Abstract
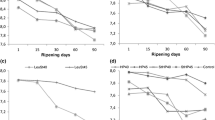
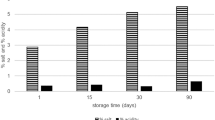
The effects of various yeast species isolated from raw-milk cheese were evaluated in Beyaz cheese. Four batches of cheeses were produced, in which the control cheese involved only commercial starter culture while YL, DH and KL cheeses were produced with the incorporation of individual Yarrowia lipolytica, Debaryomyces hansenii and Kluyveromyces lactis, respectively. The chemical composition, microbial counts, sensory attributes, volatile compounds and textural properties of cheeses were determined on days 1, 30, and 60 during the ripening period. The results obtained demonstrated that chemical, microbial and sensory properties of cheese varied depending on yeast species. The cheese with Y. lipolytica was the most preferred and it contained more short chain fatty acids, particularly butyric acid. This result could be due to the higher fat content and advanced lipolytic activity. The ripening index of DH was found to be higher than the other cheeses, showing an advanced proteolytic activity in relation to lower hardness in the texture profile. K. lactis was associated with lactose metabolism and promoted the development of Lactococcus spp. The results highlighted a potential use of yeasts as adjunct cultures in Beyaz cheese to develop the sensory properties such as texture and flavor.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarbati A, Marini E, Galli E, Canonico L, Ciani M, Comitini F (2021) Characterization of wild yeasts isolated from artisan dairies in the Marche region, Italy, for selection of promising functional starters. LWT 139:110531
Alzobaay A, Alzobaay W (2018) Role of Debaryomyces hansenii yeast in improving the microbial and sensory properties of monterey cheese. AJVS 11(1):8–14
Atanassova MR, Fernandez-Otero C, Rodriguez-Alonso P, Fernandez IC, Garabal JI, Centeno JA (2016) Characterization of yeasts isolated from artisanal short-ripened cows cheeses produced in Galicia (NW Spain). Food Microbiol 53:172–181
Belloch C, Querol A, Barrio E (2011) Yeasts and Molds: Kluyveromyces spp Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences. Elsevier, London, pp 754–76.
Bourne M (2002) Food texture and viscosity: Concept and measurement, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Carbonell M, Nunez M, Fernandez-Garcia E (2002) Evolution of the volatile components of ewe raw milk La Serena cheese during ripening. Correl Flavour Charact Le Lait 82:683–698
Clark S, Costello M (2009) Dairy products evaluation competitions. In: Clark S, Costello M, Drake M, Bodyfelt F (eds) The sensory evaluation of dairy products. Springer, New York, pp 43–71
Curioni PMG, Bosset JO (2002) Key odorants in various cheese types as determined by gas chromatography-olfactometry. Int Dairy J 12(12):959–984
De Freitas I, Pinon N, Berdague JL, Tournayre P, Lortal S, Thierry A (2008) Kluyveromyces lactis but not Pichia fermentans used as adjunct culture modifies the olfactory profiles of cantalet cheese. J Dairy Sci 91(2):531–543
Delgado FJ, González-Crespo J, Cava R, García-Parra J, Ramírez R (2010) Characterisation by SPME–GC–MS of the volatile profile of a Spanish soft cheese P.D.O. Torta del Casar during ripening. Food Chem. 118(1):182–189
El Soda M, Madkor A, Tong S (2000) Adjunct cultures: Recent developments and potential significance to the cheese industry. J Dairy Sci 83:609–619
Fröhlich Wyder MT, Arias-Roth E, Jakob E (2019) Cheese yeasts. Yeast 36(3):129–141
Harrigan WF, McCance ME (1976) Laboratory methods in food and dairy microbiology. Gulf professional publishing, London
Hayaloglu AA, Guven M, Fox PF, McSweeney PLH (2005) Influence of starters on chemical, biochemical, and sensory changes in Turkish white-brined cheese during ripening. J Dairy Sci 88:3460–3474
Kesenkaş H, Akbulut N (2006) Yeasts as adjunct starter sultures used in cheese production. Ege Üniv Ziraat Fak Derg 43(2):165–174
Leclercq-Perlat MN, Corrieu G, Spinnier HE (2004) Comparison of volatile compounds produced in model cheese medium deacidified by Debaryomyces hansenii or Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Dairy Sci 87:1545–1550
McSweeney P (2004) Biochemistry of cheese ripening. Int J Dairy Technol 57(2/3):147–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0307.2004.00147.x
McSweeney PLH, Fox PF (1997) Chemical methods for the characterization of proteolysis in cheese during ripening. Lait 77:41–76
Moio L, Addeo F (1998) Grana Padano cheese aroma. J Dairy Res 65:317–333
Montel MC, Buchin S, Mallet A, Delbes-Paus C, Vuitton D, Desmasures N et al (2014) Traditional cheeses: rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int J Food Microbiol 177:136–154
Ozturkoglu-Budak S, Figge MJ, Houbraken J, de Vries RP (2016a) The diversity and evolution of microbiota in traditional Turkish Divle Cave cheese during ripening. Int Dairy J 58:50–53
Ozturkoglu-Budak S, Wiebenga A, Bron PA, de Vries RP (2016b) Protease and lipase activities of fungal and bacterial strains derived from an artisanal raw ewe’s milk cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 237:17–27
Ozturkoglu-Budak S, Gursoy A, Aykas DP, Koçak C, Dönmez S, de Vries RP, Bron PA (2016c) Volatile compound profiling of Turkish Divle Cave cheese during production and ripening. J Dairy Sci 99(7):1–12
Pena-Serna C, Penna A, Lopes Filho J (2016) Zein-based blend coatings: impact on the quality of a model cheese of short ripening period. J Food Eng 171:208–213
Price EJ, Linforth RST, Dodd CER, Phillips CA, Hewson L, Hort J, Gkatzionis K (2014) Study of the influence of yeast inoculum concentration (Yarrowia lipolytica and Kluyveromyces lactis) on blue cheese aroma development using microbiological models. Food Chem 145:464–472
Settanni L, Moschetti G (2010) Non-starter lactic acid bacteria used to improve cheese quality and provide health benefits. Food Microbiol 27(6):691–697
Sorensen LM, Gori K, Petersen MA, Jespersen L, Arneborg N (2011) Flavour compound production by Yarrowia lipolytica, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Debaryomyces hansenii in a cheese-surface model. Int Dairy J 21:970–978
Sousa MJ, Ardö Y, McSweeney PLH (2001) Advances in the study of proteolysis during cheese ripening. Int Dairy J 11:327–345
Tekin A, Hayaloglu AA (2023) Understanding the mechanism of ripening biochemistry and flavour development in brine ripened cheeses. Int Dairy J 137:105508
Tsigie YA, Wang C, Kasim NS, Diem Q, Huynh L, Ho Q, Truong C, Ju Y (2012) Oil Production from Yarrowia lipolytica Po1g using rice bran hydrolysate. J Biotechnol Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/378384
Upadhyay VK, McSweeney PLH, Magboul AAA, Fox PF (2004) Proteolysis in cheese during ripening. In: McSweeney PLH, Fox P, Cotter P, Everett D (eds) Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, vol 1. Academic Press London, pp 273–300
Yalçın S, Ergül Ş, Özbaş Z (2011) Importance of yeasts in cheese microflora. GIDA 36(1):55–62
Zhang L, Huang C, Johansen PG, PetersenMA PMM, Lund MN, Jespersen L, Arneborg N (2021) The utilisation of amino acids by Debaryomyces hansenii and Yamadazyma triangularis associated with cheese. Int Dairy J 121:105135
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public or commercial sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BS-D: formal analysis, Writing–original draft, contributed to the design and analysis of the research, SO-B: formal analysis, Writing–original draft, contributed to the design and analysis of the research, and also to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares there is no conflicts to declare.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sevinc-Demircan, B., Ozturkoglu-Budak, S. Use of yeast isolates of cheese origin as adjunct culture in Beyaz cheese: Influence on sensorial, textural and quality characteristics. J Food Sci Technol 60, 2670–2680 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05791-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05791-3