Abstract
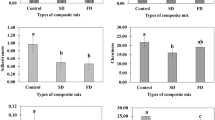
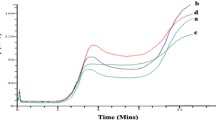
Four different Multigrain Premixes (MGPs) namely MGP I, MGP II, MGP III, MGP IV were developed to select the best premix for preparation of biscuits based on nutritional value and biscuit quality. The MGPs were prepared using cereals (barley, sorghum, maize, oats), pulses (chickpea dhal, green gram, peas, soya flour), millets (pearl millet, finger millet) and wheat germ each at 20 % level. The MGPs developed had 22.91–27.84 % protein, 16.82–18.72 % dietary fiber and 3.11–3.46 % minerals. The wheat flour was replaced with MGPs separately at different levels of 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 %. The incorporation of these MGPs significantly (p ≤ 0.05) decreased the water absorption (56.0–50.9 %), peak viscosity (273.67–154.92 RVU), biscuit spread ratio (10.28–8.15) and increased the pasting temperature (67.10–79.20 °C), dough hardness (311.66–460.26 N) and biscuit breaking strength (13.25–28.68 N). SEM studies showed that incorporation of MGP disrupted the protein matrix. Among the MGPs, MGP III was found to be more suitable even at the 40 % level for obtaining nutritious multigrain biscuits with higher protein, dietary fiber, and mineral content.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC International (2000) Approved methods of the Association of Cereal Chemists International (10th Ed.) St. Paul, Minnesota, USA
Aleem ZMD, Genitha TR, Syed IS (2012) Effects of defatted soy flour incorporation on physical, sensorial and nutritional properties of biscuits. J Food Proc Technol 3:4
Amado R, Arrigoni E (1992) Nutritive and functional properties of wheat germ. Int Food Ingredients 4:30–34
Anuradha DD, Sharduli SK, Sahoo AK, Ranvee RC, Dandge PB (2010) Effect of supplementation of malted finger millet flour on the nutritional and sensorial quality characteristics of cake. Adv J Food Sci Technol 2:67–71
Asp NG, Johabsson CG, Hallmer H, Siljestrom M (1983) Rapid enzymatic assay of insoluble and soluble dietary fiber. J Agric Food Chem 31:476–482
Bourne MC (1978) Texture profile analysis. Food Technol 32(62–66):72
Callejo MJ, Bujeda C, Rodriguez G, Chaya C (2009) Alveoconsistograph evaluation of rheological properties of rye dough’s. Span J Agric Res 7:638–644
Crassina A, Sheetal G, Venkateshwara RG (2012) Effect of native and germinated finger millet flour on rheological and sensory characteristics of biscuits. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:2413–2420
Dachana KB, Jyotsna R, Indrani D, Prakash J (2010) Effect of dried Moringa (Moringa oleifera lam) leaves on rheological, microstructural, nutritional, textural and organoleptical characteristics of cookies. J Food Qual 33:660–677
Flint O, Moss R, Wade P (1970) A comparative study of microstructure of different types of biscuits and their dough. Food Trade Rev 40:32–39
Francine Z, Yulia B, Susan D, Arntfield (2011) Physical and nutritional evaluation of wheat cookies supplemented with pulse flours of different particle sizes. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:2070–2076
Gains CS (1991) Instrumental measurement of the hardness of cookies and crackers. Cereal Foods World 36:989–991–994, 996
Gunathilake KDPP, Yalegama C, Kumara AAN (2009) Use of coconut flours as a source of protein and dietary fiber in wheat bread. Asian Food Agro-Ind 2:382–391
Hamaker BR, Griffin VK (1993) Effect of disulfide bond-containing protein on rice starch gelatinization and pasting. Cereal Chem 70:377–380
Hoseney CR (1994) Principles of cereal science and technology. AACC Press, St. Paul, p. 87
Indrani D, Sowmya C, Jyotsna R, Venkateshwara RG (2010) Multigrain bread – its dough rheology, microstructure, quality and nutritional characteristics. J Texture Stud 41:302–319
Indrani D, Shwetha P, Soumya C, Jyotsna R, Venkateshwara RG (2011) Effect of multigrain on rheological, micro structural and quality characteristics of north Indian parotta –an Indian flat bread. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:719–724
Izydorczyk MS, Dexte JE (2008) Barley b-glucans and arabinoxylans: molecular structure, physicochemical properties, and uses in food products–a review. Food Res Int 41:850–868
Jyotsna R, Shwetha L, Jyothilakshmi VRG (2012) Influence of green gram flour (Phaseolus Aureus) on the rheology, microstructure and quality of cookies. J Texture Stud 43:350–360
Khan MA, Mahesh C, Semwal AD, Sharma GK (2015) Effect of spinach powder on physico-chemical, rheological, nutritional and sensory characteristics of chapathi premixes. J Food Sci Technol 52(4):2359–2365
Kulp K, Olewink M, Lorenz K (1991) Starch functionality in cookie systems. Cereal Chem 43:53–57
Kumar KA, Sharma GK, Khan MA, Semwal AD (2015) Optimization of multigrain premix for high protein and dietary fibre biscuits using response surface methodology (RSM). Food Nutr Sci 6:747–756. doi:10.4236/fns.2015.69077
Larmond E (1997) Laboratory methods for sensory evaluation of foods. Canada Department of Agri.Publication, Ottawa
Lee KA, Brennand CP (2005) Physico-chemical, textural and sensory properties of a fried cookie system containing soy protein isolate. Int J Food Sci Technol 40:501–508
Malhotra M, Verma V (2015) Demand for bakery on the raise due to low price and high nutrient value. FnBnews.com. http://www.fnbnews.com/article/print.asp?articleid=36564
Mc Watters KH (1977) Cooking, baking properties of defatted peanut, soybean and field pea flours. Cereal Chem 55:853–863
Nandeesh K, Jyotsna R, Venkateswara RG (2009) Effect of differently treated wheat bran on rheology, microstructure and quality characteristics of soft dough biscuits. J Food Proc Preser 35:179–200
Nielsen SS (1998) Color analysis. In: Food analysis. 2nd ed. Aspen Publishers, Inc., Gaithersburg, pp 601–612
Nirmala M, Jyotsna R, Jeyarani T, Venkateshwara RG (2011) Influence of debittered, defatted fenugreek seed powder and flax seed powder on the rheological characteristics of dough and quality of cookies. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:336–344
Pomeranz Y, Meyer D, Seibel W (1984) Wheat, wheat-rye and rye dough and bread studied by scanning electron microscope. Cereal Chem 61:53–59
Ritika B, Baljeet SY, Nisha D (2012) Effect of incorporation of plantain and chickpea flours on the quality characteristics of biscuits. J Food Sci Technol 49:207–213
Rojas JT, Rosell CM, Benedito DBC, Perez MI, Lluch MA (2000) The baking process of wheat rolls followed by cryo scanning electron microscopy. Eur Food Res Technol 212:57–63
Sanaa R, El-syed MAA (2006) Pasting properties of starch and protein in selected cereals and quality of their food products. Food Chem 95:9–18
Santiago P, Elias M, Carlos O, Maria H, Sanchez (2013) Effect of soy flour and whey protein concentrates on cookie colour LWT Food Sci Technol 50:120–125
Shivani B, Sudha ML (2011) Nutritional, micro structural, rheological and quality characteristics of biscuits using processed wheat germ. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:474–479
Sridevi SPL, Sarojini KS (2013) Formulation of value added biscuits using defatted coconut flour. Am J Food Technol 8:207–212
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1960) Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw – Hill, New York, pp. 99–131
Declaration of conflicting interest
This article has not been published previously and neither is under consideration for publication elsewhere. The publication is approved by all authors and tacitly by the responsible authorities where the work was carried out, and that, if accepted, it will not be published elsewhere, including electronically in the same form, in English or in any other language, without the written consent of the copyright-holder.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.A., Sharma, G.K., Khan, M.A. et al. Development of multigrain premixes—its effect on rheological, textural and micro-structural characteristics of dough and quality of biscuits. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7759–7770 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1950-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1950-9