Abstract
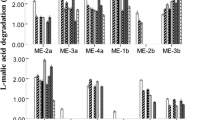
The use of malolactic starter cultures, often offer no guarantee of microbiological success due to the chemical and physical factors (pH, ethanol, SO2, nutrient availability) that occur during the winemaking process. This study was born with the aim of improving the performance of the lactic acid bacteria used as a starter culture in the de-acidification of wines. Two commercial strains of Oenococcus oeni, were used. Was evaluated the effect of exogenous l-proline added during the bacterial growth, on the improvement of their survival in the presence of different ethanol concentrations and their ability to degrade l-malic acid in synthetic wine with the presence of 12% (v/v) and 13% (v/v) of ethanol. The results showed that l-proline improve ethanol tolerance and so the malolactic performances of O. oeni. This work represents an important strategy to ensure good vitality and improve the performance of the malolactic starter.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baliarda A, Robert H, Jebbar M, Blanco C, Deschamps A, Le Marrec C (2003) Potential osmoprotectants for the lactic acid bacteria Pediococcus pentosaceus and Tetragenococcus halophila. Int J Food Microbiol 84:13–20
Betteridge A, Grbin P, Jiranek V (2015) Improving Oenococcus oeni to overcome challenges of wine malolactic fermentation. Trends in Biotechnol 33:547–553
Betteridge AL, Sumby KM, Sundstrom JF, Grbin PR, Jiranek V (2018) Application of directed evolution to develop ethanol tolerant Oenococcus oeni for more efficient malolactic fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:921–932
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carillo P, Gibon Y (2011) Protocol: extraction and determination of L-proline. PrometheusWiki. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/211353600_PROTOCOL_Extraction_and_determination_of_proline. Accessed 12 Feb 2020
Chu-Ky S, Tourdot-Marechal R, Marechal PA, Guzzo J (2005) Combined cold, acid, ethanol shocks in Oenococcus oeni: Effects on membrane fluidity and cell viability. Biochim Biophys Acta 1717:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.09.015
Da Silveira MG, San Romão MV, Loureiro-Dias MC, Rombouts FM, Abee T (2002) Flow cytometric assessment of membrane integrity of ethanol-stressed Oenococcus oeni cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6087–6093 (7a)
Da Silveira MG, Golovina EA, Hoekstra FA, Rombouts FM, Abee T (2003) Membrane fluidity adjustments in ethanol-stressed Oenococcus oeni cells. Appl Environ Microb 69:5826–5832
De Leonardis A, Testa B, Macciola E, Lombardi SJ, Iorizzo M (2015) Exploring enzyme and microbial technology for the preparation of green table olives. Eur Food Res Technol 242:363–370
Hoffmann TV, Blohn C, Stanek A, Moses S, Barzantny H, Bremer E (2012) Synthesis, release, and recapture of compatible solute l-proline by osmotically stressed Bacillus subtilis cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5753–5762
Huffer S, Clark ME, Ning JC, Blanch HW, Clark DS (2011) Role of alcohols in growth, lipid composition, and membrane fluidity of yeasts, bacteria, and archaea. Appl Environ Microb 77:6400–6408
Iorizzo M, Testa B, Lombardi SJ, García-Ruiz A, Muñoz-González C, Bartolomé B, Moreno-Arribas MV (2016) Selection and technological potential of Lactobacillus plantarum bacteria suitable for wine malolactic fermentation and grape aroma release. LWT-Food Sci Technol 73:557–566
Kumar TK, Samuel D, Jayaraman G, Srimathi T, Yu C (1998) The role of proline in the prevention of aggregation during protein folding in vitro. Biochem Mol Biol Int 46:509–517
Liang X, Zhang L, Natarajan SK, Becker DF (2013) Proline mechanisms of stress survival. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:998–1011. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5074
Liu XT, Hou CL, Zhang J, Zeng XF, Qiao SY (2014) Fermentation conditions influence the fatty acid composition of the membranes of Lactobacillus reuteri I 5007 and its survival following freeze drying. Lett Appl Microbiol 59:398–403
Lombardi SJ, Pannella G, Iorizzo M, Moreno-Arribas MV, Tremonte P, Succi M, Sorrentino E, Macciola VD, Renzo M, Coppola R (2018) Sequential inoculum of Hanseniaspora guilliermondii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae for winemaking Campanino on an industrial scale. World J Microb Biot 34:161
Maitre M, Weidmann S, Dubois-Brissonnet F, David V, Covès J, Guzzo J (2014) Adaptation of the wine bacterium Oenococcus oeni to ethanol stress: role of the small heat shock protein Lo18 in membrane integrity. App Environ Microbiol 80:2973–2980. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.04178-13
Margalef-Català M, Araque I, Weidmann S, Guzzo J, Bordons A, Reguant C (2016) Protective role of glutathione addition against wine-related stress in Oenococcus oeni. Food Res Int 90:8–15
Marielle B, Sarrah G (2017) Assessment of bacterial membrane fluidity by flow cytometry. J Microbiol Meth 143:50–57
Martos GI, Minahk CJ, Font de Valdez G, Morero R (2007) Effects of protective agents on membrane fluidity of freeze dried Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:282–288
Papadimitriou K, Alegría Á, De Bron PA, Angelis M, Gobbetti M, Kleerebezem M, Turroni F (2016) Stress physiology of lactic acid bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80:837–890
Samuel D, Kumar TK, Ganesh G, Jayaraman G, Yang PW, Chang MM, Trivedi VD, Wang SL, Hwang KC, Chang DK, Yu C (2000) l-proline inhibits aggregation during protein refolding. Protein Sci 9:344–352
Silveira MG, Baumgärtner M, Rombouts FM, Abee T (2004) Effect of adaptation to ethanol on cytoplasmic and membrane protein profiles of Oenococcus oeni. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2748–2755
Succi M, Pannella G, Tremonte P, Tipaldi L, Coppola R, Iorizzo M, Lombardi SJ, Sorrentino E (2017) Sub-optimal pH preadaptation improves the survival of Lactobacillus plantarum strains and the malic acid consumption in wine-like medium. Front Microbiol 8:470
Takagi H, Sakai K, Morida K, Nakamori S (2000) l-proline accumulation by mutation or disruption of the l-proline oxidase gene improves resistance to freezing and desiccation stresses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184:103–108
Testa B, Lombardi SJ, Tremonte P, Succi M, Tipaldi L, Pannella G, Sorrentino E, Iorizzo M, Coppola R (2014) Biodiversity of Lactobacillus plantarum from traditional Italian wines. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:2299–2305
Testa B, Lombardi SJ, Macciola E, Succi M, Tremonte P, Iorizzo M (2019) Efficacy of olive leaf extract (Olea europaea L. cv Gentile di Larino) in marinated anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus, L.) process. Heliyon 5:e01727
Testa B, Lombardi SJ, Iorizzo M, Letizia F, Martino C, Di Renzo M, Strollo D, Tremonte P, Pannella G, Ianiro M, Sorrentino E, Succi M, Coppola R (2020) Use of strain Hanseniaspora guilliermondii BF1 for a winemaking process of white grapes Vitis vinifera cv Fiano. Eur Food Res Technol 246:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03424-8
Van de Guchte M, Serror P, Chervaux C, Smokvina T, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (2002) Stress responses in lactic acid bacteria. A Van Leeuw J Microb 82:187–216
Wen-ying Z, Zhen-kui K (2013) Advanced progress on adaptive stress response of Oenococcus oeni. J Northeast Agri Univ (English Edition) 20:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1006-8104(13)60015-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Martino, C., Testa, B., Letizia, F. et al. Effect of exogenous proline on the ethanolic tolerance and malolactic performance of Oenococcus oeni. J Food Sci Technol 57, 3973–3979 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04426-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04426-1