Abstract
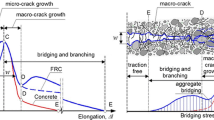
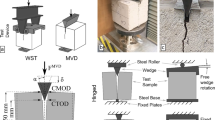
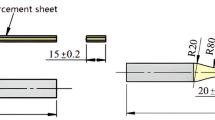
Most of the civil infrastructure are made up of concrete. Concrete is a highly heterogeneous brittle material and under cyclic loading understanding the progress of crack occurring within the material and the structure leading to its degradation is a complicated issue. In view of this, in the present study, studies on the monotonic and fatigue behaviour of notched prism of plain and fibre reinforced concrete (FRC) are carried out. Six prisms are tested under single point monotonic loading to obtain the behaviour of the plain concrete and FRC prisms. The crack mouth opening displacement (CMOD) of plain concrete and FRC are measured using calibrated clip gauge attached. From load versus CMOD response, fracture energy is calculated. It is found that the FRC gives better ductility than plain concrete. Nine specimens each of plain concrete and FRC are tested under fatigue loading. Three load ranges are chosen for carrying out the fatigue study. Minimum load is set as 20 % of the ultimate load and the maximum load are varied as 65, 75 and 85 % of the average ultimate load carrying capacity obtained from the monotonic testing of the prisms. Number of cycles to failure for plain concrete and FRC under each load range is obtained. It is observed that the inclusion of fibres improved the flexural fatigue performance of concrete.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swamy R N. Development of concrete technology, vol. 1. Applied Science Publishers Ltd (1979) p 221.
Shah S P, Mater Struct, 23 (1990) 457.
Zhang J, Stang H, and Victor C L, Int J Fatigue, 21 (1999) 1033.
Cachima P B, Figueiras J A, and Pereira P A A, Cem Concr Compos, 24 (2002) 211.
Singh S P, and Kaushik S K, Cem Concr Compos, 25 (2003) 779.
Lee M K, and Barr B I G, Cem Concr Compos, 26 (2004) 299.
Heeralal M, Rathish Kumar P, and Rao Y V, Archit Civ Eng, 7 (2009) 19.
Kaur G, Singh S P, and Kaushik S K, Int J Emerg Technol Adv Eng, 2 (2012) 436.
Goel S, Singh S P, Eng Struct, 74 (2014) 65.
Rilem T C S, Mater Struct, 18 (1985) 285.
Acknowledgments
This paper is being published with the kind permission of the Director, CSIR-Structural Engineering Research Centre, Chennai, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banjara, N.K., Ramanjaneyulu, K., Sasmal, S. et al. Flexural Fatigue Performance of Plain and Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 373–377 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0770-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0770-y