Abstract
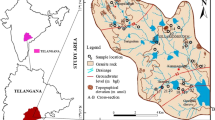
Groundwater is used for both drinking and irrigation purposes. Thus, its monitoring and understanding the processes controlling its quality are crucial in terms of sustainable use. Groundwater samples were collected from 11 deep aquifer wells located in the Harran plain, Southeastern Anatolia during four seasons and analyzed for TDS, EC, pH, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, F−, SO42−, HCO3−, NO3−. Techniques such as ANOVA, correlation analyses, heat-mapping and Principal Component Analyses (PCA) were used to investigate main factors controlling seasonal and spatial variations in groundwater quality parameters. Grounwater quality parameters were also associated with topographical parameters [elevation, slope, flow direction, flow accumulation, and Topo Wetness Index (TWI)]. According to WHO standards, average values of all parameters investigated were in general within allowable limits for drinking water with a few exceptions for NO3−, SO42− and F− that exceeded threshold limits at some locations. Seasonal variations in all water quality parameters except EC, TDS and SO42− were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Parameters such as EC, TDS, Ca2+, Mg2+, NO3−, F− were the main parameters controlling the qualities of groundwater sampled according to PCA analyses results, which separated the wells into two main groups; the wells located in the lower parts of the plain with higher values of EC, TDS, TWI, Flow Accumulation and the wells located in upper part of the plain with higher EC, TDS, elevation, slope and Flow Direction. Spatial variations in selected groundwater quality variables by topographical parameters ranged from 40.7 to 94.8%. Overall, the results of the study will contribute to good groundwater management efforts on a local and global scale.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Any data and material used in this study can be provided upon request.
Code availability
Codes running statistical analysis performed in the study can be provided upon request.
References
ASTM (The American Society for Testing and Materials) (2001) Standard guide for sampling ground-water monitoring wells, D4448-01
ASTM (The American Society for Testing and Materials) (2005) Standard guide for field preservation of ground-water samples, D6517-00
Atasoy AD (2008) Environmental problems in vertisol soils: the example of the Harran plain. Fresenius Environ Bull 17(7a):837–843
Atasoy AD, Yesilnacar MI (2010) Effect of high sulfate concentration on the corrosivity: a case study from groundwater in Harran plain, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 166:595–607
Aydemir S, Sönmez O (2009) Ameliorative effect of indigenous calcite on sodium-saturated claysytems. Soil Sci 173:96–107
Bilgili AV, Yeşilnacar I, Akihiko K, Nagano T, Aydemir A, Hızlı HS, Bilgili A (2018) Post-irrigation degradation of land and environmental resources in the Harran plain, southeastern Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 190:660
Bindal S, Kumar A, Mallick J, Shashtri S, Kumar P, Singh CK (2020) Geochemical, topographical, and meteorological controls on groundwater arsenic contamination in Sharda river basin of Uttar Pradesh. India J Clim Change 6:71–87
Brejda JJ, Karlen DL, Smith JL, Allan DL (2000) Identification of regional soil quality factors and indicators: II. northern Mississippi Loess hills and Palouse Prairie soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:2125–2135
DSİ (Devlet Su İşleri) (2003) Harran Ovasında Tuzluluk ve Drenaj Problemi, Özet Rapor, 10s. DSİ XV. Bölge Müdürlüğü, Şanlıurfa, Türkiye
Ganiyu SA, Badmus BS, Olurin OT, Ojekunle ZO (2018) Evaluation of seasonal variation of water quality using multivariate statistical analysis and irrigation parameter indices in Ajakanga area, Ibadan. Nigeria Appl Water Sci 8:35
Gnanachanddrasamy G, Dushiyanthan C, Rajakumar JT, Zhou Y (2020) Assessment of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in the lower Vellar river basin; using geographical information system (GIS) and water quality index (WQI). Environ Dev Sustain 22:759–789
Gulgundi MS, Shetty A (2018) Grounwater quality assessment of urban Bengaluru using multivariate statistical techniques. Appl Water Sci 8:43
Hair JF, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2011) PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. J Mark Theory Pract 19(2):139–151
Jeelani GH, Shah RA, Hussain A (2014) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater in Kashmir Valley, India. J Earth Syst Sci 123:1031–1043
Karanth (1987) Groundwater assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi
Khan A, Khan HH, Umar R (2017) Impact of land-use on groundwater quality: GIS-based study from an alluvial aquifer in the western Ganges basin. Appl Water Sci 7:4593–4603
Kim HS, Park SR (2016) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater highly polluted with nitrate in an agricultural area of Hongseong. Korea Water 8:345
Kim HR, Yu SOJ, Kim KH, Lee JH, Moniruzzaman M, Kim HK, Yun ST (2019) Nitrate contamination and subsequent hydrogeochemical processes of shallow groundwater in agro-livestock farming districts in South Korea. Agr Ecosyst Environ 273:50–61
Liu J, Gao Z, Wang M, Li Y, Ma Y, Shi M, Zhang H (2018) Study on the dynamic characteristics of groundwater in the valley plain of Lhasa City. Environ Earth Sci 77:646
Luo W, Gao X, Zhang X (2018) Geochemical processes controlling the groundwater chemistry and fluoride contamination in the Yuncheng Basin, China—an area with complex hydrogeochemical conditions. PLOS ONE 13(7):e0199082
Maskooni EK, Kompanizare M, Afzali SF (2017) Chemical assessment of dam water irrigation effects on groundwater qualities in Bigherd plain, Fars province, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76:238
Masoud AA (2013) Spatio-temporal evaluation of the groundwater quality in Kafr Al-Zayat District. Egypt Hydrol Process 27:2987–3002
Machiwal D, Jha MK (2015) Identifying sources of groundwater contamination in a hard-rock aquifer system using multivariate statistical analyses and GIS-based geostatistical modeling techniques. J Hydrol Reg Stud 4(Part A):80–110
Mulyadi A, Dede M, Widiawaty MA (2020) Spatial interaction of groundwater and surface topographic using geographically weighted regression in built-up area. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 477:012023
Nosetto MD, Acosta AM, Jayawickreme DH, Ballesteros SI, Jackson RB, Jobbagy EG (2013) Land-use and topography shape soil and groundwater salinity incentral Argentina. Agric Water Manag 129:120–129
Prasad YS, Rao VB (2018) Monitoring and assessment of groundwater quality in a khondalitic terrain, Andhra Pradesh. India Environ Monit Assess 190:426
Prusty P, Farooq SH, Zimik HV, Barik SS (2018) Assessment of the factors controlling groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer adjacent to the Bay of Bengal. India Environ Earth Sci 77:762
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 18 May 2020
Sahu P, Kisku GC, Singh PK, Kumar V, Kumar P, Shukla N (2018) Multivariate statistical interpretation on seasonal variations of fluoride-contaminated groundwater quality of Lalganj Tehsil, Raebareli Disrict (UP). India Environ Earth Sci 77:484
Sorensen R, Zinko U, Seibert J (2005) On the calculation of the topographic wetness index: evaluation of different methods based on field observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 2:1807–1834
Srivistava PK, Han D, Gupta M, Mukherjee S (2012) Integrated framework for monitoring groundwater pollution using geographical information system and multivariate analysis. Hydrol Sci J 57(7):1453
Stephen R, Jeannin PY, Alexander EC, Davies GJ, Schindel GM (2017) Contrasting definitions for the term ‘karst aquifer.’ Hydrogeol J 25:1237–1240
Suthar S, Garg VK, Jangir S, Kaur S, Goswami N, Singh S (2008) Fluoride contamination in drinking water in rural habitations of Northern Rajasthan, India. Environ Monit Assess 145:1–6
Tardu T, Başkurt T, Güven A, Us E, Dinçer A, Tuna ME, Tezcan ÜŞ (1987) Structural and stratigraphic aspects of Akçakale Graben and its oil potential. Seventh Petroleum Congress of Turkey, 36–49
USEPA (1992a) Guidelines for water use. USEPA, Washington, Tech. Report 81, pp 252
USEPA (1992b) Guidelines for water reuse. EPA 625/R-92/004. Office of Water, Washington, DC, and Office of Res and Development, Cincinnati, OH
Wang ZW, Chen HW, Li FL (2019) Identifying spatial heterogeneity of groundwater and its response to anthropogenic activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:294352–299448
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality; First addendum to 3rd edn, Recommendation, Geneva, p 595
WHO (2007) Water for pharmaceutical use in quality assurance of pharmaceuticals a compendium of guidelines and related materials, 2nd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 170–187
WHO (2017) WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0
Yesilnacar MI, Yenigun I (2011) Effect of irrigation on a deep aquifer: a case study from the semi-arid Harran Plain, GAP Project, Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0299-6
Yeşilnacar İ, Yetiş Demir A, Dülgergil ÇT, Kumral M, Atasoy AD, Rastgeldi Doğan T, Tekiner Sİ, Bayhan İ, Aydogdu M (2016) Geomedical assessment of an area having high-fluorid groundwater in southeastern Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 75:162
Yeşilnacar MI, Gulluoglu MS (2008) Hydrochemical characteristics and the effects of irrigation on groundwater quality in Harran plain, GAP project, Turkey. Environ Geology 54:183–196
Yolcubal I, Ateş Gündüz ÖC, Kurtuluş N (2019) Origin of salinization and pollution sources and geochemical processes in urban coastal aquifer (Kocaeli, NW Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 78:181
Zhai Y, Lei Y, Zhou J, Li M, Wang J, Teng Y (2015) The spatial and seasonal variability of the groundwater chemistry and quality in the exploited aquifer in the Daxing District, Beijing. China Environ Monit Assess 187:43
Acknowledgements
This study has been financially supported by Turkish Republic Harran University Scientific Research Commission (HUBAK; Grant Number: 19007). The authors would like to thank Dr. Fred Ernst for helping with manuscript language.
Funding
Financial Support for this study has been provided by Turkish Republic Harran University Scientific Research Commission (HUBAK; Grant Number: 19007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yenigun, I., Bilgili, A.V., Yesilnacar, M.I. et al. Seasonal and spatial variations in water quality of deep aquifer in the Harran plain, GAP project, southeastern Anatolia, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 80, 568 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09858-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09858-2