Abstract
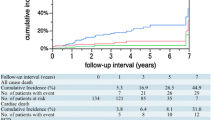
Long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes after sirolimus (SES: Cypher Bx Velocity) and paclitaxel (PES: TAXUS Express)-eluting stent implantation were firstly compared in Japan. During PES-available period from May 2007 to February 2009, 1068 nonrandomized consecutive de novo native coronary lesions treated either with a PES (682 lesions) or SES were enrolled in this study, and a retrospective examination was conducted in April 2013. During that interval, the use ratio of drug-eluting stent (i.e. SES plus PES) was 94.2 %. By adjusting the baselines with a propensity score matching analysis produced 383 lesions in each arm, the incidence of the clinical endpoint (1500-day cardiac death, nonfatal recurrent myocardial infarction, and definite stent thrombosis) after placement of SES (2.1 %; mean follow-up, 1400 ± 290 days) was not significantly different from that in the PES group (2.6 %; 1394 ± 325 days, p = 0.637). SES did not relate to the clinical endpoint (hazard ratio 1.04; 95 % CI 0.29–3.76; p = 0.949). In the baseline-adjusted angiographic followed up lesions (n = 234 in each arm), the incidence of binary restenosis (percent diameter stenosis [%DS] >50 %) in the SES group (12.0 %; mean follow-up, 477 ± 281 days) was not significantly different from that in the PES group (14.5 %; 497 ± 341 days, p = 0.431). SES did not relate to binary restenosis (Odds ratio 0.73; 95 % CI 0.40–1.32; p = 0.295). In conclusion, the present propensity score matched lesion-based analysis firstly showed the statistical equivalent long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes after either SES or PES placement for de novo native coronary lesion in Japanese patients in a daily practice environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukumoto A, Otsuji S, Takiuchi S, Ikushima M, Asano K, Terasoma K, et al. Comparison of real-world clinical outcomes between Cypher- and Taxus-eluting stents: the GARA–GARA study. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2011;26:202–8.
Ishikawa T, Nakano Y, Mutoh M. Retrospective comparison of midterm clinical and angiographic outcomes after the implantation of paclitaxel- and sirolimus-eluting stents for de novo coronary complex lesions in nonrandomized Japanese patients. Intern Med. 2012;51:2695–701.
Ishikawa T, Mutoh M, Nakano Y, Suzuki T, Nakata K, Murakami A, et al. Post-discharge clinical and angiographic outcomes of patients presenting within 48 hours of STEMI treated with paclitaxel- or sirolimus-eluting stents. J Cardiol. 2012;60:174–9.
Tsujita H, Hamazaki Y, Nishikura T, Yokota H, Kondo S, Hosokawa S, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus paclitaxel-eluting stents for coronary intervention in patients with renal failure on hemodialysis. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2013;28:9–15.
Mutoh M, Ishikawa T, Hasuda T, Okada H, Endo A, Miyanaga S, et al. Predictors of target lesion revascularization and documented stent thrombosis beyond 30 days after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation-retrospective analysis in consecutive 1070 angiographic follow-up lesions. Circ J. 2007;71:1328–31.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Nakagawa Y, Tamura T, Kadota K, Yasumoto H, et al. j-Cypher Registry Investigators. Antiplatelet therapy and stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation 2009; 119:987–95.
Ishikawa T, Nakano Y, Endoh A, Kubota T, Suzuki T, Nakata K, et al. Significantly lower incidence of early definite stent thrombosis of drug-eluting stents after unrestricted use in Japan using ticlopidine compared to western countries using clopidogrel: a retrospective comparison with western mega-studies. J Cardiol. 2009;54:238–44.
Kubota T, Ishikawa T, Mutoh M. Retrospective comparison of the clinical and angiographic outcomes of the sirolimus-eluting stent and the bare-metal stent in 2031 nonrandomized consecutive de novo native coronary lesions. Intern Med. 2011;50:2463–70.
Ishikawa T, Mutoh M, Nakano Y, Endoh A, Kubota T, Suzuki T, et al. Retrospective comparison of clinical and angiographic outcomes after primary stenting using sirolimus-eluting and bare-metal stents in nonrandomized consecutive 568 patients with first ST-segment elevated myocardial infarctions. J Cardiol. 2011;57:44–52.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Nakagawa Y, Kawai K, Miyazaki S, Muramatsu T, et al; on Behalf of the j-Cypher Registry Investigators. Very late stent thrombosis and late target lesion revascularization after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: five-year outcome of the j-Cypher Registry. Circulation 2012;125:584–91.
Kotani J, Ikari Y, Kyo E, Nakamura M, Yokoi H, Furuno K, et al. Five-year outcomes of Cypher™ coronary stent: report from J-PMS Study. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2012;27:63–71.
Cutlip DE, Windecker S, Mehran R, Boam A, Cohen DJ, van Es GA, et al; Academic Research Consortium Academic Research Consortium. Clinical end points in coronary stent trials: a case for standardized definitions. Circulation 2007;115:2344–51.
Moliterno DJ. Healing Achilles–sirolimus versus paclitaxel. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:724–7.
Ellis SG, Popma JJ, Lasala JM, Koglin JJ, Cox DA, Hermiller J, et al. Relationship between angiographic late loss and target lesion revascularization after coronary stent implantation. Analysis from the TAXUS-IV trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:1193–200.
Ishikawa T, Nakano Y, Hino S, Suzuki T, Murakami A, Tsutsumi J, et al. Propensity-matched lesion-based comparison of midterm outcomes of TAXUS Express and TAXUS Liberté stents for de novo native coronary stenosis. J Cardiol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print].
Kubota T, Ishikawa T, Nakano Y, Endoh A, Suzuki T, Sakamoto H, et al. Retrospective comparison of clinical and angiographic outcomes after sirolimus-eluting and bare-metal stents implantation for nonrandomized consecutive 312 severe calcified lesions using rotablator. Int Heart J. 2011;52:65–71.
Mehran R, Dangas G, Abizaid AS, Mintz GS, Lansky AJ, Satler LF, et al. Angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis: classification and implications for long-term outcome. Circulation. 1999;100:1872–8.
Räber L, Wohlwend L, Wigger M, Togni M, Wandel S, Wenaweser P, et al. Five-year clinical and angiographic outcomes of a randomized comparison of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents: results of the Sirolimus-Eluting Versus Paclitaxel-Eluting Stents for Coronary Revascularization LATE trial. Circulation. 2011;123:2819–28.
Morice MC, Colombo A, Meier B, Serruys P, Tamburino C, Guagliumi G, et al; REALITY Trial Investigators. Sirolimus- vs paclitaxel-eluting stents in de novo coronary artery lesions: the REALITY trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006;295:895–904.
Galløe AM, Thuesen L, Kelbæk H, Thayssen P, Rasmussen K, Hansen PR, et al; SORT OUT II Investigators. Comparison of paclitaxel- and sirolimus-eluting stents in everyday clinical practice. JAMA 2008;299:409–16.
Mayor M, Malik AZ, Minor RJ Jr, Deshpande MC, Strauss WE, Maloney TH, et al. One-year outcomes from the TAXUS express stent versus cypher stent. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:930–6.
Agostoni P, Cosgrave J, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Sangiorgi GM, Ge L, Melzi G, et al. Angiographic analysis of pattern of late luminal loss in sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99:593–8.
Park CB, Hong MK, Kim YH, Park DW, Han KH, Lee CW, et al. Comparison of angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis between sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stent. Int J Cardiol. 2007;120:387–90 [Epub 2007 Feb 8].
Solinas E, Dangas G, Kirtane AJ, Lansky AJ, Franklin-Bond T, Boland P, et al. Angiographic patterns of drug-eluting stent restenosis and one-year outcomes after treatment with repeated percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102:311–5. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.03.060 [Epub 2008 May 24].
Gao Z, Yang Y, Xu B, Chen J, Qiao S, Li J, et al. Three year follow-up of the sirolimus-eluting stent and the paclitaxel-eluting stent in daily practice. Clin Cardiol. 2009;32:E63–7. doi:10.1002/clc.20550.
Kimura T, Isshiki T, Hayashi Y, Oshima S, Namura M, Nakashima H, et al. Incidence and outcome of surgical procedures after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: a report from the j-Cypher registry. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2010;25:29–39.
Endo A, Ishikawa T, Suzuki T, Kashiwagi Y, Mutoh M. Direct microscopic observation of striations in a fractured section of a sirolimus-eluting stent (Cypher Bx Velocity®) indicates induction of stent fracture by continuous shear stress. Int Heart J. 2011;52:248–51.
Imai M, Kadota K, Goto T, Fujii S, Yamamoto H, Fuku Y, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and clinical sequelae of angiographic peri-stent contrast staining after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2011;123:2382–91.
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakano, Y., Ishikawa, T., Hino, S. et al. Propensity score matched lesion-based comparison of long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes after placement of sirolimus (Cypher Bx Velocity) and paclitaxel (TAXUS Express)-eluting stents for de novo native coronary stenosis. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 29, 93–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-013-0215-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-013-0215-7