G, Sanchez-Serrano J, Alonso E (1988) Mutants of Rhizobium phaseoli HM Mel− obtained by means of elevated temperatures. Zentralbl Mikrobiol 143:529–532
Biter AB, Lee S, Sung N, Tsai FT (2012) Structural basis for intersubunit signaling in a protein disaggregating machine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:12515–12520
Bontemps C et al (2010) Burkholderia species are ancient symbionts of legumes. Mol Ecol 19:44–52
Boscari A, Van de Sype G, Le Rudulier D, Mandon K (2006) Overexpression of BetS, a Sinorhizobium meliloti high-affinity betaine transporter, in bacteroids from Medicago sativa nodules sustains nitrogen fixation during early salt stress adaptation. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19:896–903
Botsford JL, Lewis TA (1990) Osmoregulation in Rhizobium meliloti: production of glutamic acid in response to osmotic stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:488–494
Brígido C, Robledo M, Menéndez E, Mateos PF, Oliveira S (2012) A ClpB chaperone knockout mutant of Mesorhizobium ciceri shows a delay in the root nodulation of chickpea plants. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 25:1594–1604
Bryant G, Koster KL, Wolfe J (2001) Membrane behaviour in seeds and other systems at low water content: the various effects of solutes. Seed Sci Res 11:17–25
Buchanan BB, Balmer Y (2005) Redox regulation: a broadening horizon. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:187–220
Bushby H, Marshall K (1977) Some factors affecting the survival of root-nodule bacteria on desiccation. Soil Biol Biochem 9:143–147
Carrasco JA et al (2005) Isolation and characterisation of symbiotically effective Rhizobium resistant to arsenic and heavy metals after the toxic spill at the Aznalcollar pyrite mine. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1131–1140
Casteriano A (2013) Physiological mechanisms of desiccation tolerance in rhizobia. University of Sydney
Casteriano A, Wilkes MA, Deaker R (2013) Physiological changes in rhizobia after growth in peat extract may be related to improved desiccation tolerance. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3998–4007
Catroux G, Hartmann A, Revellin C (2001) Trends in rhizobial inoculant production and use. Plant Soil 230:21–30
Charlson DV, Bhatnagar S, King CA, Ray JD, Sneller CH, Carter TE, Purcell LC (2009) Polygenic inheritance of canopy wilting in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Theor Appl Genet 119:587–594
Chaudri AM, Allain CM, Barbosa-Jefferson VL, Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ, McGrath SP (2000) A study of the impacts of Zn and Cu on two rhizobial species in soils of a long-term field experiment. Plant Soil 221:167–179
Chen L, Figueredo A, Villani H, Michajluk J, Hungria M (2002a) Diversity and symbiotic effectiveness of rhizobia isolated from field-grown soybean nodules in Paraguay. Biol Fertil Soils 35:448–457
Chen R, Bhagwat AA, Yaklich R, Keister DL (2002b) Characterization of ndvD, the third gene involved in the synthesis of cyclic β-(1 3),(1 6)-d-glucans in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol 48:1008–1016
Cheung K, Gu J-D (2007) Mechanism of hexavalent chromium detoxification by microorganisms and bioremediation application potential: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:8–15
Chien C-T, Maundu J, Cavaness J, Dandurand L-M, Orser CS (1992) Characterization of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae strain C1204b. FEMS Microbiol Lett 90:135–140
Cloutier J, Prévost D, Nadeau P, Antoun H (1992) Heat and cold shock protein synthesis in arctic and temperate strains of rhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2846–2853
Compant S, Clément C, Sessitsch A (2010) Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo-and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 42:669–678
Crockford AJ, Behncke C, Williams HD (1996) The adaptation of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli to oxidative stress and its overlap with other environmental stress responses. Microbiology 142:331–336
Crowe JH, Crowe LM, Oliver AE, Tsvetkova N, Wolkers W, Tablin F (2001) The trehalose myth revisited: introduction to a symposium on stabilization of cells in the dry state. Cryobiol 43:89–105
Cytryn EJ et al (2007) Transcriptional and physiological responses of Bradyrhizobium japonicum to desiccation-induced stress. J Bacteriol 189:6751–6762
da Costa MS, Santos H, Galinski EA (1998) An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in Bacteria and archaea. In: Antranikian G (ed) Biotechnology of extremophiles. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 117–153
da Silva Batista JS, Hungria M (2012) Proteomics reveals differential expression of proteins related to a variety of metabolic pathways by genistein-induced Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains. J Proteome 75:1211–1219
Das H, Mitra AK, Sengupta P, Hossain A, Islam F, Rabbani G (2004) Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables, and fish in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Environ Int 30:383–387
da-Silva JR, Alexandre A, Brígido C, Oliveira S (2017) Can stress response genes be used to improve the symbiotic performance of rhizobia? AIMS Microbiol 3:365–382
de Castro PR, dos Reis Junior FB, Zilli JE, Fischer D, Hofmann A, James EK, Simon MF (2018) Soil characteristics determine the rhizobia in association with different species of Mimosa in Central Brazil. Plant Soil 423:411–428
de Lucena DK, Pühler A, Weidner S (2010) The role of sigma factor RpoH1 in the pH stress response of Sinorhizobium meliloti. BMC Microbiol 10:265. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-265
De Meyer SE et al (2016) Symbiotic Burkholderia species show diverse arrangements of nif/fix and nod genes and lack typical high-affinity cytochrome cbb3 oxidase genes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 29:609–619
Deaker R, Roughley RJ, Kennedy IR (2004) Legume seed inoculation technology: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1275–1288
Deaker R, Hartley E, Gemell G (2012) Conditions affecting shelf-life of inoculated legume seed. Agric J 2:38–51
Deepika KV, Raghuram M, Kariali E, Bramhachari PV (2016) Biological responses of symbiotic Rhizobium radiobacter strain VBCK1062 to the arsenic contaminated rhizosphere soils of mung bean. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 134(Part 1):1–10
Defez R, Esposito R, Angelini C, Bianco C (2016) Overproduction of indole-3-acetic acid in free-living rhizobia induces transcriptional changes resembling those occurring in nodule bacteroids. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 29:484–495
Delmotte N et al (2010) An integrated proteomics and transcriptomics reference data set provides new insights into the Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroid metabolism in soybean root nodules. Proteomics 10:1391–1400
Donati AJ, Jeon J-M, Sangurdekar D, So J-S, Chang W-S (2011) The genome-wide transcriptional and physiological responses of Bradyrhizobium japonicum to paraquat-mediated oxidative stress. Appl Environ Microbiol:AEM. 00047–00011
dos Reis Jr FB et al (2010) Nodulation and nitrogen fixation by Mimosa spp. in the Cerrado and Caatinga biomes of Brazil. New Phytol 186:934–946
Drouin P, Prëvost D, Antoun H (2000) Physiological adaptation to low temperatures of strains of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae associated with Lathyrus spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 32:111–120
Duzan HM, Mabood F, Souleimanov A, Smith DL (2006) Nod Bj-V (C 18: 1, MeFuc) production by Bradyrhizobium japonicum (USDA110, 532C) at suboptimal growth temperatures. J Plant Physiol 163:107–111
Eaglesham A, Ayanaba A (1984) Tropical stress ecology of rhizobia, rootnodulation and legume fixation. Curr Dev Biol N Fix:1–35
Encarnación S, Guzmán Y, Dunn MF, Hernández M, del Vargas M, Mora J (2003) Proteome analysis of aerobic and fermentative metabolism in Rhizobium etli CE3. Proteomics 3:1077–1085
Estrada-De Los Santos P, Rojas-Rojas FU, Tapia-García EY, Vásquez-Murrieta MS, Hirsch AM (2016) To split or not to split: an opinion on dividing the genus. Burkholderia Ann Microbiol 66:1303–1314
Fonseca MB et al (2012) Nodulation in Dimorphandra wilsonii Rizz.(Caesalpinioideae), a threatened species native to the Brazilian Cerrado. PLoS One 7:e49520
Garau G, Yates RJ, Deiana P, Howieson JG (2009) Novel strains of nodulating Burkholderia have a role in nitrogen fixation with papilionoid herbaceous legumes adapted to acid, infertile soils. Soil Biol Biochem 41:125–134
Gehlot HS et al (2012) Nodulation of legumes from the Thar desert of India and molecular characterization of their rhizobia. Plant Soil 357:227–243
Gemell L, Hartley E, Herridge D (2005) Point-of-sale evaluation of preinoculated and custom-inoculated pasture legume seed. Anim Prod Sci 45:161–169
Gilbert KB, Vanderlinde EM, Yost CK (2007) Mutagenesis of the carboxy terminal protease CtpA decreases desiccation tolerance in Rhizobium leguminosarum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 272:65–74
Giller KE, Witter E, Mcgrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414
González E, Gálvez L, Royuela M, Aparicio-Tejo P, Arrese-Igor C (2001) Insights into the regulation of nitrogen fixation in pea nodules: lessons from drought, abscisic acid and increased photoassimilate availability. Agron 21:607–613
Gopalakrishnan S, Sathya A, Vijayabharathi R, Varshney RK, Gowda CL, Krishnamurthy L (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobia: challenges and opportunities 3. Biotech 5:355–377
Gouffi K, Pica N, Pichereau V, Blanco C (1999) Disaccharides as a new class of nonaccumulated osmoprotectants for Sinorhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1491–1500
Graham PH (1992) Stress tolerance in Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium, and nodulation under adverse soil conditions. Can J Microbiol 38:475–484
Graham PH et al (1994) Acid pH tolerance in strains of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium, and initial studies on the basis for acid tolerance of Rhizobium tropici UMR1899. Can J Microbiol 40:198–207
Guan D-w et al (2012) Analysis of two Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains with different symbiotic matching for nodulation by primary proteomic. J Integr Agric 11:1377–1383
Gutnick D, Bach H (2000) Engineering bacterial biopolymers for the biosorption of heavy metals; new products and novel formulations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:451–460
Gyaneshwar P et al (2011) Legume-Nodulating Betaproteobacteria: diversity, host range, and future prospects. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 24:1276–1288. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-06-11-0172
Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M (2009) Converging concepts of protein folding in vitro and in vivo. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:574
Hartley EJ, Gemell LG, Deaker R (2012) Some factors that contribute to poor survival of rhizobia on preinoculated legume seed. Crop Pasture Sci 63:858–865
Hellweg C, Pühler A, Weidner S (2009) The time course of the transcriptomic response of Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 following a shift to acidic pH. BMC Microbiol 9:37
Herrmann L, Atieno M, Brau L, Lesueur D (2015) Microbial quality of commercial inoculants to increase BNF and nutrient use efficiency. In: Biological nitrogen fixation. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, pp 1031–1040
Hoelzle I, Streeter JG (1990) Increased accumulation of trehalose in rhizobia cultured under 1% oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3213–3215
Humann JL, Kahn ML (2015) Genes involved in desiccation resistance of rhizobia and other bacteria. In: Biological nitrogen fixation. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, pp 397–404
Hungria M, Franco AA (1993) Effects of high temperature on nodulation and nitrogen fixation by Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Soil 149:95–102
Hungria M, Vargas MA (2000) Environmental factors affecting N2 fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crop Res 65:151–164
Hussain MB, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Asgher M (2014) Can catalase and exopolysaccharides producing rhizobia ameliorate drought stress in wheat? Int J Agric Biol 16:3–13
James EK et al (1998) Photosynthetic oxygen evolution within Sesbania rostrata stem nodules. Plant J 13:29–38
Jensen JB, Peters NK, Bhuvaneswari T (2002) Redundancy in periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems for trehalose, sucrose, and maltose in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 184:2978–2986
Jeon J-M, Lee H-I, Donati AJ, So J-S, Emerich DW, Chang W-S (2011) Whole-genome expression profiling of Bradyrhizobium japonicum in response to hydrogen peroxide. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 24:1472–1481
Jiang JQ, Wei W, Du BH, Li XH, Wang L, Yang SS (2004) Salt-tolerance genes involved in cation efflux and osmoregulation of Sinorhizobium fredii RT19 detected by isolation and characterization of Tn5 mutants. FEMS Microbiol Lett 239:139–146
Johansen C, Krishnamurthy L, Saxena N, Sethi S (1994) Genotypic variation in moisture response of chickpea grown under line-source sprinklers in a semi-arid tropical environment. Field Crop Res 37:103–112
Kala T, Christi R, Bai N (2011) Effect of Rhizobium inoculation on the growth and yield of horsegram (Dolichos biflorus Linn). Plant Arch 11:97–99
Karanja NK, Wood M (1988) Selecting Rhizobium phaseoli strains for use with beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Kenya: tolerance of high temperature and antibiotic resistance. Plant Soil 112:15–22
Kaya MD, Okçu G, Atak M, Çıkılı Y, Kolsarıcı Ö (2006) Seed treatments to overcome salt and drought stress during germination in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Eur J Agron 24:291–295
Kedzierska S, Matuszewska E (2001) The effect of co-overproduction of DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE and ClpB proteins on the removal of heat-aggregated proteins from Escherichia coli ΔclpB mutant cells–new insight into the role of Hsp70 in a functional cooperation with Hsp100. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:355–360
Kempf B, Bremer E (1998) Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolarity environments. Arch Microbiol 170:319–330
Khan M, Scullion J (2002) Effects of metal (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb or Zn) enrichment of sewage-sludge on soil micro-organisms and their activities. Appl Soil Ecol 20:145–155
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA, Oves M (2009) Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the remediation of metal contaminated soils. Environ Chem Lett 7:1–19
Kobayashi R, Suzuki T, Yoshida M (2007) Escherichia coli phage-shock protein A (PspA) binds to membrane phospholipids and repairs proton leakage of the damaged membranes. Mol Microbiol 66:100–109
Krujatz F, Haarstrick A, Nörtemann B, Greis T (2012) Assessing the toxic effects of nickel, cadmium and EDTA on growth of the plant growth-promoting Rhizobacterium Pseudomonas brassicacearum. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1281–1293
Lafay B, Burdon JJ (1998) Molecular diversity of rhizobia occurring on native shrubby legumes in southeastern Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3989–3997
Lakzian A, Murphy P, Turner A, Beynon JL, Giller KE (2002) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae populations in soils with increasing heavy metal contamination: abundance, plasmid profiles, diversity and metal tolerance. Soil Biol Biochem 34:519–529
Latrach L, Farissi M, Mouradi M, Makoudi B, Bouizgaren A, Ghoulam C (2014) Growth and nodulation of alfalfa-rhizobia symbiosis under salinity: electrolyte leakage, stomatal conductance, and chlorophyll fluorescence. Turk J Agric For 38:320–326
Lebrazi S, Benbrahim KF (2014) Environmental stress conditions affecting the N2 fixing Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and adaptation mechanisms. Afr J Microbiol Res 8:4053–4061
Lee M-Y et al (2005) Induction of thioredoxin is required for nodule development to reduce reactive oxygen species levels in soybean roots. Plant Physiol 139:1881–1889
Lemaire B, Van Cauwenberghe J, Chimphango S, Stirton C, Honnay O, Smets E, Muasya AM (2015) Recombination and horizontal transfer of nodulation and ACC deaminase (acdS) genes within alpha-and Betaproteobacteria nodulating legumes of the cape fynbos biome. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91
Leprince O, Buitink J (2010) Desiccation tolerance: from genomics to the field. Plant Sci 179:554–564
Lesueur D, Founoune H, Lebonvallet S, Sarr A (2009) Effect of rhizobial inoculation on growth of Calliandra tree species under nursery conditions. New For 39:129–137
Lesueur D, Deaker R, Herrmann L, Bräu L, Jansa J (2016) The production and potential of biofertilizers to improve crop yields. In: Arora NK, Mehnaz, S., Balestrini, R. (ed) Bioformulations: for sustainable agriculture. pp 71-92
Li J et al (2011) Proteomic study on two Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains with different competitivenesses for nodulation. Agric Sci China 10:1072–1079
Lima AIG, Corticeiro SC, Figueira EMdAP (2006) Glutathione-mediated cadmium sequestration in Rhizobium leguminosarum. Enzym Microb Technol 39:763–769
Lira Junior MA, Lima AST, Arruda JRF, Smith DL (2005) Effect of root temperature on nodule development of bean, lentil and pea. Soil Biol Biochem 37:235–239
Manchanda G, Garg N (2008) Salinity and its effects on the functional biology of legumes. Acta Physiol Plant 30:595–618
Mandal SM, Gouri SS, De D, Das BK, Mondal KC, Pati BR (2011) Effect of arsenic on nodulation and nitrogen fixation of blackgram (Vigna mungo). Indian J Microbiol 51:44–47
Meena KK et al (2017) Abiotic stress responses and microbe-mediated mitigation in plants: the omics strategies. Front Plant Sci 8
Mhadhbi H, Aouani ME (2008) Growth and nitrogen-fixing performances of Medicago truncatula-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbioses under salt (NaCl) stress: micro-and macro-symbiont contribution into symbiosis tolerance. In: Biosaline Agriculture and High Salinity Tolerance. pp 91–98
Michiels J, Verreth C, Vanderleyden J (1994) Effects of temperature stress on bean-nodulating Rhizobium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1206–1212
Miller-Williams M, Loewen PC, Oresnik IJ (2006) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm1021. Microbiol 152:2049–2059
Mnasri B, Aouani ME, Mhamdi R (2007) Nodulation and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under water deficiency. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1744–1750
Moulin L, James EK, Klonowska A, Miana de Faria S, Simon MF (2015) Phylogeny, diversity, geographical distribution, and host range of legume-nodulating betaproteobacteria: what is the role of plant taxonomy? de Bruijn FJ Biol nitrogen Fixat Chichester: Wiley:177–190
Mouradi M, Bouizgaren A, Farissi M, Latrach L, Qaddoury A, Ghoulam C (2016) Seed osmopriming improves plant growth, nodulation, chlorophyll fluorescence and nutrient uptake in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) – rhizobia symbiosis under drought stress. Sci Hortic 213:232–242
Münchbach M, Dainese P, Staudenmann W, Narberhaus F, James P (1999) Proteome analysis of heat shock protein expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. FEBS J 264:39–48
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nandal K, Sehrawat AR, Yadav AS, Vashishat R, Boora K (2005) High temperature-induced changes in exopolysaccharides, lipopolysaccharides and protein profile of heat-resistant mutants of Rhizobium sp.(Cajanus). Microbiol Res 160:367–373
Nandasena KG, O'Hara GW, Tiwari RP, Sezmiş E, Howieson JG (2007) In situ lateral transfer of symbiosis islands results in rapid evolution of diverse competitive strains of Mesorhizobia suboptimal in symbiotic nitrogen fixation on the pasture legume Biserrula pelecinus L. Environ Microbiol 9:2496–2511
Neudorf KD, Vanderlinde EM, Tambalo DD, Yost CK (2015) A previously uncharacterized tetratricopeptide-repeat-containing protein is involved in cell envelope function in Rhizobium leguminosarum. Microbiol 161:148–157
Nomura M et al (2010) Differential protein profiles of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 bacteroid during soybean nodule development. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56:579–590
O'Connell KP, Thomashow MF (2000) Transcriptional organization and regulation of a polycistronic cold shock operon in Sinorhizobium meliloti RM1021 encoding homologs of the Escherichia coli major cold shock gene cspA and ribosomal protein gene rpsU. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:392–400
Paço A, Brígido C, Alexandre A, Mateos PF, Oliveira S (2016) The symbiotic performance of chickpea rhizobia can be improved by additional copies of the clpB chaperone gene. PLoS One 11:e0148221
Pajuelo E, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Dary M, Palomares AJ (2008) Toxic effects of arsenic on Sinorhizobium–Medicago sativa symbiotic interaction. Environ Pollut 154:203–211
Pal A, Paul AK (2008) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: central elements in heavy metal bioremediation. Indian J Microbiol 48:49
Parker MA (2015) The spread of Bradyrhizobium lineages across host legume clades: from Abarema to Zygia. Microb Ecol 69:630–640
Paudyal S, Aryal RR, Chauhan S, Maheshwari D (2007) Effect of heavy metals on growth of Rhizobium strains and symbiotic efficiency of two species of tropical legumes. Sci World 5:27–32
Pauly N et al (2006) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and glutathione: key players in the legume–Rhizobium symbiosis. J Exp Bot 57:1769–1776
Payakapong W, Tittabutr P, Teaumroong N, Boonkerd N, Singleton PW, Borthakur D (2006) Identification of two clusters of genes involved in salt tolerance in Sinorhizobium sp. strain BL3. Symbiosis 41:47–53
Peix A, Ramírez-Bahena MH, Velázquez E, Bedmar EJ (2015) Bacterial associations with legumes. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 34:17–42
Platero R et al (2016) Novel Cupriavidus strains isolated from root nodules of native Uruguayan Mimosa species. Appl Environ Microbiol:AEM. 04142–04115
Potts M (1994) Desiccation tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev 58:755
Queitsch C, Hong S-W, Vierling E, Lindquist S (2000) Heat shock protein 101 plays a crucial role in thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:479–492
Raju RM et al (2014) Post-translational regulation via Clp protease is critical for survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003994
Ramos JL, Gallegos M-T, Marqués S, Ramos-González M-I, Espinosa-Urgel M, Segura A (2001) Responses of gram-negative bacteria to certain environmental stressors. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:166–171
Reeve WG et al (2004) Probing for pH-regulated proteins in Sinorhizobium medicae using proteomic analysis. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 7:140–147
Reichman S (2007) The potential use of the legume–rhizobium symbiosis for the remediation of arsenic contaminated sites. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2587–2593
Remigi P, Zhu J, Young JPW, Masson-Boivin C (2016) Symbiosis within symbiosis: evolving nitrogen-fixing legume symbionts. TIM 24:63–75
Riccillo PM, Muglia CI, de Bruijn FJ, Roe AJ, Booth IR, Aguilar OM (2000) Glutathione is involved in environmental stress responses in <em>Rhizobium tropici</em>, Including acid tolerance. J Bacteriol 182:1748–1753. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.182.6.1748-1753.2000
Robinson B, Russell C, Hedley M, Clothier B (2001) Cadmium adsorption by rhizobacteria: implications for New Zealand pastureland. Agric Ecosyst Environ 87:315–321
Rodrigues CS, Laranjo M, Oliveira S (2006) Effect of heat and pH stress in the growth of chickpea mesorhizobia. Curr Microbiol 53:1–7
Romdhane SB, Trabelsi M, Aouani ME, De Lajudie P, Mhamdi R (2009) The diversity of rhizobia nodulating chickpea (Cicer arietinum) under water deficiency as a source of more efficient inoculants. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2568–2572
Roughley RJ, Gemell LG, Thompson JA, Brockwell J (1993) The number of Bradyrhizobium SP. (Lupinus) applied to seed and its effect on rhizosphere colonization, nodulation and yield of lupin. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1453–1458
Sadowsky MJ (2005) Soil stress factors influencing symbiotic nitrogen fixation. In: Nitrogen fixation in agriculture, forestry, ecology, and the environment. Springer, pp 89–112
Saikia SP, Bora D, Goswami A, Mudoi KD, Gogoi A (2012) A review on the role of Azospirillum in the yield improvement of non leguminous crops. Afr J Microbiol Res 6:1085–1102
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati S (2003) Removal of metal ions from aqueous solution by polysaccharide produced from Bacillus firmus. Water Res 37:4231–4235
Sankhla IS et al (2017) Molecular characterization of nitrogen fixing microsymbionts from root nodules of Vachellia (acacia) jacquemontii, a native legume from the Thar Desert of India. Plant Soil 410:21–40
Sarma AD, Emerich DW (2005) Global protein expression pattern of Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids: a prelude to functional proteomics. Proteomics 5:4170–4184
Sassi-Aydi S, Aydi S, Abdelly C (2014) Inorganic nitrogen nutrition enhances osmotic stress tolerance in Phaseolus vulgaris: lessons from a drought-sensitive cultivar. HortScience 49:550–555
Schneider KA et al (1997) Improving common bean performance under drought stress. Crop Sci 37:43–50
Serraj R (2003) Effects of drought stress on legume symbiotic nitrogen fixation: physiological mechanisms. Indian J Exp Biol 41:1136–1141
Shirkey B et al (2000) Active Fe-containing superoxide dismutase and abundant sodF mRNA in Nostoc commune (cyanobacteria) after years of desiccation. J Bacteriol 182:189–197
Silhavy TJ, Kahne D, Walker S (2010) The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2
Silvente S, Sobolev AP, Lara M (2012) Metabolite adjustments in drought tolerant and sensitive soybean genotypes in response to water stress. PLoS One 7:e38554
Smith E, Smith J, Smith L, Biswas T, Correll R, Naidu R (2003) Arsenic in Australian environment: an overview. J Environ Sci Health A 38:223–239
Smith SE, Facelli E, Pope S, Smith FA (2010) Plant performance in stressful environments: interpreting new and established knowledge of the roles of arbuscular mycorrhiza. Plant Soil 326:3–20
Soussi M, Santamaria M, Ocana A, Lluch C (2001) Effects of salinity on protein and lipopolysaccharide pattern in a salt-tolerant strain of Mesorhizobium ciceri. J Appl Microbiol 90:476–481
Sprent JI, Ardley J, James EK (2017) Biogeography of nodulated legumes and their nitrogen-fixing symbionts. New Phytol 215:40–56
Stępkowski T, Watkin E, McInnes A, Gurda D, Gracz J, Steenkamp ET (2012) Distinct Bradyrhizbium communities nodulate legumes native to temperate and tropical monsoon Australia. Mol Phylogenet Evol 63:265–277
Streeter JG (1985) Accumulation of alpha, alpha-trehalose by Rhizobium bacteria and bacteroids. J Bacteriol 164:78–84
Streeter JG (2003) Effect of trehalose on survival of Bradyrhizobium japonicum during desiccation. J Appl Microbiol 95:484–491
Sugawara M, Cytryn EJ, Sadowsky MJ (2010) Functional role of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Trehalose biosynthesis and metabolism genes during physiological stress and nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1071–1081
Turner NC, Wright GC, Siddique K (2001) Adaptation of grain legumes (pulses) to water-limited environments. Adv Agron 71:193–231
Vanderlinde EM, Harrison JJ, Muszyński A, Carlson RW, Turner RJ, Yost CK (2010) Identification of a novel ABC transporter required for desiccation tolerance, and biofilm formation in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae 3841. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71:327–340
Vriezen JAC, de Bruijn FJ, Nüsslein K (2007) Responses of rhizobia to desiccation in relation to osmotic stress, oxygen, and temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3451–3459
Wdowiak-Wróbel S, Małek W, Leszcz A, Typek R, Dawidowicz AL (2016) Effect of osmotic stress on Astragalus cicer microsymbiont growth and survival. Eur J Soil Biol 76:46–52
Wei W, Jiang J, Li X, Wang L, Yang S (2004) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants from Sinorhizobium meliloti and characterization of genes involved in salt tolerance. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:278–283
Wu G, Kang H, Zhang X, Shao H, Chu L, Ruan C (2010) A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J Hazard Mater 174:1–8
Yates RJ, Howieson JG, Nandasena KG, O'Hara GW (2004) Root-nodule bacteria from indigenous legumes in the north-west of Western Australia and their interaction with exotic legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1319–1329
Yelton M, Yang S, Edie S, Lim S (1983) Characterization of an effective salt-tolerant, fast-growing strain of Rhizobium japonicum. Microbiol 129:1537–1547
Zahran HH (1999) Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and nitrogen fixation under severe conditions and in an arid climate. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:968–989
Zhang X, Harper R, Karsisto M, Lindström K (1991) Diversity of Rhizobium bacteria isolated from the root nodules of leguminous trees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 41:104–113
Zhang F, Lynch DH, Smith DL (1995) Impact of low root temperatures in soybean [Glycine max.(L.) Merr.] on nodulation and nitrogen fixation. Environ Exp Bot 35:279–285
Zhang JJ et al (2012) Distinctive Mesorhizobium populations associated with Cicer arietinum L. in alkaline soils of Xinjiang, China. Plant Soil 353:123–134
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Dr. Lambert Brau for editing this manuscript and for his useful comments to improve its content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atieno, M., Lesueur, D. Opportunities for improved legume inoculants: enhanced stress tolerance of rhizobia and benefits to agroecosystems. Symbiosis 77, 191–205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0585-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0585-9