Abstract
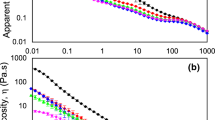
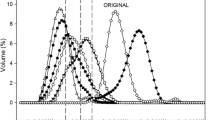
Milk fat-based whipping cream is primarily comprised of cream and whole milk. It has melt-in-the-mouth texture and unique milk flavor. However, milk fat-based whipping cream suffers from poor emulsion stability and foam firmness. The effects of monoacylglycerols (MAGs) with different saturation degrees (M1: 98% saturation, M2: 70% saturation and M3: 30% saturation) on emulsion properties (average particle size, viscosity, and emulsion stability) and whipping properties (overrun, firmness, shape retention ability, and foam stability) of milk fat-based whipping creams were investigated in this study. MAGs significantly decreased particle sizes (from 2.84 to 1.16 μm) and enhanced viscosity (from 350 to 490 cP) of the milk fat-based emulsions (emulsion without MAGs: M0, 5.01 μm, 298 cP) (P < 0.05). MAGs increased the stability of the milk fat-based emulsions with lesser phase separation during centrifugation tests and lower changes in particle sizes and viscosities during temperature cycling tests. Emulsion M1 with highest degree of saturation is less likely to destabilize and phase inverse. The decrease sharply in conductivity can be attributed to the entrapment of large amounts of air. Following that, the conductivity of M1 with low variation indicating high whipping resistance and less likely to coalescence and phase separation. Adding MAGs can significantly enhance overrun (M1: 205.3%, M2: 198.5%, M3: 141.4%) as compared to the control sample (M0: 97.9%) (P < 0.05). In emulsions containing MAGs with high degree of saturation (M1 and M2), firmness (M1: 95 g, M2: 109 g) and shape retention ability of the whipped creams were reduced as compared to control emulsion without MAG (M0: 173 g), but the foam stability (M1: 89%, M2: 91%) was enhanced (M0: 81%); M3 (firmness: 507 g; foam stability: 66%) has the contrasted effects. Whipping cream M2 demonstrated the best whipping properties with high overrun (198.46%), good firmness (109 g), shape retention ability and foam stability (91%). Good quality whipping creams can be obtained by selecting suitable MAGs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Abbreviations
- MAGs:
-
Monoacylglycerols
References
Athari B, Nasirpour A, Saeidy S, Esehaghbeygi A (2021) Physicochemical properties of whipped cream stabilized with electrohydrodynamic modified cellulose. J Food Process Preserv 45(9):1–8
Cao ZY, Liu ZL, Zhang HJ, Wang J, Ren SC (2020) Protein particles ameliorate the mechanical properties of highly polyunsaturated oil-based whipped cream: a possible mode of action. Food Hydrocoll 99:105350
Daviesa E, Dickinsona E, Bee RD (2001) Orthokinetic destabilization of emulsions by saturated and unsaturated monoglycerides. Int Dairy J 11(10):827–836
Fredrick E (2011) Fat crystallization and partial coalescence in dairy creams: role of monoacylglycerols. PhD Dissertation, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292335230
Fredrick E, Heyman B, Moens K, Fischer S, Verwijlen T, Moldenaers P, Van Der Meeren P, Dewettinck K (2013a) Monoacylglycerols in dairy recombined cream: II. The effect on partial coalescence and whipping properties. Food Res Int 51(2):936–945
Fredrick E, Moens K, Heyman B, Fischer S, Van Der Meeren P, Dewettinck K (2013b) Monoacylglycerols in dairy recombined cream: I. The effect on milk fat crystallization. Food Res Int 51(2):892–898
Gafour W, Aly E (2020) Organoleptic, textural and whipping properties of whipped cream with different stabilizer blends. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 19(4):425–433
Jiang J, Jin Y, Liang XY, Piatko M, Campbell S, Lo SK, Liu YF (2018) Synergetic interfacial adsorption of protein and low-molecular-weight emulsifiers in aerated emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 81:15–22
Kim H-J, Bot A, De Vries ICM, Golding M, Pelan EG (2013) Effects of emulsifiers on vegetable-fat based aerated emulsions with interfacial rheological contributions. Food Res Int 53(1):342–351
Kováčová R, Štětina J, Čurda L (2010) Influence of processing and κ-carrageenan on properties of whipping cream. J Food Eng 99(4):471–478
Li ML, Li Y, Wang RC, Wang YN, Li Y, Zhang LB (2020a) Effects of triglycerol monostearate on physical properties of recombined dairy cream. Int Dairy J 103:104622
Li Y, Li Y, Yuan DD, Wang YN, Li ML, Zhang LB (2020b) The effect of caseins on the stability and whipping properties of recombined dairy creams. Int Dairy J 105:104658
Liang EL, Siva SP, Yong KH, Chan ES, Tey BT (2020) Recent advances of characterization techniques for the formation, physical properties and stability of Pickering emulsion. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 277:102117
Liu PL, Huang LH, Liu TX, Cai YJ, Zeng D, Zhou FB, Zhao MM, Deng XL, Zhao QZ (2021) Whipping properties and stability of whipping cream: the impact of fatty acid composition and crystallization properties. Food Chem 347:128997
Liu ZL, Cao ZY, Zhao MM, Zhang HJ, Wang J, Sun BG (2022) Synergistic influence of protein particles and low-molecular-weight emulsifiers on the stability of a milk fat-based whippable oil-in-water emulsion. Food Hydrocoll 127:107520
Mcclements DJ (2011) Edible nanoemulsions: fabrication, properties, and functional performance. Soft Matter 7(6):2297–2316
Moens K (2018) Fat crystal networks in relation to partial coalescence. PhD. Dissertation, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328091809
Rouimi S, Schorsch C, Valentini C, Vaslin S (2005) Foam stability and interfacial properties of milk protein–surfactant systems. Food Hydrocoll 19(3):467–478
Rousseau D (2000) Fat crystals and emulsion stability—a review. Food Res Int 33(1):3–14
Singh P, Kumar R, Sabapathy SN, Bawa AS (2008) Functional and edible uses of soy protein products. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 7(1):14–28
Sugimoto T, Mori T, Mano JI, Mutoh TA, Shiinoki Y, Matsumura Y (2001) Effects of fat crystallization on the behavior of proteins and lipids at oil droplet surfaces. J Am Oil Chem Soc 78(2):183–188
Szymańska I, Żbikowska A, Marciniak-Łukasiak K (2019) Effect of addition of a marine algae (Chlorella protothecoides) protein preparation on stability of model emulsion systems. J Dispers Sci Technol 41(5):699–707
Tamime AY (2009) Dairy fats and related products. Wiley, Ayr, pp 61–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444316223.ch4
Wang ZJ, Liang GJ, Chen WP, Qie XJ, Fu LW, Li X, He ZY, Zeng MM, Goff HD, Chen J (2022) Effects of soy proteins and hydrolysates on fat globule coalescence and whipping properties of recombined low-fat whipped cream. Food Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09714-7
Wu S, Wang G, Lu Z, Li Y, Zhou X, Chen L, Cao J, Zhang L (2016) Effects of glycerol monostearate and Tween 80 on the physical properties and stability of recombined low-fat dairy cream. Dairy Sci Technol 96(3):377–390
Zhao QZ, Kuang WM, Long Z, Fang M, Liu DL, Yang B, Zhao MM (2013) Effect of sorbitan monostearate on the physical characteristics and whipping properties of whipped cream. Food Chem 141(3):1834–1840
Zhao QZ, Zhao MM, Yang B, Cui C (2009) Effect of xanthan gum on the physical properties and textural characteristics of whipped cream. Food Chem 116(3):624–628
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge the Wilmar Biotechnology Research and Development Center (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., for kind support and providing a facility for the study.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Wilmar Biotechnology Research and Development Center (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Project Nos.WRD-02-C-22-019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xueli Wei: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft. Lingzhi Cheong: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing. Jingjing Gong: Methodology, Formal analysis. Hong Zhang: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. Xuebing Xu and Yanlan Bi: Conceptualization, Methodology and resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Compliance with ethics approval.
Consent to participate
All authors have seen and agreed with the contents of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors are aware of its submission to JFST.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Zhang, H., Cheong, L. et al. Effects of monoacylglycerols with different saturation degrees on physical and whipping properties of milk fat-based whipping creams. J Food Sci Technol 60, 2468–2476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05769-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05769-1