Abstract
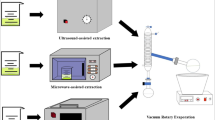
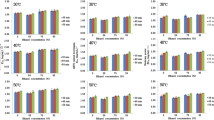
The aim of this paper is to investigate the combined impact of pulsed electric field (PEF) and ultrasound (US) to evaluate the physicochemical, bioactive compounds and chemical structure of almond extract. Almond extract was first treated with PEF and then with US. Combined treatment (PEF–US) has attained the highest value of total phenolics, total flavonoids, condense tannins, anthocyanin contents and antioxidant activity in DPPH, reducing power and metal chelating activity than all other treatments. Among all those treatments, there was slightly visible difference in the color. Moreover, FT-IR spectra indicate that the effect of PEF-US on almond extract did not produce new carbonyl compounds, but led to the higher concentration of these compounds. This study demonstrated that the PEF-US could be useful for the extraction of bioactive compounds as well as improving the stability of volatile compounds.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aadil RM, Zeng X-A, Han Z, Sun D-W (2013) Effects of ultrasound treatments on quality of grapefruit juice. Food Chem 141:3201–3206
Aadil RM et al (2018) Combined effects of pulsed electric field and ultrasound on bioactive compounds and microbial quality of grapefruit juice. J Food Process Preserv 42:e13507
Abenoza M, Benito M, Saldaña G, Álvarez I, Raso J, Sánchez-Gimeno A (2013) Effects of pulsed electric field on yield extraction and quality of olive oil. Food Bioproc Technol 6:1367–1373
Babu MA, Suriyakala M, Gothandam K (2012) Varietal impact on phytochemical contents and antioxidant properties of Musa acuminata (banana). J Pharm Sci Res 4:1950
Borràs E, Amigo JM, van den Berg F, Boqué R, Busto O (2014) Fast and robust discrimination of almonds (Prunus amygdalus) with respect to their bitterness by using near infrared and partial least squares-discriminant analysis. Food Chem 153:15–19
Corrales M, Toepfl S, Butz P, Knorr D, Tauscher B (2008) Extraction of anthocyanins from grape by-products assisted by ultrasonics, high hydrostatic pressure or pulsed electric fields: a comparison. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 9:85–91
Cravotto G, Boffa L, Mantegna S, Perego P, Avogadro M, Cintas P (2008) Improved extraction of vegetable oils under high-intensity ultrasound and/or microwaves. Ultrasonics sonochem 15:898–902
Cvetković A, Jurina T, Valinger D, JURINJAK TUŠEK A, Benković M, GAJDOŠ KLJUSURIĆ J (2018) The estimation of kinetic parameters of the solid-liquid extraction process of the lavender flower (Lavandula × hybrida L.). Croat J Food Sci Technol 10:64–72
Gabrić D, Barba F, Roohinejad S, Gharibzahedi SMT, Radojčin M, Putnik P, Bursać Kovačević D (2018) Pulsed electric fields as an alternative to thermal processing for preservation of nutritive and physicochemical properties of beverages: a review. J Food Proc Eng 41:e12638
Gama T, Wallace HM, Trueman SJ, Hosseini-Bai S (2018) Quality and shelf life of tree nuts: a review. Sci Hortic 242:116–126
Grimi N, Mamouni F, Lebovka N, Vorobiev E, Vaxelaire J (2010) Acoustic impulse response in apple tissues treated by pulsed electric field. Biosys Eng 105:266–272
Ince AE, Sahin S, Sumnu G (2014) Comparison of microwave and ultrasound-assisted extraction techniques for leaching of phenolic compounds from nettle. J Food Sci Technol 51:2776–2782
Jeyaratnam N, Nour AH, Akindoyo JO (2016) Comparative study between hydrodistillation and microwave-assisted hydrodistillation for extraction of Cinnamomum Cassia oil. J Eng Appl Sci 11:2647–2652
Lee J, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE (2005) Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: collaborative study. J AOAC Inter 88:1269–1278
Lin S, Guo Y, You Q, Yin Y, Liu J (2012) Preparation of antioxidant peptide from egg white protein and improvement of its activities assisted by high-intensity pulsed electric field. J Sci Food Agri 92:1554–1561
Liu B, Ma Y, Liu Y, Yang Z, Zhang L (2013) Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and antioxidant activity of flavonoids from Adinandra nitida leaves. Trop J Pharm Res 12:1045–1051
Lu CW, Yin YG (2018) Comparison of antioxidant activity of ginseng root extracts obtained by pulsed electric field and hydrolytic enzyme processing. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 185(1):157
Lucchesi ME, Chemat F, Smadja J (2004) Solvent-free microwave extraction of essential oil from aromatic herbs: comparison with conventional hydro-distillation. J Chromatogr A 1043:323–327
Luengo E, Álvarez I, Raso J (2013) Improving the pressing extraction of polyphenols of orange peel by pulsed electric fields. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 17:79–84
Maksimović Z, Malenčić Đ, Kovačević N (2005) Polyphenol contents and antioxidant activity of Maydis stigma extracts. Biores Technol 96:873–877
Martín O, Zhang Q, Castro A, Barbosa-Cánovas G, Swanson B (1994) Revisión: empleo de pulsos eléctricos de alto voltaje para la conservación de alimentos. Microbiología e ingeniería del proceso. Rev Esp Cienc Tecnol Aliment 1:1–34
Mtaoua H, Sánchez-Vega R, Ferchichi A, Martín-Belloso O (2017) Impact of high-intensity pulsed electric fields or thermal treatment on the quality attributes of date juice through storage. J Food Process Preserv 41:e13052
O’sullivan J, Murray B, Flynn C, Norton I (2016) The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food hydrocol 53:141–154
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS, Vyvyan JA (2008) Introduction to spectroscopy, 4th edn. Brookescole Publishers, California
Ravanfar R, Tamadon AM, Niakousari M (2015) Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of anthocyanins from red cabbage using Taguchi design method. J Food Sci Technol 52:8140–8147
Reátegui JLP, da Fonseca Machado AP, Barbero GF, Rezende CA, Martínez J (2014) Extraction of antioxidant compounds from blackberry (Rubus sp.) bagasse using supercritical CO2 assisted by ultrasound. J Supercritl Fluids 94:223–233
Rhazi N, Hannache H, Oumam M, Sesbou A, Charrier B, Pizzi A, Charrier-El Bouhtoury F (2015) Green extraction process of tannins obtained from Moroccan Acacia mollissima barks by microwave: modeling and optimization of the process using the response surface methodology RSM. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.04.032
Roobab U, Aadil RM, Madni GM, Bekhit AED (2018) The impact of nonthermal technologies on the microbiological quality of juices: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 17:437–457
Saldaña G, Cebrián G, Abenoza M, Sánchez-Gimeno C, Alvarez I, Raso J (2017) Assessing the efficacy of PEF treatments for improving polyphenol extraction during red wine vinifications. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 39:179–187
Santhirasegaram V, Razali Z, Somasundram C (2013) Effects of thermal treatment and sonication on quality attributes of Chokanan mango (Mangifera indica L.) juice. Ultrason Sonochem 20:1276–1282
Shoji T (2007) Polyphenols as natural food pigments changes during food processing. Am J Food Technol 2:570–581
Singh B, Singh N, Thakur S, Kaur A (2017) Ultrasound assisted extraction of polyphenols and their distribution in whole mung bean, hull and cotyledon. J Food Sci Technol 54:921–932
Soria AC, Villamiel M (2010) Effect of ultrasound on the technological properties and bioactivity of food: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 21:323–331
Szalontai B, Kóta Z, Nonaka H, Murata N (2003) Structural consequences of genetically engineered saturation of the fatty acids of phosphatidylglycerol in tobacco thylakoid membranes. An FTIR study. Biochemistry 42:4292–4299
Teh SS, Niven BE, Bekhit AEDA, Carne A, Birch EJ (2015) Microwave and pulsed electric field assisted extractions of polyphenols from defatted canola seed cake. Inter J Food Sci Technol 50:1109–1115
Tiwari B, O’donnell C, Patras A, Brunton N, Cullen P (2009) Stability of anthocyanins and ascorbic acid in sonicated strawberry juice during storage. Eur Food Res Technol 228:717–724
Wu C, Wang F, Liu J, Zou Y, Chen X (2015) A comparison of volatile fractions obtained from Lonicera macranthoides via different extraction processes: ultrasound, microwave, Soxhlet extraction, hydrodistillation, and cold maceration. Integ Med Res 4:171–177
Yan C, XING YU J, Xing T, XIAO QING C (2008) Comparison of volatile components from Marchantia convoluta obtained by microwave extraction and phytosol extraction. J Chilean Chem Soc 53:1518–1522
Zhou Y, Zhao X, Huang H (2015) Effects of pulsed electric fields on anthocyanin extraction yield of blueberry processing by-products. J Food Process Preserv 39:1898–1904
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the National “Thirteenth Five” Key Research Project (2017YFD0400502), the 111 Project (B17018), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21576099) and the S&T projects of Guangdong Province (2017B020207001 and 2015A030312001). In addition, Muhammad Faisal Manzoor is in receipt of a financial support for PhD scholarship from the China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manzoor, M.F., Zeng, XA., Rahaman, A. et al. Combined impact of pulsed electric field and ultrasound on bioactive compounds and FT-IR analysis of almond extract. J Food Sci Technol 56, 2355–2364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03627-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03627-7