Abstract
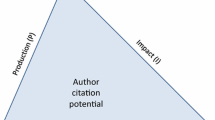
This article mainly aims to investigate the relevance of a scientific productivity model (based on experts’ opinions) to highly cited authors. To this end, this study intends to first identify the scientific productivity model based on experts’ opinions and then examine it among the highly cited authors’ community. The present study was conducted by a mixed quantitative and qualitative method on two statistical communities, 12 experts (who were mainly active in scientific productivity), and 235 highly cited authors in the world participated in this research. Research data were collected using such tools as a checklist, questionnaires, and the Clarivate Analytics-WoS database and analyzed with SPSS-19 and LISREL 8 software. The scientific productivity model of highly cited authors was examined by the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). This three-factor model (including individual, organizational, and bibliometric factors), which according to CFA load factors, shows that (1) the bibliographic factor (loading factor 1), (2) the individual factor (loading factor 0.69), and (3) the organizational factor (loading factor 0.63) are effective among highly cited authors (based on the scientific productivity model). Besides, the scientific productivity model fits among the community of highly cited authors through the world based on experts’ opinions. The combination of quantitative and qualitative factors presented in this model can effectively provide the basis for individual and organizational scientific development and pave the way for individuals and organizations to promote scientific productivity. In addition, the result of this research can be effective for improving and developing scientometric indicators.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
We confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the supplementary of the article.
Notes
According to the economic definition of productivity: the ratio of “output” to “input.”.
See Ruiz-Castillo (2016) for more information.
For the sake of brevity, data on prioritizing “each factor’s items” based on experts’ opinions are provided in the supplementary section.
Field weighted citation index.
References
Abramo, G., & D’Angelo, C. A. (2014). How do you define and measure research productivity?. Scientometrics, 101(2), 1129–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1269-8
Abramo, G., D’Angelo, C. A., & Caprasecca, A. (2009). The contribution of star scientists to overall sex differences in research productivity. Scientometrics, 81(1), 137–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-008-2131-7
Addis, E., & Pagnini, C. (2010). Scientific excellence. Meta-analysis of gender and science research–Topic report, pp. 1–90, Retrieved 2018, Dec. 25, from http://www.genderandscience.org/doc/TR5_Excellence.pdf
Aksnes, D. W., & Taxt, R. E. (2004). Peer reviews and bibliometric indicators: A comparative study at a Norwegian university. Research Evaluation, 13(1), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.3152/147154404781776563
Ali Beigi, A. H. (2008). Research productivity analysis of faculty members: A case study of Razi University. Research and Planning in Higher Education, 13(4), 125–155. [In Persian].
Allison, P. D., & Long, J. S. (1990). Departmental effects on scientific productivity. American Sociological Review, 55(4), 469–478. https://doi.org/10.2307/2095801
Ayre, C., & Scally, A. J. (2014). Critical values for Lawshe’s content validity ratio: revisiting the original methods of calculation. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 47, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748175613513808
Azoulay, P., Ding, W., & Stuart, T. (2007). The determinants of faculty patenting behavior: demographics or opportunities?. Economic Behavior & Organization, 63(4), 599–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2006.05.015
Bean, J. P. (1982, March). A causal model of faculty research productivity. Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, (pp. 3–30). New York: American Educational Research Association.
Bland, C. J., Center, B. A., Finstad, D. A., Risbey, K. R., & Staples, J. G. (2005). A theoretical, practical, predictive model of faculty and department research productivity. Academic Medicine, 80(3), 225–237.
Boaden, R. J., & Cilliers, J. J. (2001). Quality and the research assessment exercise: Just one aspect of performance? Quality Assurance in Education, 9(1), 5–13. https://doi.org/10.1108/09684880110381283
Boardman, C., & Bozeman, B. (2015). Academic faculty as intellectual property in university-industry research alliances. Economics of Innovation and New Technology, 24(5), 403–420. Https://doi/abs/10.1080/10438599.2014.988499.
Bonaccorsi, A., & Daraio, C. (2003). A robust nonparametric approach to the analysis of scientific productivity. Research Evaluation, 12(1), 47–69. https://doi.org/10.3152/147154403781776726
Bornmann, L., de Moya Anegón, F., & Leydesdorff, L. (2010, September, 9–11). Does scientific advancement lean on the shoulders of mediocre research? An investigation of the Ortega hypothesis [Paper presentation]. In Eleventh International Conference on Science and Technology Indicators, University of Leiden, Netherlands. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jesper-Schneider/publication/230764749_Dynamic_research_profile_visualisation_using_cluster_transition/links/0deec52ffe9cd473ef000000/Dynamic-research-profile-visualisation-using-cluster-transition.pdf#page=43
Brocato, J. J. (2001). The research productivity of family medicine department faculty: A national study. Michigan State University.
Brown, T. A., & Moore, M. T. (2012). Confirmatory factor analysis. Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling, 361, 379.
Carvalho, R., & Batty, M. (2006). The geography of scientific productivity: Scaling in US computer science. Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 20(10), 10–12.
Chadegani, A. A., Salehi, H., Yunus, M. M., Farhadi, H., Fooladi, M., Farhadi, M., & Ebrahim, N. A. (2013). A comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of Science and Scopus databases. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1305.0377
Coccia, M. (2017). Diversity of scientific outputs for scientific fields: appropriate indicators for measuring the scientific performance. Working Paper CocciaLab, 18, Retrieved 2018, Dec, 11. From https://papers.ssrn.com/Sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2966965
Cole, J. R., & Cole, S. (1972). The Ortega hypothesis: citation analysis suggests that only a few scientists contribute to scientific progress. Science, 178(4059), 368–375. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.178.4059.368
Cole, J. R., & Zuckerman, H. (1987). Marriage, motherhood and research performance in science. Scientific American, 256(2), 119–125.
Cole, S., & Phelan, T. J. (1999). The scientific productivity of nations. Minerva, 37(1), 1–23.
Corallo, A., Latino, M. E., Menegoli, M., De Devitiis, B., & Viscecchia, R. (2019). Human factor in food label design to support consumer healthcare and safety: A systematic literature review. Sustainability, 11(15), 4019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11154019
Crane, D. (1965). Scientists at Major and Minor Universities: A study of productivity and recognition. American Sociological Review, 30(5), 699–714.
Creswell, J. W. (1985). Faculty research performance: Lessons from the sciences and the social sciences. Association for the Study of Higher Education.
Creswell, J. W. (2003). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed approaches. Sage.
Dundar, H., & Lewis, D. R. (1998). Determinants of research productivity in higher education. Research in Higher Education, 39(6), 607–631. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018705823763
Edwards, S. A., & McCarrey, M. W. (1973). Measuring Performance of Researchers. Research Management, 16(1), 34–41.
Erfanmanesh, M. A., Didegah, F., & Omidvar, S. (2017). Research productivity and impact of Library and Information Science in the Web of Science. Malaysian Journal of Library & Information Science, 15(3), 85–95.
Fahimnia, F., Chakoli, N. A. R., & Bamir, M. (2017). Investigating the effect of individual and organizational factors on research productivity for faculty members in Tehran University. Scientometics Research, 2(4), 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-011-9410-6
Finkelstein, M. J. (1984). The American academic profession: A synthesis of social scientific inquiry since World War II. Ohio State University Press.
Fox, M. F. (1983). Publication productivity among scientists: A critical review. Social Studies of Science, 13(2), 285–305. https://doi.org/10.1177/030631283013002005
Frey, B. B., ed. (2018). The SAGE encyclopedia of educational research, measurement, and evaluation. Los Angeles: Sage.
Friedman, M. (1937). The use of ranks to avoid the assumption of normality implicit in the analysis of variance. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 32(200), 675–701.
Garfield, E. (1973). More of forecasting Noble Prizes and the most cited scientists of 1972! Current Contents, 40(1), 5–7.
Godin, B. (2009). The value of science: Changing conceptions of scientific productivity, 1869 to circa 1970. Social Science Information, 48(4), 547–586. https://doi.org/10.1177/0539018409344475
Goodall, A. (2015). The leaders of the world’s top 100 universities. International Higher Education, Retrieved 2019, June, 20, from https://ejournals.bc.edu/index.php/ihe/article/-download/7877/7028
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. National academy of Sciences, 102(46), 16569–16572. Retrieved 2019, June, 25, from https://www.pnas.org/doi/pdf/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Hirsch, I., Milwitt, W., & Oakes, W. J. (1958). Increasing the productivity of scientists. Harvard Bussiness Review, 36, 66–76.
Hooman, H. A. (2010). A practical guide to qualitative research. SAMT. [in Persian].
Hu, Q., & Gill, T. G. (2000). Is faculty research productivity: Influential factors and implications. Information Resources Management Journal (IRMJ), 13(2), 15–25.
Huber, J. C. (1998). Cumulative advantage and success-breeds-success: The value of time pattern analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 49(5), 471–476. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4571(19980415)49:5%3c471::AID-ASI8%3e3.0.CO;2-T
Hunter, L. A., & Leahey, E. (2010). Parenting and research productivity: New evidence and methods. Social Studies of Science, 40(3), 433–451. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312709358472
Kenna, R., Mryglod, O., & Berche, B. (2017). A scientists’ view of scientometrics: not everything that counts can be counted. Condensed Matter Physics, 20(1), 20–65. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.10407
Kosmulski, M. (2018). Are you in top 1%?. Scientomerics, 114(2), 557–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2526-4
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607–610. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316447003000308
Lancho-Barrantes, B. S., Ceballos, H. G., & Cantú-Ortiz, F. J. (2019). Factors that influence scientific productivity from different countries: a causal approach through multiple regression using panel data. BioRxiv. Retrieved 2019, june, 25, from https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2019/02/25/558254.full.pdf
Larivière, V., Macaluso, B., Archambault, É., & Gingras, Y. (2010). Which scientific elites? On the concentration of research funds, publications and citations. Research Evaluation, 19(1), 45–53. https://doi.org/10.3152/095820210X492495
Lawshe, C. H. (1975). A qualitative approach to content validity. Personnel Psychology, 28(8), 563–575.
López, R., de Hierro, A. F., Sánchez, M., Puente-Fernández, D., Montoya-Juárez, R., & Roldán, C. (2021). A fuzzy delphi consensus methodology based on a fuzzy ranking. Mathematics, 9(18), 2323. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182323
Lotka, A. J. (1926). The frequency distribution of scientific productivity. Journal of the Washington Academy of Science, 16(12), 317–323.
Más-Bleda, A., Thelwall, M., Kousha, K., & Aguillo, F. I. (2014). Successful researchers publicizing research online: An outlink analysis of European highly cited scientists’ personal websites. Journal of Documentation, 70(1), 148–172. https://doi.org/10.1108/JD-12-2012-0156
Mendez, E. (2012). What’s in good?. International Development Research Centre, 2–29. Retrieved 2018, Dec. 15, from: https://id-bnc-Idrc.dspacedirect.org/bitstream/handle/10625/50267/IDL-50267.pdf
Merton, R. K. (1968). The Matthew effect in science: the reward and communication systems of science are considered. Science, 159(3810), 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.159.3810.56
Parker, J., Lortie, C., & Allesina, S. (2010). Characterizing a scientific elite: the social characteristics of the most highly cited scientists in environmental science and ecology. Scientometrics, 85(1), 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0234-4
Pelz, D. C. (1956). Some social factors related to performance in a research organization. Administrative Science Quarterly, 1(3), 310–325. https://doi.org/10.2307/2390926
Pranckutė, R. (2021). Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications, 9(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications9010012
Price, D. J. (1970). Citation measures of hard science, soft science, technology, and nonscience. Communication among Scientists and Engineers, 13(1), 3–22.
Prpić, K. (1996). Characteristics and determinants of eminent scientists’ productivity. Scientometrics, 36(2), 185–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02017313
Ramsden, P. (1994). Describing and explaining research productivity. Higher Education, 28(2), 207–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01383729
Rivera, L., Mairesse, J., & Cowan, R. (2017). Gender gaps and scientific productivity in middle-income countries: evidence from Mexico. United States: Inter-American Development Bank.
Rodgers, R., & Rodgers, N. (1999). The sacred spark of academic research. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 9(3), 473–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jpart.a024419
Ruiz-Castillo, J. (2016). Research output indicators are not productivity indicators. Informetrics. Retrieved 2021, June, 12, from https://e-archivo.uc3m.es/bitstream/handle/10016-/22136/we1601.pdf
Saberi, M., Mohammad Khani, K., & Arasteh, H. R. (2016). Investigating the influential factors on scientific productivity of faculty and presenting a model to improve it (a case study of Azas Islamic University 8 region). Research in Educational Systems, 29(9), 55–81. [In Persian]
Sahel, J. A. (2011). Quality versus quantity: assessing individual research performance. Science Translational Medicine, 3(84), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3002249
Sánchez-Jiménez, R., Guerrero-Bote, V. P., & Moya-Anegón, F. (2017). The role of guarantor in scientific collaboration: The neighbourhood matters. Journal of Informetrics, 11(1), 103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2016.11.004
Sandström, U., & van den Besselaar, P. (2016). Quantity and/or quality? The importance of publishing many papers. PLoS ONE, 11(11), 149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166149
Sotudeh, H., & Yaghtin, M. (2015). Indicators and models of researchers’ scientific productivity. Science and Technology Policy, 3(1), 47–59. [In Persian].
Tavakol, M., & Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. International Journal of Medical Education, 2, 53. https://doi.org/10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd
Teeluckdharry, N. B., Teeroovengadum, V., & Seebaluck, A. (2021). Scale development in marketing research. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Teodorescu, D. (2000). Correlates of faculty publication productivity: A cross-national analysis. Higher Education, 39(2), 201–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003901018634
Tijssen, R. J. (2003). Scoreboards of research excellence. Research Evaluation, 12(2), 91–103. https://doi.org/10.3152/147154403781776690
Tijssen, R. J., Visser, M. S., & Van Leeuwen, T. N. (2002). Benchmarking international scientific excellence: Are highly cited research papers an appropriate frame of reference? Scientometrics, 54(3), 381–397. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016082432660
Tol, R. S. (2013). Identifying excellent researchers: A new approach. Informetrics, 7(4), 803–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2013.06.003
Turner, S. P., & Chubin, D. E. (1979). Chance and eminence in science: Ecclesiastes II. Information (international Social Science Council), 18(3), 437–449. https://doi.org/10.1177/053901847901800306
Uzzi, B., Mukherjee, S., Stringer, M., & Jones, B. (2013). Atypical combinations and scientific impact. Science, 342(6157), 468–472. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1240474
Van Noorden, R. (2011). A profusion of measures: scientific performance indicators are proliferating--leading researchers to ask afresh what they are measuring and why. Richard Van Noorden surveys the rapidly evolving ecosystem. Nature, 465(7300), 864–867.
Van Raan, A. F. (2006). Comparison of the Hirsch-index with standard bibliometric indicators and with peer judgment for 147 chemistry research groups. Scientometrics, 67(3), 491–502. https://doi.org/10.1556/Scient.67.2006.3.10
Vinkler, P. (2017). Core indicators and professional recognition of scientometricians. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(1), 234–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.23589
Vinzi, V. E., Chin, W. W., Henseler, J., & Wang, H. (2010). Handbook of partial least squares (Vol. 201, No. 0). Berlin: Springer.
Visser, M., Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2021). Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quantitative Science Studies, 2(1), 20–41. https://doi.org/10.1162/qss_a_00112
Witte, K., & Rogge, N. (2010). To publish or not to publish? On the aggregation and divers of research pertormance. Scientometrics, 85(3), 657–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0286-5
Yazici, B., & Yolacan, S. (2007). A comparison of various tests of normality. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 77(2), 175–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/10629360600678310
Zerem, E. (2017). The ranking of scientists based on scientific publications assessment. Biomedical Information, 75, 107–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2017.10.007
Acknowledgements
This article is the outcome of a part of a Ph.D. thesis entitled “Designing a Scientific Productivity Model Based on Experts’ Opinions and Testing it Among World’s Top Authors, Based On Two Scientometrics Indicators (including highly cited indicators and FWCIFootnote 5)”, supported by Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz. A group of world-famous scientific productivity experts has sincerely collaborated in this work. Therefore, the authors express their gratitude and appreciation to all these respected collaborators.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Osare, F., Keshvari, M. Evaluation of a Scientific Productivity Model among World Highly Cited Authors: a Study Based on Experts’ Opinions. J Knowl Econ (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-023-01613-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-023-01613-1