Abstract
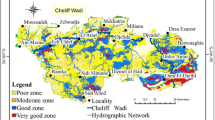
In this research, a standard methodology has been applied to delineate groundwater resource potential zonation based on integrated remote sensing (RS), geographic information system (GIS), and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) techniques in Leylia–Keynow watershed, southwest of Iran. A total of five sets of criteria/factors (including lineament density, rainfall, lithology, slope, and drainage density) believed to be influencing groundwater storage potential in the area were selected. Each criterion/factor was assigned appropriate weight based on Saaty’s 9-point scale and the weights were normalized through the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). The process was integrated in the GIS environment to produce the groundwater potential prediction map for the area. The fi9-p groundwater prospect map obtained was classified as excellent potential, very good potential, good potential, moderate potential, and poor potential zone. The obtained results indicated that only 21% (122 km2) of the study area exhibit poor groundwater potential, whereas most of the regions (326 km2) in the research showed good to excellent groundwater potential. Also, about 24% (141 km2) was classified as having moderate groundwater potential. The good to excellent potential zones are characterized by the higher lineament density, higher rainfall, and lithology type such as limestone, whereas the poor to moderate groundwater potential zones are characterized by the lesser lineament density, lower rainfall, lithology type of shale and marl as well as shale and limestone. Based on the obtained evidences, the tectonic structures had an important role in fracturing and crushing of limestone units in the area and so are vital for karst and ground water sources development. The demarcation of groundwater potential zones in the Leylia–Keynow watershed will be helpful for future planning, development and management of the groundwater resources.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel OT, Tijani M (2011) Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach to groundwater potential assessment in the basement terrain of Ekiti area southwestern Nigeria. Mater Geoenviron 58(3):303–328
Adiat KAN, Nawawi MNM, Abdullah K (2012) Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based elementary multi criteria decision analysis as a spatial prediction tool–A case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. J Hydrol 440:75–89
Althuwaynee OF, Pradhan B, Park HJ, Lee JH (2014) A novel ensemble bivariate statistical evidential belief function with knowledge-based analytical hierarchy process and multivariate statistical logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping. CATENA 114:21–36
Arkoprovo B, Adarsa J, Shashi Prakash S (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using satellite remote sensing and geographic information techniques: a case study from Ganjam district, Orissa, India. Res J Recent Sci 9:59–66
Bera K, Bandyopadhyay J (2012) Groundwater potential mapping in Dulung watershed using remote sensing and GIS techniques, West Bengal, India. Int J Sci Res Publ 2(12):1–7
Chandio IA, Matori ANB, WanYusof KB, Talpur MAH, Balogun AL, Lawal DU (2013) GIS-based analytic hierarchy process as a multicriteria decision analysis instrument: a review. Arab J Geosci 6(8):3059–3066
Chitsazan M, Vardanjani HK, Karimi H, Charchi A (2015) A comparison between karst development in two main zones of Iran: case study—Keyno anticline (Zagros Range) and Shotori anticline (Central Iran). Arab J Geosci 8(12):10833–10844
Chowdary VM, Chakraborthy D, Jeyaram A, Krishna Murthy YVN, Sharma JR, Dadhwal VK (2013) Multi-criteria decision making approach for watershed prioritization using analytic hierarchy process technique and GIS. Water Resour Manag 27:3555–3571
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur District, West Bengal using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ Earth Sci 59(6):1209–1222
Chung CJF, Fabbri AG (2003) Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Nat Hazards 30(3):451–472
Deepika B, Avinash K, Jayappa KS (2013) Integration of hydrological factors and demarcation of groundwater prospect zones: insights from remote sensing and GIS techniques. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1319–1338
Dinesh Kumar PK, Gopinath G, Seralathan P (2007) Application of remote sensing and GIS for the demarcation of groundwater potential zones of a river basin in Kerala, southwest cost of India. Int J Remote Sens 28(24):5583–5601
Dunning DJ, Ross QE, Merkhofer MW (2000) Multiattribute utility analysis for addressing Section 316 (b) of the Clean Water Act. Environ Sci Policy 3:7–14
Eastman JR (2003) IDRISI Kilimanjaro: guide to GIS and image processing. Clark Labs, Clark University, Worcester, pp 328
Edet AE, Okereke CS, Teme SC, Esu EO (1998) Application of remote-sensing data to groundwater exploration: a case study of the Cross River State, southeastern Nigeria. Hydrogeol J 6:394–404
Ettazarini S (2007) Groundwater potential index: a strategically conceived tool for water research in fractured aquifers. Environ Geol 52:477–487
Flug M, Seitz HLH, Scott JF (2000) Multicriteria decision analysis applied to Glen Canyon Dam. J Water Resour Plan Manage ASCE 126(5):270–276
Gitas IZ, Ayanz JSM, Chuvieco BDE, Camia A (2014) Advances in remote sensing and GIS applications in support of forest fire management. Int J Wildland Fire 23:603–605
Gowd SS (2004) Electrical resistivity survey to delineate groundwater potential aquifers in Peddavanka watershed, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 46:118–131
Hajkowicz S, Higgins A (2008) A comparison of multiple criteria analysis techniques for water resource management. Eur J Oper Res 184:255–265
Israil M, Al-hadithi M, Singhal DC (2006) Application of a resistivity survey and geographical information system (GIS) analysis for hydrogeological zoning of a piedmont area, Himalayan foothill region, India. Hydrogeol J 14:753–759
Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manag 21(2):427–467
Jha MK, Chowdary VM, Chowdhury A (2010) Groundwater assessment in Salboni Block, West Bengal (India) using remote sensing, geographical information system and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Hydrogeol J 18(7):1713–1728
Joubert A, Stewart TJ, Eberhard R (2003) Evaluation of water supply augmentation and water demand management options for the City of Cape Town. J Multi-Criteria Decis Anal 12(1):17–25
Junge B, Alabi T, Sonder K, Marcus S, Abaidoo R, Chikoye D, Stahr K (2010) Use of remote sensing and GIS for improved natural resources management: case study from different agroecological zone of West Africa. Int J Remote Sens 31:5116–6141
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh NS (2014) Identification of potential groundwater recharge zones in Vaigai upper basin, Tamil Nadu, using GIS-based analytical hierarchical process (AHP) technique. Arab J Geosci 7:1385–1401
Kumar T, Gautam AK, Kumar T (2014) Appraising the accuracy of GIS multi-criteria decision making technique for delineation of groundwater potential zone. Water Resour Manage 28:4449–4466
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of groundwater potential in a Semi-Arid region of india using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour Manage 25:1359–1386
Madrucci V, Taioli F, Cesar De Araujo C (2008) Groundwater favorability map using GIS multicriteria data analysis on crystalline terrain, Sao Paulo State, Brazil. J Hydrol 357:153–173
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing. GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3(2):189–196
Malczewski J (1999) GIS and Multicriteria decision analysis. Wiley, New York
Mallick J, Singh CK, Al-Wadi H, Ahmed M, Rahman A, Shashtri S, Mukherjee S (2014) Geospatial and geostatistical approach for groundwater potential zone delineation. Hydrol Processes. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10153
Manap MA, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF, Pradhan B, Surip N (2011) A knowledge-driven GIS modeling technique for groundwater potential mapping at the Upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6:1621–1637
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2014) Regional prediction of groundwater potential mapping in a multifaceted geology terrain using GIS-based Dempster-Shafer model. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1391-1
Moghaddam DD, Rezaei M, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghie ZS, Pradhan B (2013) Groundwater spring potential mapping using bivariate statistical model and GIS in the Taleghan watershed Iran. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1161-5
Mohammadi-Behzad HR (2016) Investigation of recharge sources karstic aquifers by using physico-chemical parameters and stable isotopes (18O and 2H) in NE Khuzestan. Unpublished PhD thesis, Ahvaz, University of Shahid Chamran, p 222
Muheeb MA, Rasheed AJ (2009) Evaluation of aquifers vulnerability to contamination in the Yarmouk river watershed, Jordan, based on DRASTIC method. Arab J Geosci 3:273–282
Murthy KSR, Mamo AG (2009) Multi-criteria decision evaluation in groundwater zones identification in Moyale-Teltele subbasin, South Ethiopia. Int J Remote Sens 30:2729–2740
Nampak H, Pradhan B, Manap MA (2014) Application of GIS based data driven evidential belief function model to predict groundwater potential zonation. J Hydrol 513:283–300
Pandian M, Kumanan CJ (2013) Geomatics approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques in part of Trichy and Karur district, Tamilnadu, India. Appl Water Sci 5(2):234–240
Pietersen K (2006) Multiple criteria decision analysis (MCDA): a tool to support sustainable management of groundwater resources in South Africa. Water SA 32(2):119–128
Pinto D, Shrestha S, Babel MS, Ninsawat S (2015) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the Comoro watershed, Timor Leste using GIS, remote sensing and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0270-6
Pourghasemi HR, Moradi HR, Fatemi Aghda SM, Gokceoglu C, Pradhan B (2012) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping with probabilistic likelihood ratio and spatial multi-criteria evaluation models (North of Tehran, Iran). Arab J Geosci 7(5):1857–1878
Pradhan B (2009) Groundwater potential zonation for basaltic watersheds using satellite remote sensing data and GIS techniques. Cent Eur J Geosci 1(1):120–129
Prasad RK, Mondal NC, Banerjee P, Nanda Kumar MV, Singh VS (2008) Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hard rock through the application of GIS. Environ Geol 55:467–475
Rahmati O, Nazari Samani A, Mahdavi M, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2014) Groundwater potential mapping at Kurdistan region of Iran using analytic hierarchy process and GIS. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1668-4
Rao YS, Jugran DK (2003) Delineation of groundwater potential zones and zones of groundwater quality suitable for domestic purposes using remote sensing and GIS. Hydrol Sci J 48(5):821–833
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty TL (1986) Axiomatic foundation of the analytic hierarchy process. Manage Sci 32:841–855
Saaty TL (1992) The hierarchon: a dictionary of hierarchies. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh, p 496
Sener E, Davraz A, Ozcelik M (2005) An integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigations: a case study in Burdur, Turkey. Hydrogeol J 13(5–6):826–834
Shahid S, Nath SK, Roy J (2000) Groundwater potential modeling in a softrock area using a GIS. Int J Remote Sens 21(9):1919–1924
Shekhar S, Pandey AC (2014) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in hard rock terrain of India using remote sensing, geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques. Geocarto Int 30(4):402–442
Solomon S, Quiel F (2006) Groundwater study using remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) in the central highlands of Eritrea. Hydrogeol J 14:729–741
Sree Devi PDS, Srinivasulu S, Raju KK (2001) Hydrogeomorphological and groundwater prospects of the Pageru river basin by using remote sensing data. Environ Geol 40:1088–1094
Srivastava PK, Bhattacharya AK (2006) Groundwater assessment through an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS and resistivity techniques: a case study from a hard rock terrain. Int J Remote Sens 27(20):4599–4620
Subba Rao N, Chakradhar GKJ, Srinivas V (2001) Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing techniques in and around Gunur town, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 29:69–78
Teeuw RM (1995) Groundwater exploration using remote sensing and a low-cost geographical information system. Hydrogeol J 3:21–30
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the facilities provided by the Chairman, Department of Geology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi-Behzad, H.R., Charchi, A., Kalantari, N. et al. Delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing (RS), geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques: a case study in the Leylia–Keynow watershed, southwest of Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 34, 1307–1319 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0420-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0420-7