Abstract
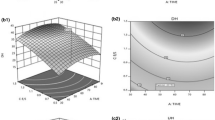
This study aimed to investigate the potential of egg white protein hydrolysate (EWH) as a functional food by identifying the optimum production conditions for EWH with response surface methodology (the results of the sensory evaluation were considered as an essential quality indicator). At the same time, its physicochemical and biological activity was also evaluated. The optimal economic production conditions were selected: substrate concentration of 12.5%, enzyme content of 7.5%, and hydrolysis time at 100 min. The degree of hydrolysis (DH %) was 13.51%. In addition, to the better acceptance of the evaluation, it also helps to reduce the production cost of the protein hydrolysate, which is beneficial to future processing and applications. The antioxidant capacity experiments showed that EWH has good antioxidant activity, which presents a dose-dependent relationship. Hence, this study provides a theoretical basis for future research and application of EWH for processing applications, including dietary supplementation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- EWH:
-
Egg white hydrolysate
- DH:
-
Degree of hydrolysis
- ABS:
-
Absorbance
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
References
Araiza-Calahorra A, Mondor M, Boesch C, Orfila C, Goycoolea FM, Hernández-Álvarez AJ (2022) Chapter 8 - Proteins, peptides, and protein hydrolysates as immunomodulatory and antioxidant agents for the formulation of functional foods. In: Hernández-Ledesma B, Martínez-Villaluenga C (eds) Current advances for development of functional foods modulating inflammation and oxidative stress. Academic Press, New York, pp 137–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823482-2.00016-9
Box GEP, Behnken DW (1960) Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 2(4):455–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1960.10489912
Bueno Gavilá E, Abellán A, Girón F, Cayuela J, Tejada L (2021) Bioactivity of hydrolysates obtained from chicken egg ovalbumin using artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) Proteases. Foods 10:246. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020246
Chalamaiah M, Yu W, Wu J (2018) Immunomodulatory and anticancer protein hydrolysates (peptides) from food proteins: a review. Food Chem 245:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.087
Gazme B, Rezaei K, Udenigwe CC (2022) Epitope mapping and the effects of various factors on the immunoreactivity of main allergens in egg white. Food Funct 13(1):38–51. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1FO01867A
He P, Wang Q, Zhan Q, Pan L, Xin X, Wu H et al (2021) Purification and characterization of immunomodulatory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of duck egg ovalbumin. Food Funct 12(2):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO02674C
Ho H-Y, Ciou J-Y, Qiu Y-T, Hsieh S-L, Shih M-K, Chen M-H et al (2021) Improvement of foaming characteristics and stability of sterilized liquid egg with egg white hydrolysate (EWH). Foods 10(6):1326
Horimoto Y, Lim LT (2017) Effects of different proteases on iron absorption property of egg white hydrolysates. Food Res Int 95:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.02.024
Huang X, Ahn DU (2019) How can the value and use of egg Yolk be increased? J Food Sci 84(2):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14430
Huang P-H, Lu H-T, Wang Y-T, Wu M-C (2011) Antioxidant activity and emulsion-stabilizing effect of pectic enzyme treated pectin in soy protein isolate-stabilized oil/water emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 59(17):9623–9628. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf202020t
Huang P-H, Chiu C-S, Lu W-C, Li P-H (2022) Effect of compositions on physicochemical properties and rheological behavior of gelatinized adzuki-bean cake (Yokan). LWT 168:113870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113870
Jalili-Firoozinezhad S, Filippi M, Mohabatpour F, Letourneur D, Scherberich A (2020) Chicken egg white: hatching of a new old biomaterial. Mater Today 40:193–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2020.05.022
Jiang Z, Kimura Y, Shirouchi B, Tanaka Y, Tsai W-T, Yuan X et al (2021) Dietary egg white protein hydrolysate improves orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats by promoting hepatic phospholipid synthesis and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression. J Nutr Biochem 98:108820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108820
Johny LC, Kudre TG, Suresh PV (2022) Production of egg white hydrolysate by digestion with pineapple bromelain: optimization, evaluation and antioxidant activity study. J Food Sci Technol 59(5):1769–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05188-0
Kiewiet G, Faas M, de Vos P (2018) Immunomodulatory protein hydrolysates and their application. Nutrients 10:904. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070904
Kurutas EB (2016) The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state. Nutr J 15(1):71–71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-016-0186-5
Lee JH, Paik HD (2019) Anticancer and immunomodulatory activity of egg proteins and peptides: a review. Poult Sci 98(12):6505–6516. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez381
Li J, Zhai J, Gu L, Su Y, Gong L, Yang Y et al (2021) Hen egg yolk in food industry—a review of emerging functional modifications and applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 115:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.06.031
Liu J, Jiang H, Zhang M, Gong P, Yang M, Zhang T et al (2022) Ions-regulated aggregation kinetics for egg white protein: a promising formulation with controlled gelation and rheological properties. Int J Biol Macromol 200:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.185
López-Martínez MI, Moreno-Fernández S, Miguel M (2021) Development of functional ice cream with egg white hydrolysates. Int J Gastron Food Sci 25:100334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2021.100334
Mendis E, Rajapakse N, Kim S-K (2005) Antioxidant properties of a radical-scavenging peptide purified from enzymatically prepared fish skin gelatin hydrolysate. J Agric Food Chem 53(3):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048877v
Monkos K (2015) On the possibility of indirect determination of the glass transition temperature of proteins from viscosity measurements and Avramov’s model. Curr Topics Biophys 37(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.2478/ctb-2014-0076
Moraes PZ, Júnior JEGP, Martinez CS, Moro CR, da Silva GC, Rodriguez MD et al (2022) Multi-functional egg white hydrolysate prevent hypertension and vascular dysfunction induced by cadmium in rats. J Funct Foods 94:105131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2022.105131
Moreno-Fernández S, Garcés-Rimón M, Miguel M (2020) Egg-derived peptides and hydrolysates: a new bioactive treasure for cardiometabolic diseases. Trends Food Sci Technol 104:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.08.002
Nasiru MM, Umair M, Boateng EF, Alnadari F, Khan K-UR, Wang Z et al (2022) Characterisation of flavour attributes in egg white protein using HS-GC-IMS combined with E-nose and E-tongue: effect of high-voltage cold plasma treatment time. Molecules (basel, Switzerland) 27(3):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030601
Nasri M (2017) Protein hydrolysates and biopeptides: production, biological activities, and applications in foods and health benefits. A Review. Adv Food Nutr Res 81:109–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2016.10.003
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V et al (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8416763–8416763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Pv S (2022) Protein hydrolysate from duck egg white by Flavourzyme® digestion: process optimisation by model design approach and evaluation of antioxidant capacity and characteristic properties. LWT 156:113018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.113018.
Rabiei S, Rezaei M, Nikoo M, Khezri M, Rafieian-Kopai M, Anjomshoaa M (2022) Antioxidant properties of Klunzinger’s mullet (Liza klunzingeri) protein hydrolysates prepared with enzymatic hydrolysis using a commercial protease and microbial hydrolysis with Bacillus licheniformis. Food Sci Technol Int 28(3):233–246. https://doi.org/10.1177/10820132211005297
Srinivas US, Tan BWQ, Vellayappan BA, Jeyasekharan AD (2019) ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol 25:101084–101084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.101084
Su Y, Wang Y, McClements DJ, Lu C, Chang C, Li J et al (2021) Selective adsorption of egg white hydrolysates onto activated carbon: Establishment of physicochemical mechanisms for removing phenylalanine. Food Chem 364:130285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130285
Sun X, Acquah C, Gazme B, Boachie RT, Nwachukwu ID, Udenigwe CC (2021) Mechanisms of plastein formation influence the IgE-binding activity of egg white protein hydrolysates after simulated static digestion. Food Chem 345:128783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128783
Taktak W, Nasri R, López-Rubio A, Hamdi M, Gómez-Mascaraque LG, Nasri M et al (2021) Enzymatic production of novel European Eel proteins hydrolysates: biological activities, techno-functional properties and maltodextrin-hydrolysates efficient electrosprayability. Int J Pept Res Ther 27(2):1129–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10156-x
Tian Y, Zhu H, Zhang L, Chen H (2022) Consumer preference for nutritionally fortified eggs and impact of health benefit information. Foods 11(8):1145
Villalpando-Rodriguez GE, Gibson SB (2021) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulates different types of cell death by acting as a rheostat. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:9912436–9912436. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9912436
Wang Z, Liu X, Xie H, Liu Z, Rakariyatham K, Yu C et al (2021) Antioxidant activity and functional properties of Alcalase-hydrolyzed scallop protein hydrolysate and its role in the inhibition of cytotoxicity in vitro. Food Chem 344:128566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128566
Wen C, Zhang J, Feng Y, Duan Y, Ma H, Zhang H (2020) Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from watermelon seed protein hydrolysates and their cytoprotective effects on H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem 327:127059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127059
WHO (2007) Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition: report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation [WHO technical report]. 2007. Geneva: World Health Organization WHO technical report series ; no. 935
Wu L, Jiang A, Jing Y, Zheng Y, Yan Y (2017) Antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysate from Douchi by membrane ultrafiltration. Int J Food Prop 20(5):997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1192644
Xiao N, Huang X, He W, Yao Y, Wu N, Xu M et al (2021) A review on recent advances of egg byproducts: Preparation, functional properties, biological activities and food applications. Food Res Int 147:110563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110563
Yap P-G, Gan C-Y (2020) Chicken egg white—advancing from food to skin health therapy: optimization of hydrolysis condition and identification of tyrosinase inhibitor peptides. Foods 9(9):1312
Zhang Y-H, Bai J, Jiang W-N, Zhao C-R, Ji J-J, Wang J-Z et al (2020) Promising hen egg-derived proteins/peptides (EDPs) for food engineering, natural products and precision medicines. Res Vet Sci 128:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.11.011
Acknowledgements
The authors want to acknowledge all the individuals who volunteered for this study.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Republic of China (Grant No. 110-2320-B-992 -001-MY3, 111-2622-E-992 -002—and 111-2221-E-328 -001 -MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, C-YH and SHH; methodology, S-LH, C-WH and J-YC; software, C-KC, and S-LH; investigation, C-CH, and C-WT; resources, C-YH; data curation, SHH, C-CH, and C-YH; writing—original draft preparation, P-HH, and SHH; writing—review and editing, SHH, C-YH, and P-HH; visualization, C-WH, and M-KS, and M-HC; supervision, C-YH, and S-LH; project administration, J-YC, C-WH, and M-KS.; funding acquisition, C-YH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Consent to participate
Before the sensory evaluation of this research, we provided informed consent (supplement material “Informed consent”) to the participants and confirmed that these experiments were conducted according to established ethical guidelines, and informed consent was obtained from the participants, then give them the evaluation and questionnaire (supplement material “Egg white hydrolysates evaluation and questionnaire”).
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, CY., Hazeena, S.H., Hsieh, SL. et al. Investigation of the optimal production conditions for egg white hydrolysates and physicochemical characteristics. J Food Sci Technol 60, 1600–1611 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05708-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05708-0