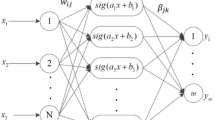
Abstract
The detection and localization of water pipe leaks are essential for maintaining the efficiency and sustainability of water distribution systems. Traditional methods, such as visual inspection, acoustic detection, and pressure testing, are often labour-intensive, time-consuming, and may not provide real-time monitoring, leading to significant water loss, infrastructure damage, and increased operational costs. Advances in machine learning and deep learning technologies offer a promising alternative, enabling the development of automated, accurate, and timely leak detection systems. This study presents a simulation-based approach to generate datasets for leak detection and localization within pipe systems. We implemented and compared five models: Ridge Regression, Lasso Regression, Decision Tree Regression, Support Vector Regression, and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Among these, Decision Tree Regression and ANN demonstrated superior performance in accurately detecting and localizing leaks. Our findings suggest that ANN is particularly effective for leak localization, providing a robust solution to minimize water loss, infrastructure damage, and environmental impact while ensuring the reliability of water distribution systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi A, Al-Dujaili A, Duan Y, Al-Shamma O, Santamaría J, Fadhel M, Al-Amidie M, Farhan L (2021) Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J Big Data. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8
Coelho J, Glória A, Sebastião P (2020) Precise water leak detection using machine learning and real-time sensor data. IoT 1:474–493. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot1020026
Daniel I, Cominola A (2023). Estimating irregular water demands with physics-informed machine learning to inform leakage detection.
El-Zahab S, Abdelkader EM, Zayed T (2018) An accelerometer-based leak detection system. Mech Syst Signal Process 108:276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.030
Fan X, Zhang X, Yu XB (2021) Machine learning model and strategy for fast and accurate detection of leaks in water supply network. J Infrastruct Preserv Resil 2:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43065-021-00021-6
Gupta A (2018) A selective literature review on leak management techniques for water distribution system. Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-1985-6
Huang L, Kun D, Guan M, Huang W, Song Z, Wang Q (2022) Combined usage of hydraulic model calibration residuals and improved vector angle method for burst detection and localization in water distribution systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001575
Kafle MD, Fong S, Narasimhan S (2022) Active acoustic leak detection and localization in a plastic pipe using time delay estimation. Appl Acoust 187: 108482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108482
Kammoun M, Kammoun A, Abid M (2021) Experiments based comparative evaluations of machine learning techniques for leak detection in water distribution systems. Water Supply. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.248
Leonzio DU, Bestagini P, Marcon M, Quarta GP, Tubaro S (2023) Water leak detection and localization using convolutional autoencoders, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10095760.
Levinas D, Perelman G, Ostfeld A (2021) Water leak localization using high-resolution pressure sensors. Water 13:591
Li R, Huang H, Xin K, Tao T (2015) A review of methods for burst/leakage detection and location in water distribution systems. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 15:429. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2014.131
Liu H, Fang H,Yu X, Wang F, Yang X,Xia Y (2024) Multi-leakage localization in water supply pipes based on convolutional blind source separation. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 144: 105576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2023.105576
Marvin G, Grbčić L, Družeta S, Kranjčević L (2023) Water distribution network leak localization with histogram-based gradient boosting. J Hydroinformatics. 25:663. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2023.102
Marzola I, Alvisi S, Franchini M (2022) A comparison of model-based methods for leakage localization in water distribution systems. Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03329-4
Mashhadi N, Shahrour I, Attoue N, El Khattabi J, Aljer A (2021) Use of machine learning for leak detection and localization in water distribution systems. Smart Cities 4:1293
Mazaev G, Weyns M, Vancoillie F, Vaes G, Ongenae F, Van Hoecke S (2022a) Probabilistic leak localization in water distribution networks using a hybrid data-driven and model-based approach. Water Supply. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2022.416
Mazaev G, Weyns M, Vancoillie F, Vaes G, Ongenae F, Van Hoecke S. (2022). Leak localization in water distribution networks by directly fitting the learning parameters of a Gaussian Naive Bayes Classifier. 4854–4859. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData55660.2022.10020580.
Moubayed A, Sharif M, Luccini M, Primak S, Shami A (2021) Water leak detection survey: challenges & research opportunities using data fusion & federated learning. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064445
Mucke N, Pandey P, Jain S, Bohté S, Oosterlee C (2023) A probabilistic digital twin for leak localization in water distribution networks using generative deep learning. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136179
Punukollu H, Vasan A, Raju K (2022) Leak detection in water distribution networks using deep learning. ISH J Hydraul Eng 29:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2022.2134742
Romero-Ben L, Alves D, Blesa J, Cembrano G, Puig V, Duviella E (2023) Leak detection and localization in water distribution networks: review and perspective. Annu Rev Control 55:392–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcontrol.2023.03.012
Shukla H, Piratla K (2020) Leakage detection in water pipelines using supervised classification of acceleration signals. Autom Constr 117:103256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103256
Sophocleous S, Savić D, Kapelan Z (2019) Leak localization in a real water distribution network based on search-space reduction. J Water Resour Plan Manag 145:04019024. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001079
Sourabh N, Timbadiya PV, Patel PL (2023) Leak detection in water distribution network using machine learning techniques. ISH J Hydraul Eng 29:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2023.2198988
Sousa D, Du R, da Silva B, Júnior JM, Cavalcante C, Fischione C (2023) Leakage detection in water distribution networks using machine-learning strategies. Water Supply. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2023.054
Steffelbauer D, Deuerlein J, Gilbert D, Abraham E, Piller O (2021) Pressure-leak duality for leak detection and localization in water distribution systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 148:04021106. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001515
Vrachimis S, Eliades D, Taormina R, Kapelan Z, Ostfeld A, Liu S, Kyriakou M, Pavlou P, Qiu M, Polycarpou M (2022) Battle of the leakage detection and isolation methods. J Water Resour Plan Manag 148:04022068. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001601
Wu Y, Ma X, Guo G, Jia T, Huang Y, Liu S, Fan J, Wu X (2024) Advancing deep learning-based acoustic leak detection methods towards application for water distribution systems from a data-centric perspective. Water Res 261:121999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121999
Xiao Z, Tang Z, Xu W, Meng F, Chu X, Xin K, Fu G (2019) Deep learning identifies accurate burst locations in water distribution networks. Water Res 166:115058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115058
Yussif A-M, Sadeghi H, Zayed T (2023) Application of machine learning for leak localization in water supply networks. Buildings 13:849. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13040849
Zaman D, Tiwari M, Gupta A, Sen D (2019) A review of leakage detection strategies for pressurised pipeline in steady-state. Eng Fail Anal 109:104264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.104264
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
We, the study’s authors, certify that neither people nor animals were used in this inquiry. We did not need ethical approval or consent because our research was limited to analysing new datasets for the purpose of detecting water pipe leaks using machine learning and deep learning models.
Informed consent
Consent that has been informed is not relevant. We did not use animals or human subjects in our investigation, so informed consent was not required. Our work was limited to the evaluation of fresh datasets for the purpose of locating and identifying water pipe leaks using deep learning and machine learning models.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pandian, C., Alphonse, P.J.A. Evaluating water pipe leak detection and localization with various machine learning and deep learning models. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-025-02726-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-025-02726-3